Environmental
Science
Environmental
ScienceNavigating the site:
Time line
 "Man was the measure
of all things until he became the only measure of everything."
"Man was the measure
of all things until he became the only measure of everything."
G. Tyler Miller, Environmental Science,
10th Edition, Pacific Grove, California: Thomson/Brooks Cole Publishing, 2004.
Problems in Environmental Science,
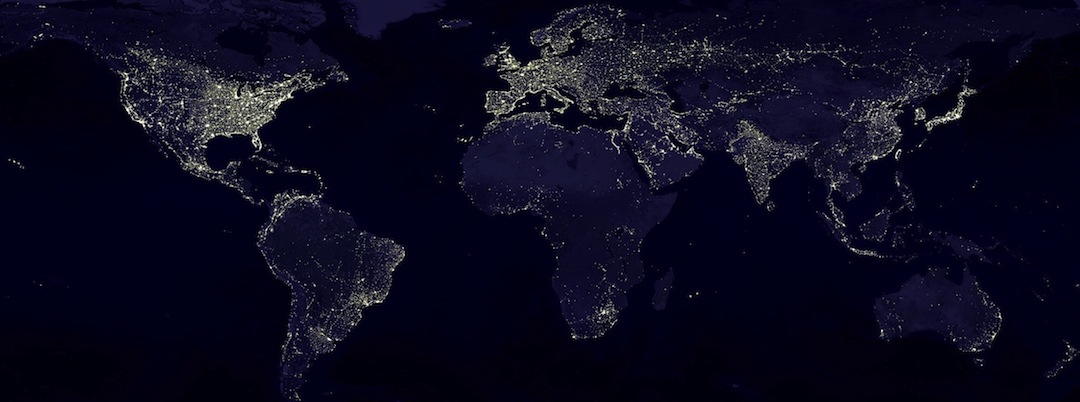
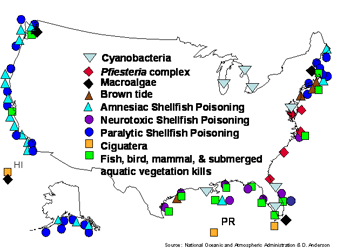
The impact of electricity on the earth's landscape.
“Environmental Problems and their causes” Ohapter 1; G.T. Miller
comprehending
what your read
Interpret (translate) one of these phrases:
“What is the use of a house if you don’t have a decent planet to put it on?”
or
“... an alarming admission that science and technology may no longer lead automatically to a better future.”(@ p. 26)
Define each these words with respect to the texts:
- sustainable
- wealth & “wealth gap”
- resource
- pollutant
- problem
- worldview
- dialectic
- earth wisdom
Whom should we believe?
Consider the two guest essays [pp. 22 & 24] and formulate an essay to explain the following: With respect to water, energy, air and land does Ehrlich & Ehrlich or Simon make a more rational and convincing argument for their respective points of view? (write for ten minutes)
draw a diagram to relate the following 15 words and explain their links
A concept map is a device for you to express the relationships that you understand between words, ideas and concepts in order to better “view” the details of an issue, the key parts of a case or the complex connections among different beliefs and facts.
Coping with an ecological crisis
“What is the use of a house if you don’t have a decent planet to put it on?”
Henry David Thoreau
Overview | Background | Detailed arguments | Summary | Conclusion
§§§
exponential power (rule of 70 { 70 / % of increase = DT })
ecology analyzes the solar & earth's natural capital stock
“planet’s ability to absorb”
ecological insults
nourish life
You & I matter because of our combined behavior we influence ecosystems
population change & life expectancy
outgrowing your clothes
affordable wardrobes
sources of wealth are derived from ecosystems**
W.E.A.L. acronym for water, energy, air, land = habitat
Three categories of resources
“Tragedy of the Commons” 1966
What is an insult to the environment?
local ecosystems (**habitat + biocommunity)
worldwide
serious problems
water and air degradation (habitat)
waste accumulation
biological diversity & food production
need to connect symptoms to root causes
P * A * T = I
Synergy: combined effect is greater than the sum of its parts
5) Conclusion: ecological perception & denial
“... an alarming admission that science and technology may no longer lead automatically to a better future.”(G. Tyler Miller, p. 26)
Defining significant terms in the readings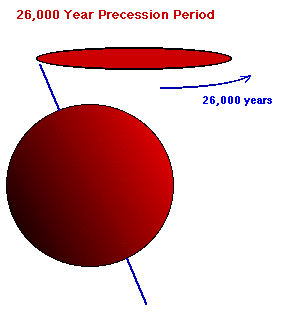
sustainable - capable of being supported, maintained or paid for without destroying the productive worth of a source of life over a long period of time, usually more than one business cycle (4-7 years), or generation (20- 25 years) or several generations. On an earth-time call the wobble of the axis of rotation causes the planet to be in a recursive 26,000 year cycle.
wealth & “wealth gap” [from the root word “weal”, German wald (forest)] generally : the accumulated and transferable objects, materials or ideas of value to a people, place or living thing.
Such as capital (solar vs. earth capital), investment or interest returned on your savings, insurance, or loaning of money.
Knowledge & inventions that are passed from one person to another.
specifically: the disparity or big difference in value between the earning power, income, wages or savings of people in a society, country, place or group.
resource - any thing used by life to maintain living or survive. [carbon, nitrogen]
pollutant - any material thing or force that is harmful to life.
such as: arsenic, uranium, acid, or electrical discharge
problem - perceived differences between an existing and a desired state of affairs.
worldview - a translation of the German WETLANSCHAUUNG meaning:
the way a person, society, or culture conceives of the world or their surroundings compared to the existence or way in which the physical or material world actually behaves.
For example:
Columbus mistakenly thought America was Asia!
Some people think you can get AIDs from toilet seats, or from touching people with AIDs, although you cannot contract the disease in either way.
dialectic - (literally two (2) ways) using two different, or opposite, ways to conceptualize a problem or clarify an argument over serious issues.
For example: multiply versus divide; synthesize versus analyze; optimism versus pessimism, good vs. bad, open vs. shut, loose vs. tight, circular vs. linear.
In philosophy, a method for discovering truth:
thesis (T) versus antithesis (A) equals synthesis (S)
T - A = Searth wisdom - the ecological perspective of relating significant necessities of life to enhancing humans' survival and the sustained recovery of their surroundings.
ecology - the study of an organism, living things, or communities in relation to their living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) conditions of existence and surroundings.* * *