Kinds and extent of natural
vegetation in proportion to area 
Florida is characterized by over twenty types of plant or vegetational associations. These identifiable vegetal and animal associations are defined with respect to three major latitudinal zones from the 1. temperate northern, 2. mixed central and 3. subtropical southern regions of the state.
Both fire and water affect the kinds of vegetation patterns seen in these subregions where the annual shift in the earth's position brings a much warmer, extensive and intensive amount of solar radiation from March to November. Soil although largely sand and mixed loam can be characterized by organic accumulations called muck, or hardened clay limestone called marl in the Everglades.
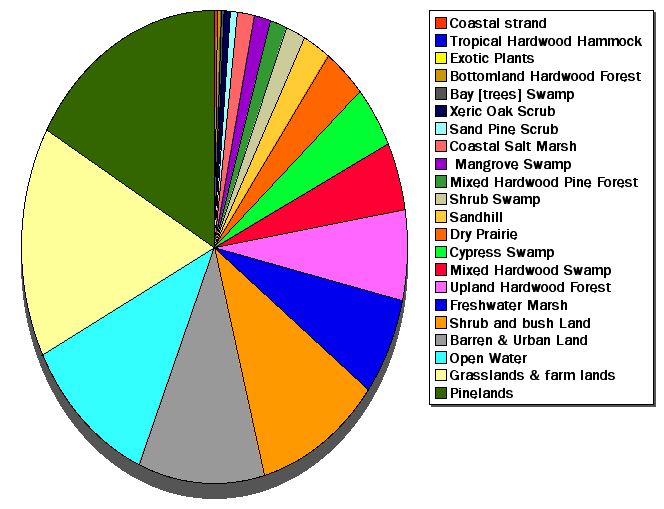
Inventory of the types of vegetative cover of land in Florida
date: place, coverage.
|
#
|
% of total acres
|
description of the Land Cover |
|
1
|
Coastal strand | |
|
2
|
Dry Prairie | |
|
3
|
17
|
Pinelands |
|
4
|
Sand Pine Scrub | |
|
5
|
2
|
Sandhill |
|
6
|
Xeric Oak Scrub | |
|
7
|
Mixed Hardwood Pine Forest | |
|
8
|
6
|
Upland Hardwood Forest |
|
9
|
Tropical Hardwood Hammock | |
|
10
|
1
|
Coastal Salt Marsh |
|
11
|
7
|
Freshwater Marsh |
|
12
|
Cypress Swamp | |
|
13
|
5
|
Mixed Hardwood Swamp |
|
14
|
Bay [trees] Swamp | |
|
15
|
Shrub Swamp | |
|
16
|
Mangrove Swamp | |
|
17
|
Hardwood Forest | |
|
18
|
11
|
Open Water |
|
19
|
16
|
Grasslands & farm lands |
|
20
|
10
|
Shrub and bush Land |
|
21
|
Exotic Plants | |
|
22
|
11
|
Barren & Urban Land |
|
23
|
21
|
all wetlands |
|
Total
|
100%
|
Terminology:
Xeric means dry, or drought tolerant
Mesic means intermediate tolerance for water
Wetlands in Florida can be characterized by fresh or salt water and by grasslands or forests depending on the loaction
| Area or habitat determinant | grasslands | forests |
| Fresh water | marshes of cattail and sawgrass | Cypress or mixed hardwoods |
| Marine (salt) water | salt marshes of Spartina | three species of mangrove trees |