|
The Imperiled Planet: An introduction. How evolutionary change, natural selection, & deep time hold the world steady and sustain the world that created us.
|
J. V. Siry Ph.D. |
|
|---|---|---|---|

|
|||
| Darwin and Mendel | Three Laws of Thermodynamics | Chapter's key points | Conclusions | |||
"How one species, Homo sapiens, has become so powerful that it can significantly undermine the ability of the Earth's environment to support much life–including our own–is a central theme of this book." The Dominant Animal. p. 3.
|
|
||
Darwin & Mendel: the two sides of a biological “coin” – behavior & inheritance.
Chapters:
# 1, Darwin and Mendel's legacy–“lessons about limits in another person's
eyes” – Darwin nor Mendel ever met one another.
# 2, The Tangled Bank– more
lessons of natural laws from all around us
# 3, Our Distant Past– “rocks of ages”
unseen remnants of a forgone world
Chapter One
About the discovery of human descent, variation and our shared ecological conditions of existence.
outline
Background | Body | Evidence | Food Webs | Detailed Analysis | Conclusion
Unknown to one another Darwin and Mendel discovered that variability and selection work in tandem to produce viable offspring—members of a potentially breeding population.
 |
|
| selection | variability |
Eight significant points are the heart of the chapter, foreshadowing the book: within limits,
“descent with modification” from a common ancestor leads to diversity over time, random
mixture generates genetic variability, immunity or resistance, and biotic potential.
Thus this hereditary composition of a population assures our effective survival, if not breeding.
moths, birds, anoles, fruit flies, human blood cells, eye color, and enzymes.
argument
Conditional (surroundings) change + genetic inheritance = descent with deviations
“it is usually very hard to select for just one characteristic.”
“a gene consists of a series of nucleotides with different bases that determine the
sequence... proteins” [with alterations = modifications = deviations]
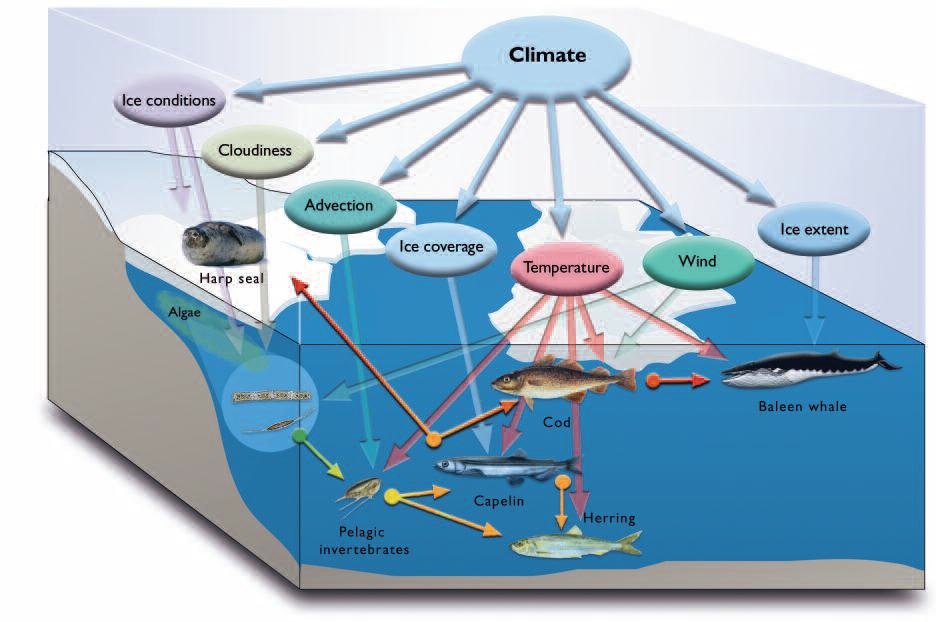
proteins (enzymes & hormones) are life’s essential constituents, act as arbiters of what variations are sustained, & shared molecules, carbohydrates and proteins are the threads that tie ecological systems together.
Limits | thermodynamics | evolution | eight summary points | conclusion
Limits – The laws of thermodynamics are just one example of how ecological systems have a limited capacity to sustain life for a time.

divergence and convergence
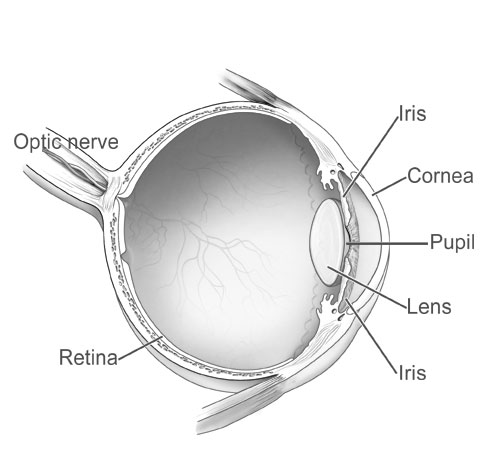
Why do your eye colors differ only within a limited range?
There is evidence that as many as 16 different genes could be responsible for eye color in humans; however, the main two genes associated with eye color variation are OCA2 and HERC2, and both are localized in Chromosome 15.[1]
Descent from a common ancestor creates a contingent inheritance of colors, shape, mass, or size, as Mendel realized with his peas. He grasped in his garden, what Darwin's saw in the world: a variety of traits inherited by descendents from a common, ancestral source.
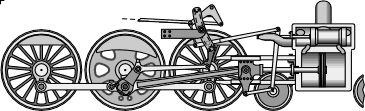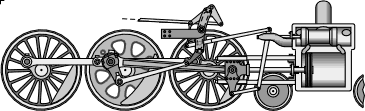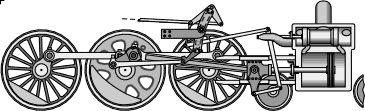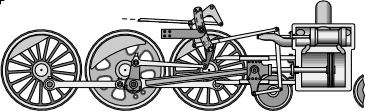
The steam engine's widespread use in the 19th century led French, German, & British investigators to study the transfer of heat from the boiling water flashed into steam inside the steam engine's boilers as this was transferred into the mechanical motion of the drive shaft and gears.
From this curiosity into the amount of heat released as mechanical motion increased the gradual discovery of three laws of thermal mechanics were articulated about the characteristic behavior of energy. this was long before anyone associated the sun's spectrum of visible light with the existence of long wave or infrared radiation, that we know today as "heat."
Three laws of thermodynamics
| 1 | energy (and matter) can neither be created nor destroyed; (E) energy is constant (k) |
|---|---|
| 2 | no transfer of energy is ever completely efficient; so that heat, as a loss, or entropy accumulates |
| 3 | eventually the universe will have insufficient energy for life |
Said another way, by Garret Hardin
1, You can’t win
2, You are bound to lose
3, You cannot get out of the game
Evolution,
descendants vary with respect to the traits they inherit and thus what survives depends on what was produced earlier[1] by variable parents and grandparents.
No living thing really evolves, but its descendants vary greatly from them & their ancestors
Some of that variable inheritance is passed on
Not all traits are passed on, but natural selection favors functional assets, or at least non-lethal traits.
So in a population many traits survive that can endow future offspring with variety
Variety is insurance against the storm
There are no guarantees of success
Life has the capacity to adapt to conditions that are not too extreme
Over time due to isolation and variation, populations give rise to new species:
Finches on the Galapagos Islands
Turtles
Rails
Eight significant points:
1. Populations change within limits [milieu’s limits + genome’s limits]
2. Natural selection favors some traits among very variable offspring’s genomes
3. Isolation (loss) and the pace of change among organisms can be rapid or slow
4. Linking evolution to genetics is the Modern synthesis and a foundation of biology
5. Artificial selection by humans and other organisms can change other creatures (fruit flies, cows, cats & dogs, sheep, GMOs]
6. Change in the hereditary composition of populations over time is due to DNA and RNA’s variability and functionally replicable chemistry.
7. Genotype & phenotype act in such a way as phenotype is selected for as an expression of genotype [eye color in humans].
8. Changes in a population’s genome is the raw material of evolution or shifts–alterations–in populations of organisms over time.
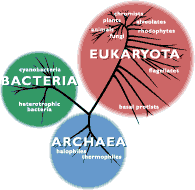
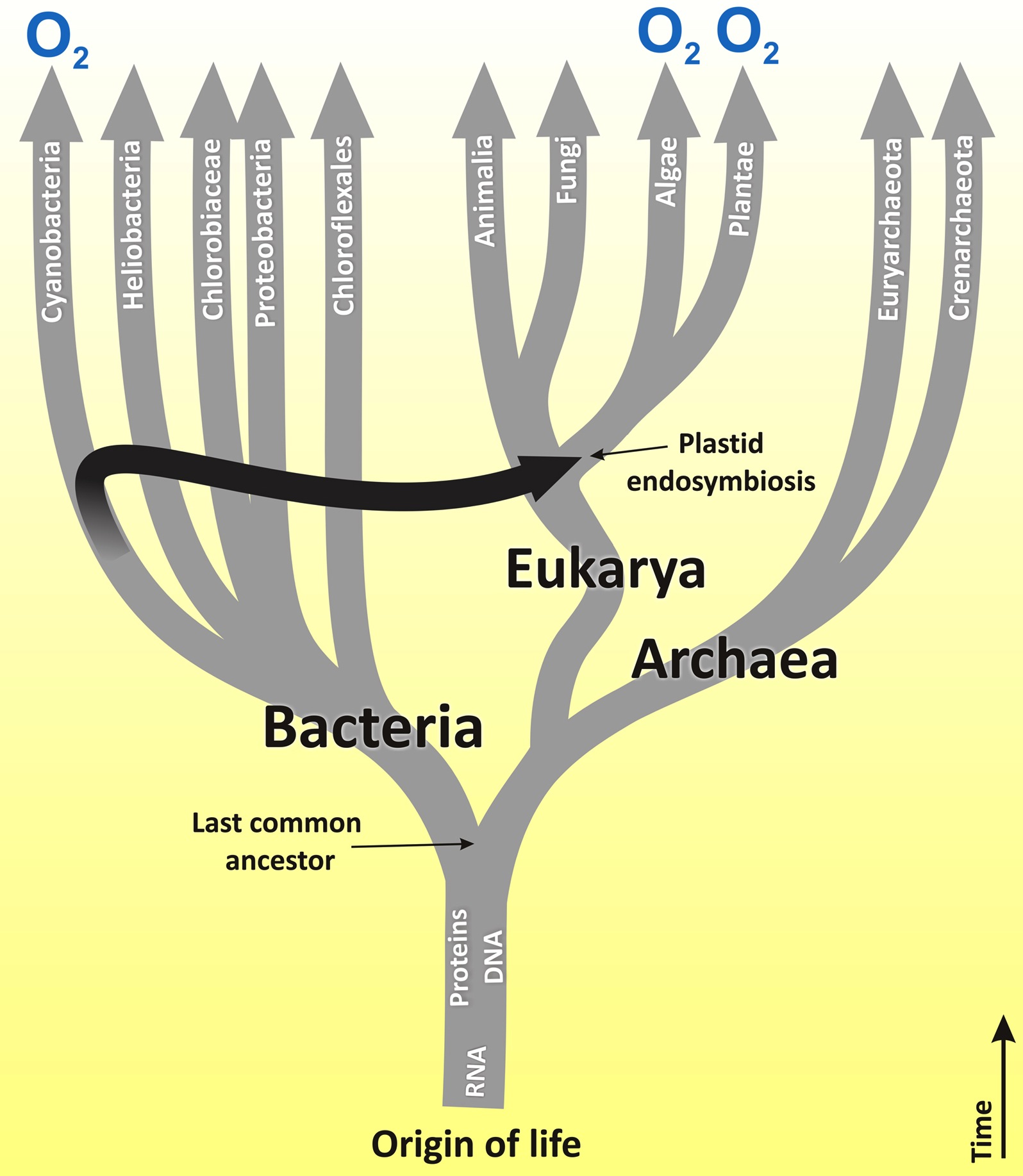
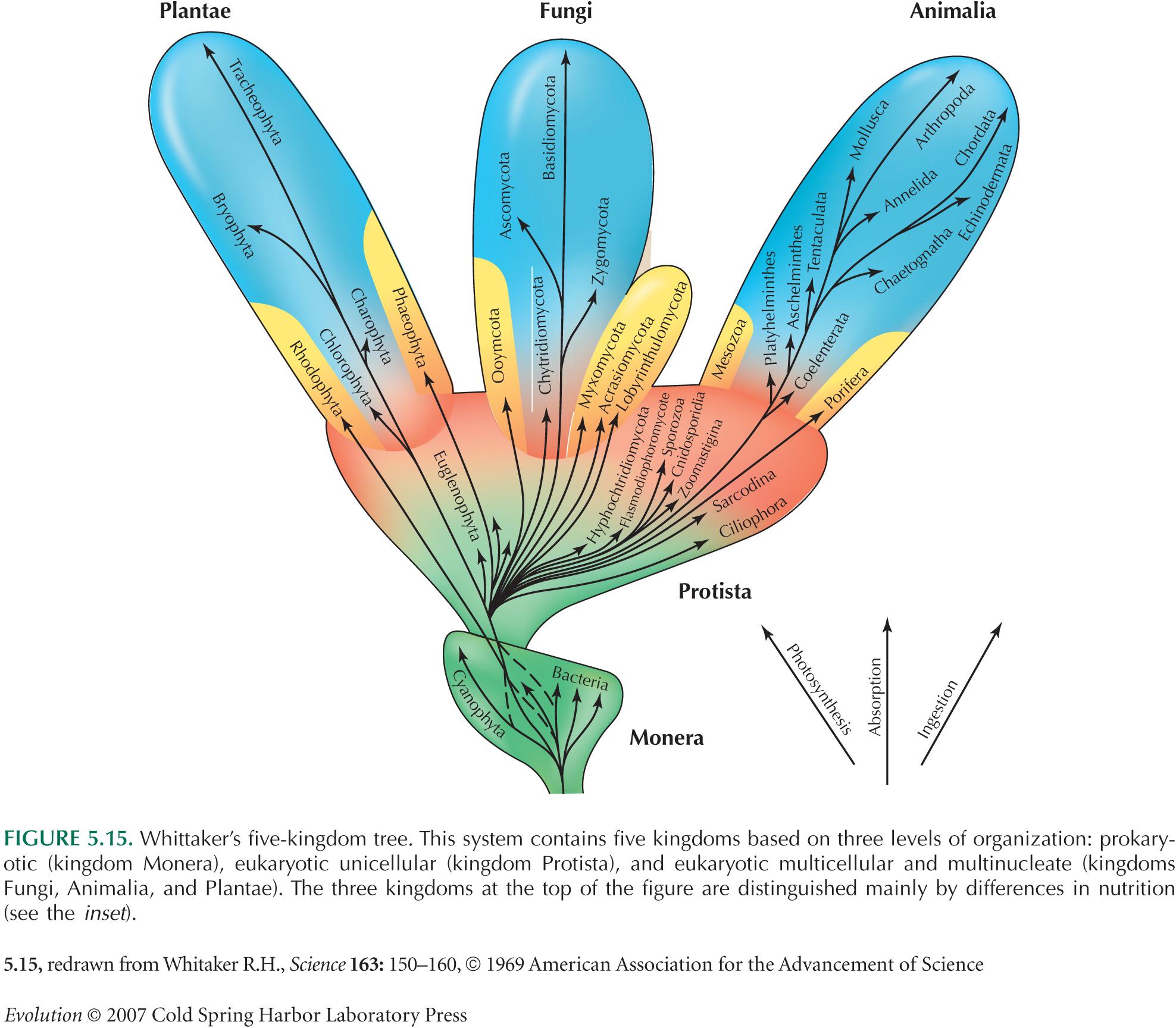
The new tree of life -- the five kingdoms of three Eukaryotes organisms and their cousins the bacteria and the Archaea, or bacterial-like creatures thriving in extreme conditions.
We like all of nature’s species are the products of variation & selection. To know truly what limits we have & how this biological treasure we are endowed with functions, we must unravel a complex puzzle among: the earth, ethology (behavior), ecology (surroundings), & molecular biology (competing means of regulatory feedback). Our task is to better know the world in us!
We are the products of the world we see around us, limited by its conditions plus our inherited and acquired traits to wither or prosper; as we can become proper caretakers, or unreasonable exploiters of an unimaginably expensive endowment, which I will call life’s diversity, beauty, and integrity on an imperiled planet.
Three ecological factors:
a. Laws enabling limits and optimization
b. descent from a common ancestor
c. inherited resistance
The complexity of life's diversity is the product of evolution despite environmental resistance.
vocabulary
- limitations of natural selection & inheritance,
- Manchester U.K. & industrial melanism,
- genotype vs. phenotype,
- diversity, diversification,
- inorganic & organic limitations,
- biotic species,
- predator – prey relations,
- populations.
- Warblers’ song,
- Monarch butterflies,
- mimicry,
- selection,
- DDT resistance.
- origins & loss in descent,
- fossils, missing links,
- Archaeopteryx,
- Tiktaalik,
- traits,
- deep time,
- ratio,
- Paleolithic,
- tool-making,
- Olduwan culture,
- exodus,
- rock-solid