Young Charles Darwin.
Naturalists altered the way people can comprehend the world. |
Young Charles Darwin. |
|
| Ideas that redefined nature from 1800-1898. | ||
What did Charles Darwin know and when did he know it?
"all life descended from a common ancestor."
We can change our minds because Darwin and Wallace upon careful observation changed their minds.
Wallace's inspiration | Why revolutionary | Critics | Evidence | Selection | Variations | Geology | Conclusion | Symbiosis
| Darwin was described as "a man of enlarged curiosity" by his uncle Wedgwood. | |
| What was Darwin thinking at this time? | Cover page of a book by Darwin's mentor, Rev. Henslow. |
1828, a credulous Christian divinity student 1833, a naive witness to creation 1837, starts work on his "Species Book" 1838, September 28, he accidentally read Malthus about "geometric increase." 1839, thoughtful agnostic 1842-44, manuscript compiler 1848, Zeitgeist of resistance (reaction) and revolution (reform) 1858, a shock in the mail, A manuscript from Alfred Russel Wallace 1859, the reluctant revolutionary |
 |
Time line of indecision |
Henslow's Botany Book |
Wallace's inspiration | Why revolutionary | Critics | Evidence | Selection | Variations | Geology | Conclusion | Symbiosis
The codiscoverer of natural selection was Alfred Russel Wallace [1823-1913], a careful collector of specimens for museums. The young Wallace wrote to Darwin in 1858 and having sent Darwin a manuscript entitled: "On the Tendency of Varieties to Depart Indefinitely from the Original Type" was quite unaware of Darwin's shock upon realizing that these two men had very similar ideas about natural speciation.

Alfred Russel Wallace was an extraordinary naturalist.
![]()
Why were Wallace's and Darwin's ideas so revolutionary?
West 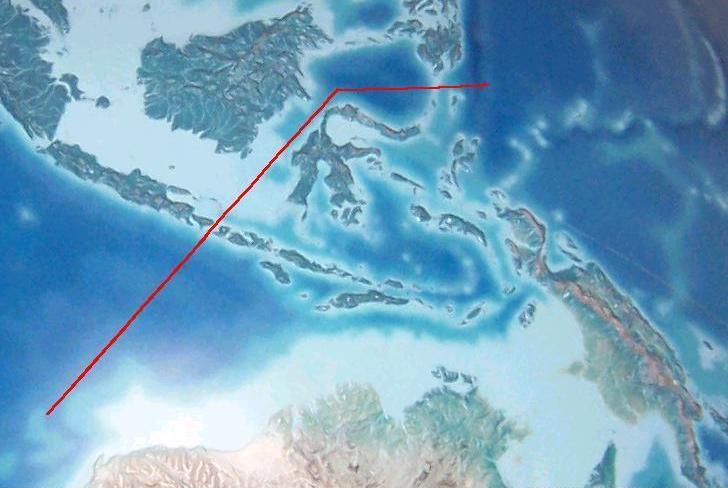 East
East
Wallace's line demarcating the divergence in species' variation and differences in abundance of species east of Bali and Java and persisting on New Guinea and Australia.
![]()
Critics charged that Darwin and Wallace had discovered the
Wallace is pictured here when he was 24 years old. He defended Darwin and published, in 1871, a book on Darwinism. In the book, Wallace marveled at the sheer number of creatures and the variety of their forms self-created by natural selection. Wallace began the book with some perspective.
"Every naturalist who has directed his attention to the subject of the geographical distribution of animals and plants, must have been interested in the singular facts which it presents. Many of these facts are quite different from what would have been anticipated, and have hitherto been considered as highly curious, but quite inexplicable. None of the explanations attempted from the time of Linnæus are now considered at all satisfactory; none of them have given a cause sufficient to account for the facts known at the time, or comprehensive enough to include all the new facts which have since been, and are daily being added. Of late years, however, a great light has been thrown upon the subject by geological investigations, which have shown that the present state of the earth and of the organisms now [2] inhabiting it, is but the last stage of a long and uninterrupted series of changes which it has undergone, and consequently, that to endeavour to explain and account for its present condition without any reference to those changes (as has frequently been done) must lead to very imperfect and erroneous conclusions."
Contributions to the Theory of Natural Selection, (New York: Macmillan, 1871). page 2.
![]()
Evidence, the quality of one's data is crucial.
Fossils as anomalies; the exceptions that do not fit the expected patterns.

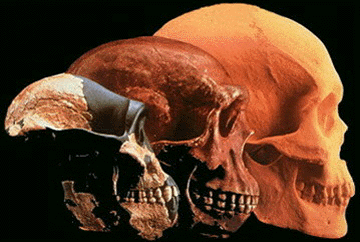
Fossil clam in sandstone & hominid skulls suggest there were previous and different conditions in the world.
Wallace's inspiration | Why revolutionary | Critics | Evidence | Selection | Variations | Geology | Conclusion | Symbiosis
The clues to evolution by means of natural selection were to be found in changes in diet and in the shape of bird's beaks.
"He found several species of finch adapted to different environmental niches."
| Darwin's Finches |  |
 |
| The same species? | broad beaked | narrower beaked |
This change in shape was all the more striking since these different species were found in the same island group while only one species was found in the entirety of South America. Why did this speciation take place? Darwin wondered, in 1835 and 1836 upon learning from other experts that he had collected more than one species in these islands, how such a situation could be explained.
![]()
Natural Selection
His example of sheep on varied terrains.
"I believe that species come to be tolerably well defined objects. . . "

Wallace's inspiration | Why revolutionary | Critics | Evidence | Selection | Variations | Geology | Conclusion | Symbiosis
Intermediate species: descent from a common species meant there were shared characteristics among different looking organisms.
"because new varieties are very slowly formed , for variation is a very slow process, and natural selection can do nothing until favourable variations chance to occur . . . "
 |
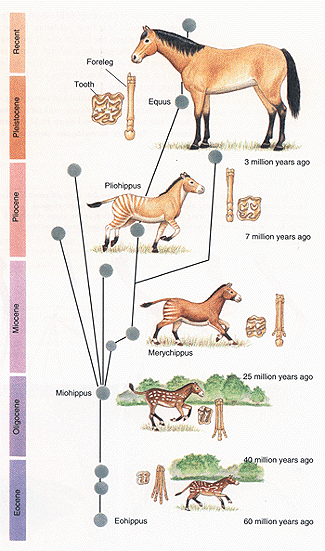 |
Paleontology of horses. |
Ascidians are in a class of the Tunicata subphylum of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders.
![]()
Wallace's inspiration | Why revolutionary | Critics | Evidence | Selection | Variations | Geology | Conclusion | Symbiosis
The centrality of Sir Charles Lyell's Geology to Wallace's and Darwin's re-conceptualization of how species could change shape given sufficient time over vast areas given sufficient isolation. Natural selection had been influencing the different survival rates of living creatures over thousands of generations.
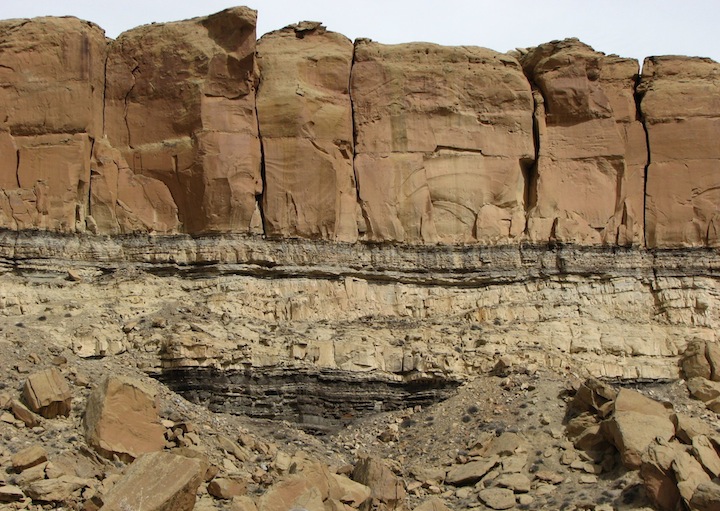
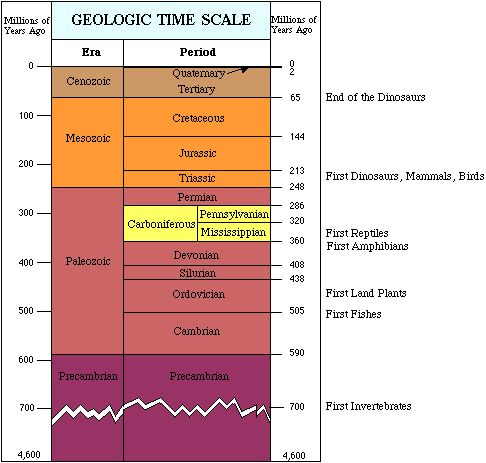

Deep time or Geological time is older than anyone in Darwin's lifetime could have ever imagined.
Life – especially bacteria & plants – has changed the face of the Earth over geological time.
Who was John Stevens Henslow,"Regius Professor of botany in 1825, having held the position of Professor of Mineralogy before that from 1822 at Christ's College," Cambridge University? – see here.
For example, it was Henslow who was interested in variation among species and arranged through proper introductions for Darwin to travel on the ship, H.M.S. Beagle fro 1833-1836. Of that event, Darwin wrote, "The voyage of the Beagle has been by far the most important event in my life, and has determined my whole career.’ (Christ's College)
See here for Darwin's family tree.
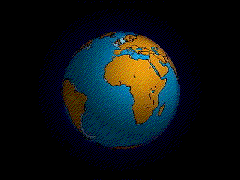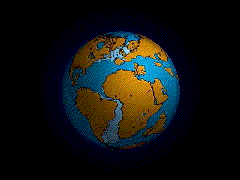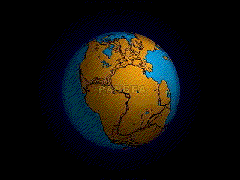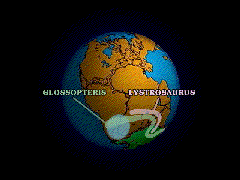 Naturalists who accepted Darwin's laws of variation & selection altered the way people can grasp the powerful shifting processes constantly at work shaping and reshaping the world and all its living inhabitants rather than seeing the Earth and its creatures as static and unchanging.
Naturalists who accepted Darwin's laws of variation & selection altered the way people can grasp the powerful shifting processes constantly at work shaping and reshaping the world and all its living inhabitants rather than seeing the Earth and its creatures as static and unchanging.
"The facts proved by geology are briefly these: —That during an immense, but unknown period, the surface of the earth has undergone successive changes; land has sunk beneath the ocean, while fresh land has risen up from it; mountain chains have been elevated; islands have been formed into continents, and continents submerged till they have become islands; and these changes have taken place, not once merely, but perhaps hundreds, perhaps thousands of times:— That all these operations have been more or less continuous, but unequal in their progress, and during the whole series the organic life of the earth has undergone a corresponding alteration."
Alfred Russel Wallace, Contributions to the Theory of Natural Selection, page, 2.
The Complete works of Charles Darwin on the Internet
Some notes from On the Origin of Species.
Wallace's inspiration | Why revolutionary? | Critics | Evidence | Selection | Variations | Geology | Symbiosis