![]()
"Darwin noted that animals change their affect in response to environmental situations–in other words, they make faces."
The limbic system of the human brain has rightly been referred to as the reptilian brain since many of its allied structures have remained structurally in place since the emergence evolutionarily of the reptiles, millions of years ago. The fishes with whom we and the reptiles share a common ancestor also possess the olfactory, pineal, midbrain and optic-parietal structures from which our very brains developed."
"The core of our emotionality including the capacity to speak and comprehend emotional language is mediated by the sexually differentiated limbic system."
R. Joseph, Limbic System. p.104.
"The hypothalamus is an exceedingly ancient structure and unlike most other brain regions it has remained somewhat similar in structure throughout phylogeny and apparently over the course of evolution."
(Crosby et. al. 1966) quoted in Limbic System, R. Joseph, pp, 15-16.
.
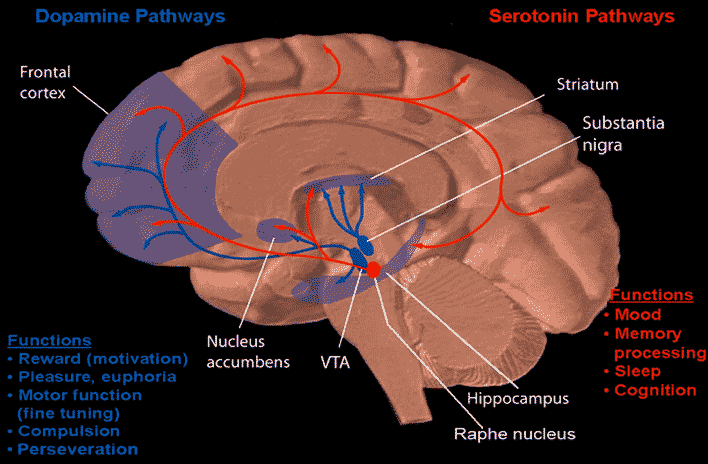
Wanting is not liking. " Wanting and liking are both involved in making an experience feel rewarding" and in the brain "lie within some some of the structures previously identified as part of the reward circuit."
"lies in a subregion of the nucleus accumbens"
"a second is found in the ventral pallidum, a deep-seated structure near the base of the forebrain."
the size of a cubic centimeter
"Yet like the islands of an archipelago, they link to one another–and to other brain regions that process pleasure signals–to form a powerful, integrated pleasure circuit."
"intense euphoria" ..."–seems to require activation of the entire network at once. Defection of any single component dampens the high."
p. 45.
"The regions the researchers identified–including the nucleus accumbens, which reclines at the base of the forebrain, and the cingulate cortex, which forms a collar around the fibrous bundle that bridges the brain's left and right halves–thus became enshrined as the operational base of the brain's reward circuit."
p. 42, Kringlebach and Berridge, "The Joyful Mind," Scientific American, August 2012, pp. 40-45.
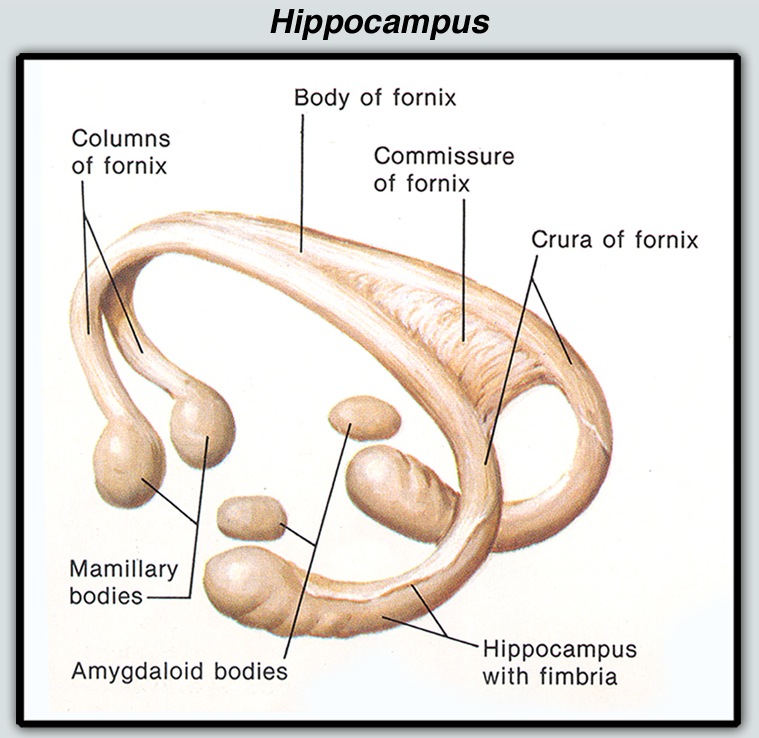
"Fear is an emotion associated with the amygdala"
"the human medial amygdala is exceedingly immature at birth. and doesn't become well myelinated until the 8th postnatal month."
"Initially the infant is fearless."
"Whereas fear is directly associated with with amygdala maturation, separation anxiety, the separation cry, and the formation of specific emotional attachment are also associated with the septal nuclei and anterior cingulate" (gyrus).
pp. 105-106.
"The hypothalamus, which monitors hunger and thirst, and governs internal homeostasis... is richly connected with the periaqueductal gray. (coordinating the activity of laryngeal, oral-facial, and inspiration -respiration cycles involved in vocalizations)
pp. 111-112.
The hypothalamus . . . "also appears to be responsible for generating quiescence such as following feeding."
Sources
Kringlebach and Berridge, "The Joyful Mind," Scientific American, August 2012, pp. 40-45.
R. Joseph, Limbic System. Cambridge, Mass.: Cosmology Science Publishers, 1990-2012.