

Charles Darwin from 1859 until 1872 completely altered the biological understanding of life on earth. Can the Origin of Species and Genesis be reconciled together in a new rendition of humanity's place in nature?
Perhaps, maybe depending in your knowing about genes, –yes or no, if you are confused– this inquiry must start with two related questions that are asked by the author:
• In what kind of world do we live?
• What is the evidence for evolution on Earth?
The Text
What Evolution Is, Ernst Mayr, 2001.
Our natural place | Evidence | What does evolve? | Conclusions
i.What describes and defines humanity’s place in nature?
Homo the genus had many secies two here are H. heidelbergebsis abd H. sapiens.
Human
origins
Creation
La Scala natura
Variety
Common ancestry
Fossils
Antiquity of the geological past.
Biological differentiation due to geographical isolation leads to speciation, and thus change over the generations through time.
A matrix of probabilities emerge from these two possible ways to understand the world:
| A) fixed kinds (ideas) | B) change (flux) | |
| 1) Infinite duration | ||
| 2) constant
world of short duration |
||
|
Type
or essence
|
Existence
& probability
|
“Already in the 1860s knowledgeable biologists and geologists accepted that evolution was a fact, but Darwin’s explanations of the how and why of evolution faced protracted opposition, as we shall show in later chapters…. some of the evidence for the actual occurrence of evolution that has been gathered since 1859.”
p. 11
ii. Evidence
“the findings would make no sense in any other explanation."
A. Fossils
B. lineage and variability (15)
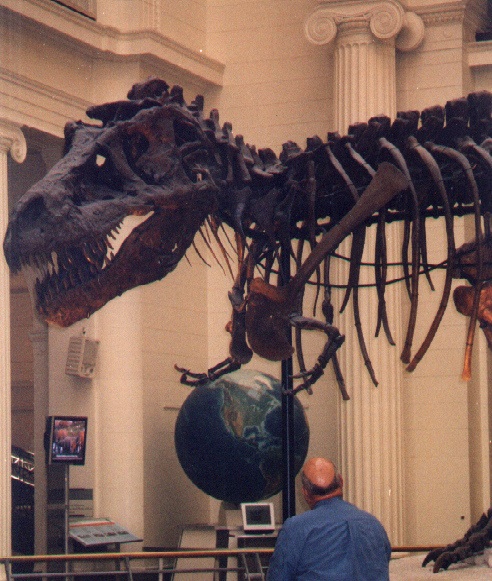

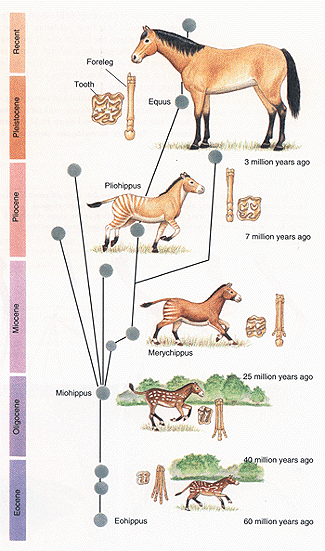
C. Common
descent
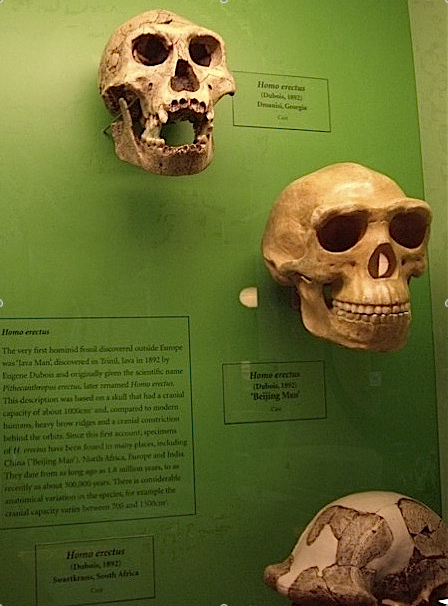

D. Morphological Similarity
E. Embryology
F. Vestigial
structures
G. Biogeography
or distribution
H. Molecular
evidence or molecular biology
The importance of molecular (DNA comparisons) analysis
The molecular clock
Evolution of the genotype as a whole
“the essentially complete DNA sequence of the entire genome”
p. 37genes are defined "as base pair sequences"
Origins of new genes (38)
Orthologous and paralogous genes
iii. What does and what does not "evolve" over time?
Offspring vary due to sexual selection when chromosome cross-over occurs.
Variations accumulate at a deferential rate among many more offspring than can survive
Over time, the surviving reproductive populations vary too greatly to breed successfully
- a. jumping genes or transposons
- b. genetic drift
- c. geographical isolation
- d. behavioral isolation mechanisms
iiii (iv). Conclusion:
The argument over Darwin's findings has removed some of the most imaginative and wonderfully bizarre qualities, in our perspective, of nature from the focus of our attention. Instead, we dwell on the exceptions to the rule, the dry to bland details of acquiring a living, and the hard to answer questions when all around us the exceptions, wonderment, and an enormously deep and certain knowledge calls out for our attention.
Darwinism | Ernst Mayr | Consequences of Darwin's Revolutions
The Complete works of Darwin on the Internet
Notes from the Origin of Species.
Related pages Darwin's Revolution | primary sources | plate tectonics
![]()
Bateson | Bronowski | Carson | Dawkins | Ehrlich | Hardin | Lewontin | Mayr | Margulis | Smil | Tattersall | Wilson
![]()
Terms | Glossary | Word webs | Basic vocabulary | Advanced Vocabulary | Antonyms | Synonyms