
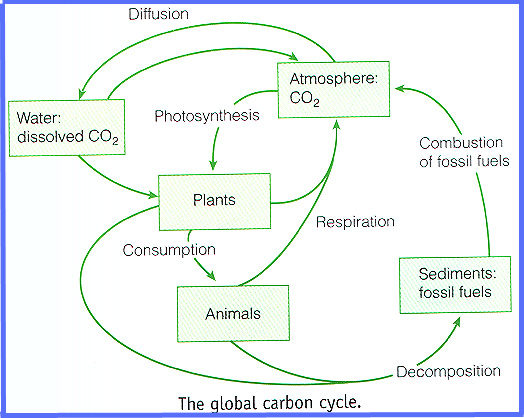
Nitrogen cycles and long-distance deforestation.
![]()
Goal: Distinguishing scientific facts from political opinions when solving problems in an articulate, precise and reliable way:
• demonstrate orally your reading comprehension
• understand by detailing in writing the structure of the argument,
• incorporate in essays & projects by explicit references to your findings,
• transfer the information to real world situations & ecological problems,
• translate complex ideas into widely understandable statements,
• argue rationally about the underlying and immediate causes of the problem,
• by analogy compare land-use and land-use changes to our long-term financial security.
![]() Read the file "“Knowing your forests from your trees: What’s afoul in the Woods?”
Read the file "“Knowing your forests from your trees: What’s afoul in the Woods?”
and
Write a response to the file: Deforestation, focusing on the following statement, for five - ten minutes:
Have you ever felt so unsure of something that it made you too confused to fully comprehend the risk you were actually in? What did you do?
Exchange your ideas and responses by reflecting with to two other students:
How was the situation you described above different from or similar to your (all of you) situation with respect to acid rain?
Key ideas:
| Reflect on this: | ||
|---|---|---|
How
What
|
How does your knowledge differ from those beliefs possessed by the public concerning the quality of the information on acid rain research? Acid Rain (precipitation) is caused to a great extent by generation of electricity and the use of mechanized transportation to the point which destruction of landscapes (Weal) has become internationally significant in the decline of forestry and agricultural productivity. |
 |
 |
Waldsterben | European forestry damage |
| is a German phrase for forestry disturbance usually caused or exacerbated by acid precipitation stemming from sulfur & nitrogen oxide emissions during fuel combustion. The ingredients in fossil fuel such as heavy metal are found as discharges into streams, soil moisture, and subsurface water that eventually find their way into rivers and estuaries ( acting a as nutrient traps) where forests, farmlands, and fisheries may be adversely affected.
|
||
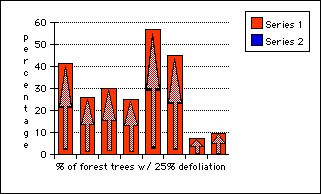
How widespread are the problems of timber loss and decrease in forestry cover?
![]()
European forestry damage in percent of affected timber:
| 41.3 | Czech & Slovak |
| 26.1 | Russia |
| 29.9 | Denmark |
| 25.2 | Germany |
| 56.7 | Un. Kgdm. |
| 45.1 | Poland |
| 7.1 | France |
| 9.7 | Romania |
Leading European Nation’s
extent of forest destruction
Nation - state and percent of forest trees 25% defoliated
![]()
Details of the damage and destructive impacts of coal, oil and gas combustion:
| acidified | growth rate | Energy use | per capita | |||
| deforestation | energy use | 1971 | 1992 | Labor force > | ||
| Un. Kgdm. | 56.7 | 1 | 3778 | 3743 | 0.1 | |
| Poland | 45.1 | 2494 | 2407 | 0.8 | ||
| Czech Republics | 41.3 | 3873 | ||||
| Denmark | 29.9 | 0.7 | 3860 | 3729 | 0 | |
| Russia | 26.1 | 5665 | ||||
| Germany | 25.2 | 0.2 | 3930 | 4358 | -0.5 | |
| Romania | 9.7 | -1.8 | 1953 | 1958 | 0.7 | |
| France | 7.1 | 2.1 | 3019 | 4034 | 0.4 | |
| Hungary | -0.3 | 1874 | 2392 | 0.3 | ||
| USA | 1.2 | 7615 | 7662 | 0.8 |
What is the underlying cause of the disturbed, damaged or destroyed=, landscape?
![]()
|
||
|---|---|---|
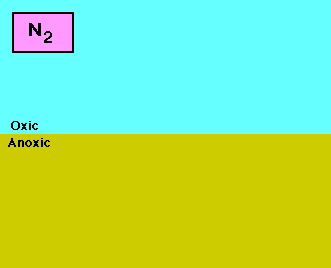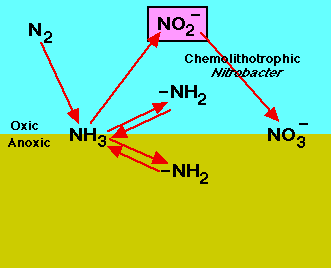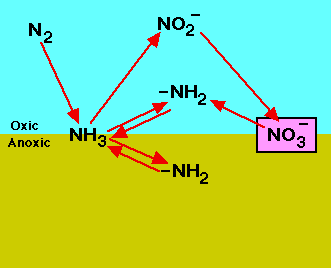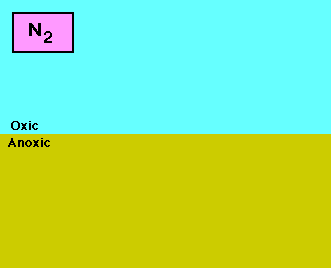
|
|
|
![]()