How many values inhere in Forests?
![]()
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | origin of the word tree | uses | economics | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
Saranac Lake, Adirondack Mountain Park, 1885.
![]() Several
economic, ecological, and political facts are relevant to answer this question.
Several
economic, ecological, and political facts are relevant to answer this question.
What is your opinion based on the facts?
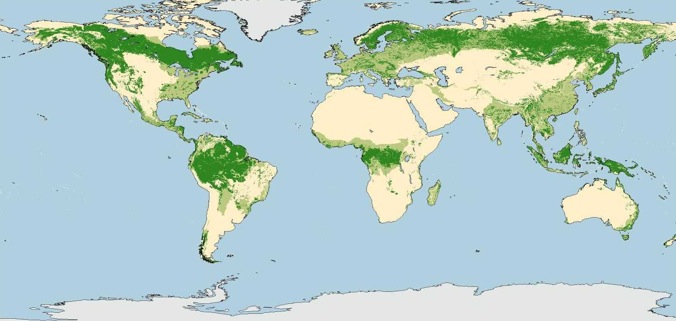
Today, forests occupy approximately one-third of Earth's land area, account for over two-thirds of the leaf area of land plants, and contain about 70% of carbon present in living things.
Trees, groves, woods and forests have been held in reverence in folklore and worshipped in ancient religions. However, forests are becoming major casualties of civilization as human populations have increased over the past several thousand years, bringing deforestation, pollution, and industrial usage problems to this important biome.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
National Arbor Day Foundation is dedicated to forests being restored, one tree at a time or more because, among many services, trees reduce erosion.
Woods, glades, groves and coppice are all terms that refer to forested places and indicate the varied meaning based on their different values to the inhabitants that forested landscapes have had in the past.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
Paleontology of prehistoric forests
 About 420 million years ago, during the Silurian Period, ancient plants and arthropods began to occupy the land. Over the millions of years that followed, these land colonizers developed and adapted to their new habitat.
About 420 million years ago, during the Silurian Period, ancient plants and arthropods began to occupy the land. Over the millions of years that followed, these land colonizers developed and adapted to their new habitat.
The first forests were dominated by giant horsetails, club mosses, and ferns that stood up to 40 feet tall.
Life on Earth continued to evolve, and in the late  Paleozoic, gymnosperms appeared. By the Triassic Period (245-208 mya), gymnosperms dominated the Earth's forests. In the Cretaceous Period (144-65m mya), the first flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared. They evolved together with insects, birds, and mammals and radiated rapidly, dominating the landscape by the end of the Period.
Paleozoic, gymnosperms appeared. By the Triassic Period (245-208 mya), gymnosperms dominated the Earth's forests. In the Cretaceous Period (144-65m mya), the first flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared. They evolved together with insects, birds, and mammals and radiated rapidly, dominating the landscape by the end of the Period.
The earth's forest landscape changed again during the Pleistocene Ice Ages — the surface of the planet that had been dominated by tropical forests for millions of years changed, and temperate forests spread in the Northern Hemisphere.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
![]()
The utility of trees.
The majority of timber harvested in the United States goes into lumber production (53%), and pulp products (32%). Other uses include veneer and plywood (7%), and fuel wood (7%).
The United States has 8% of all forest in the world, making it the fourth most forest-rich country with approximately 750 million acres of forestland. The majority of forestland in the United States is located in the Pacific Coast (including Alaska), and Southern regions. Forests are actually sources of water and have been protected over extensive regions for that reason since the 19th century.
| regions | acreage in millions | |
|---|---|---|
 |
Southern | 214 |
| Pacific Coast | 214 |
|
| North | 171 |
|
| Rocky Mountain | 151 |
|
Total acres of forest |
750 |
There are approximately 689 species of trees in the United States.
Most of the forestland in the US (57%) is managed by private individuals and companies. The remaining 43% is public land managed by local, state, and national government agencies.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
The root word perhaps ultimately from Proto-Indo-European word: *dru, – "tree," as the notion of "steadfast as an oak."
This notion is seen in the same root, Lithuanian drutas "firm," Welsh drud, Old Irish dron "strong," Welsh derw "true," Old Irish derb"sure."
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
![]()
Multiple uses: recreation, water, wildlife viewing and carbon storage.
 Between private and public land, almost 86% of all forestland in the country is available for outdoor recreation, much of which is located in the west. Between the Pacific Coast and the Rocky Mountain regions there are 10.3 acres of forestland per person, and in the northeast and southeast regions of the country there are still 2.9 acres per person to enjoy.
Between private and public land, almost 86% of all forestland in the country is available for outdoor recreation, much of which is located in the west. Between the Pacific Coast and the Rocky Mountain regions there are 10.3 acres of forestland per person, and in the northeast and southeast regions of the country there are still 2.9 acres per person to enjoy.
American forests harbor valuable habitat to thousands of species of animals.

Our forests provide more than half of the country's drinking water originates in forests, and the total amount of carbon stored by our trees offsets around 10% of US emissions from burning fossil fuels.

Conservation efforts: 20% of US forestland is under some type of conservation program, which is almost twice the world average of 11%.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
![]()
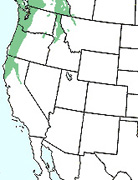
Economics of forests in Oregon and Washington.
Throughout
the Pacific Northwest lumber operations employ over 109,000 people in logging,
milling, and transport. The average wage of a mill worker or logger is $35,000
per year (1990 dollars) . The unemployment rate in the entire region is above the national average
at about 9% and in your local area it is closer to 13%. It is estimated that
one out of every four teenagers just out of high-school is looking for minimum-wage
work. This was the very sort of work that mills once provided.
 Recently collectors have asked the Forest Service to grant permits to gather
truffles -- a root-fungus -- that has become a lucrative trade item as gourmet
ingredients in fine food. The sustained yield of these forests is also connected
to the survival of salmon fishery stocks in the region. The salmon fishery is a $1 billion
sport and commercial enterprise employing 62,000 people in the Washington and
Oregon region.
Recently collectors have asked the Forest Service to grant permits to gather
truffles -- a root-fungus -- that has become a lucrative trade item as gourmet
ingredients in fine food. The sustained yield of these forests is also connected
to the survival of salmon fishery stocks in the region. The salmon fishery is a $1 billion
sport and commercial enterprise employing 62,000 people in the Washington and
Oregon region.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
![]()
Forest Ecology

Ecologically speaking –that is functionally– the "growth of the conifers in 100 - 1000 year old forests depends on a mutualistic relationship between tree roots and a class of fungi, known as mycorrhizae, that infect their roots.

 Unable to carry out photosynthesis,
these fungi attach themselves to the roots to obtain the sugars they need. The
mycorrhizae absorb water, soil nutrients and oxygen, passing these on to the
trees. Antibiotic compounds in the fungi protect the tree from root pathogens
and act as a protective sheath around the roots to bar parasites. The fungi
produce chemicals that speed up the growth of new root hairs and tips. These
two mutualistic partners, the trees and their fungi are, in turn, dependent
upon symbiotic relationships with a number of small forest rodents such as squirrels,
voles, and mice. These creatures feed on the fleshy collection of fungal spores
-- called truffles. Once consumed the spores remain undigested, passing back
into the soil to grow another generation of root fungus."
Unable to carry out photosynthesis,
these fungi attach themselves to the roots to obtain the sugars they need. The
mycorrhizae absorb water, soil nutrients and oxygen, passing these on to the
trees. Antibiotic compounds in the fungi protect the tree from root pathogens
and act as a protective sheath around the roots to bar parasites. The fungi
produce chemicals that speed up the growth of new root hairs and tips. These
two mutualistic partners, the trees and their fungi are, in turn, dependent
upon symbiotic relationships with a number of small forest rodents such as squirrels,
voles, and mice. These creatures feed on the fleshy collection of fungal spores
-- called truffles. Once consumed the spores remain undigested, passing back
into the soil to grow another generation of root fungus."
Without the decaying logs & snags about 1/3 of the mammals would die.
The endangered spotted owl feeds on these rodents and nests in old trees.
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view
See:
Trees often define borders or boundaries and make ideal buffers.
Terms to define
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | economics | origin of the word tree | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | forests as sources | valuation of | minority view
Dr. Siry
Ecological Problem Solving
Name: ____________________________________
February 18, 2015
What is the conflict over the forest?
1. How many groups of people use this forest?
2. How did this conflict over the uses of the forest occur?
3. What did you feel were the salient (key or items of over-riding importance) facts in the forest problem?
4. What was your opinion in reading page 1?
5. What was your opinion in reading page 2?
6. What is your recommendation to the superintendent of the National Forest?
Because of what specific facts, factors and reasoning?
You are a member of a technical advisory committee to the local Superintendent of the regional National Forest. The citizens committee established by the U.S. Forest Service (NFS) to encourage participation in the decision making process of forestry policy has demanded that the Forest Service open more acreage to logging in order that the local mills have sufficient timber to operate throughout the Christmas season and into the new year. The last superintendent was transferred for saying that at current logging rates the equivalent of 129 football fields / day disappear. What will you do and how will you advise this super to respond to these following issues?
The NFS is a federal land holding agency with the duty under the Multiple Use Act of 1960 to provide a variety of people access to the resources of the forest lands including, hunters, fisherman, hikers, & lumber companies. Merrill K. Ridd, geographer and Forest Service employee, wrote, in 1965, that "The object of multiple use management is very simple. It is to manage the resource complex for the most beneficial combination of both the present and future uses." Under the 1960 Legislation Congress enacting Public Law 86-517, states, in part, that: "The Secretary of Agriculture is authorized and directed to develop and administer the renewable surface resources of the national forests for multiple use and sustained yield of several products and services obtained therefrom." As Ridd points out "While the doctrine of multiple use is widely accepted, there is still some misunderstanding of how it should be accomplished." And this is why the new superintendent has appointed you as a technical adviser to inform the Service on the best course of action.
The forested area in question is 85% conifer and mixed deciduous hardwood stands covering steep slopes and some inaccessible back country canyons and mountain meadows. The area covered in aging trees includes Douglas Fir, Red Fir, Yew, Oregon Ash, Big Leaf Maple, Red Cedar, Sycamore, Sitka Spruce, Engleman Spruce, and other hardwoods. A large portion of the lands bordering the National Forest have been logged and replanted in immature lodgepole or ponderosa pine and Douglas fir. This has created a long and sinuous ecotone within the National Forest of mixed soft & hardwood conifers. The request of the citizen's advisory group would log the ecotone, an accessible swath of trees between two clusters of 500 - 1000 year old Spruce, Cedar, Yew or Fir trees, and clear an entire bank of the longest tributary stream in the National Forest.
[See the map on the bottom of this next page.]
Questions to answer | terms | paleontology | uses | origin of the word tree | economics | ecology | simulated problem | problem visualized | map | valuation of | minority view