Vaclav Smil, Chapter 2, The Biosphere. 2003
 Attributes "an extraordinary character, unique in the universe."
Attributes "an extraordinary character, unique in the universe."
Living matter gives the biosphere an extraordinary character, unique in the universe... Cosmic energy determines the pressure of life that can be regarded as the transmission of solar energy to the Earth's surface... Activated by radiation, the matter of the biosphere collects and redistributes solar energy, and converts it ultimately into free energy capable of doing work on Earth...
A new character is imparted to the planet by this powerful cosmic force. The radiations that pour upon the Earth cause the biosphere to take on properties unknown to lifeless planetary surfaces, and thus transform the face of the Earth... In its life, its death, and its decomposition an organism circulates its atoms through the biosphere over and over again.
Vladimir Vernadsky, Biosfera, 1926
Constraints "...the near impossibility of an origin of life brings home the near improbable the even was." Ernst Mayr, 1990s.
Probabilities "the immediate future is usefully conceived as a bottleneck." E. O. Wilson.

The range of any organism is constrained by climate, genetic variability, adaptive abilities, and competition.

 Here a luguncularia racemosa, specimen of the White Mangrove
flowering (spring season, Florida south of Cape Canaveral and Anclote Key on the east & west coasts) among the red & black mangroves of the tropical marine shores.
Here a luguncularia racemosa, specimen of the White Mangrove
flowering (spring season, Florida south of Cape Canaveral and Anclote Key on the east & west coasts) among the red & black mangroves of the tropical marine shores.
![]()
Probability is a branch of mathematics that deals with statistical chances or options.
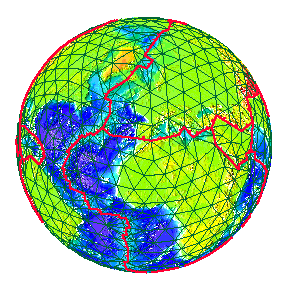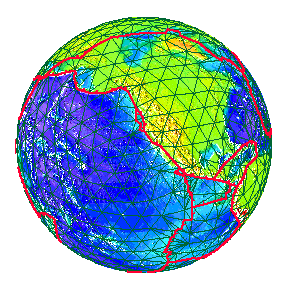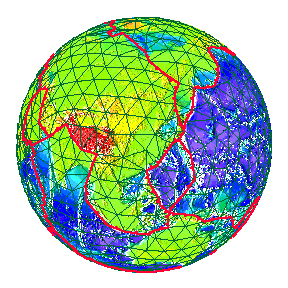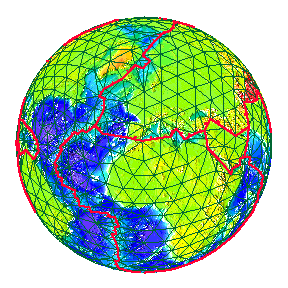

San Andreas fault as it reaches the Pacific Ocean at the Golden Gate.
![]()
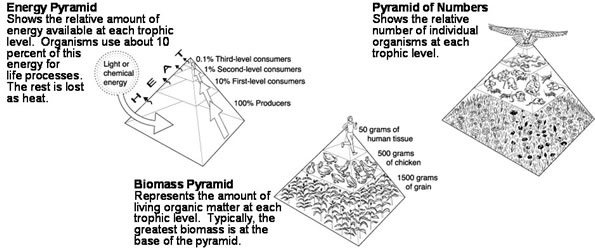
Two competing forces in ecological theory account for how life adapts well, fairly, or poorly to shifting conditions of an ecological system:
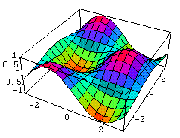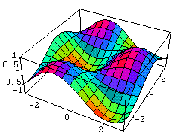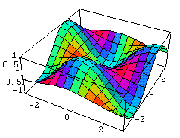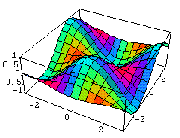
Environmental resistance [blue-to-red] is the combined affects of the conditions of existence on living things
Biological potential is [orange to green] the capability of creatures to exhaust their living condition's fertility
Together these forces enable life to thrive within a range of function called capacity.
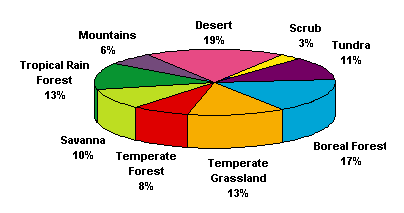
Every biome has a different capacity to sustain life.
capacity is the entire set of limitations created by environmental resistance [ER] and biological potential [BP].
Capacity: or C = BP / ER
persists in two kinds:
Biotic Wealth is the excess living material or biogenic remains not consumed by living creatures as
they seek to exploit their living conditions and compete with other species for nutrients, resources,
space and energy.
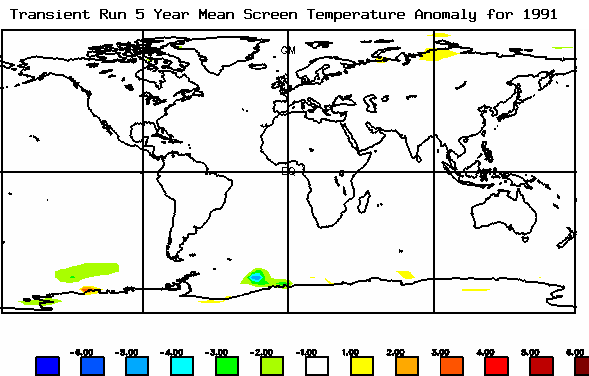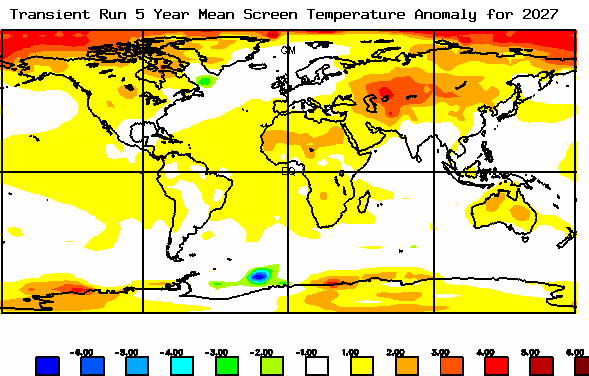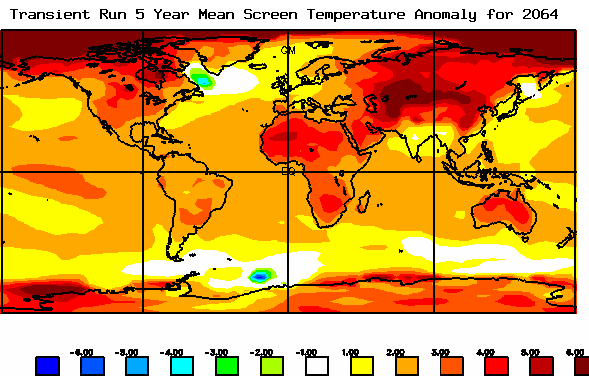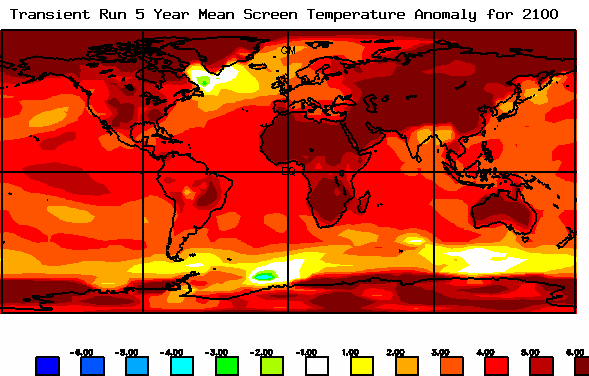
The pace at which the terrestrial surface warms will affect food, plants and soil.
The change in temperature and chemical composition of the oceans, air and landscape affect the pace at which life adapts.
Substance: reasons for life on earth have to do with ample supplies of necessary compounds, satisfactory atmospheric pressure, temperatures above freezing and moderate range of pH.
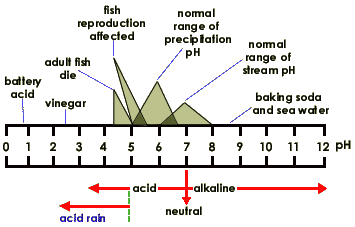
"Impressively simple," Vaclav Smil argues yet "astonishingly complex" are the
paradoxical attributes of life on Earth.
The basic "constraints. . . needed to create the environment conducive to life's. . . emergence and evolution," to Smil (Smil, 27) , are "stretched to the limits of its capacity" (Wilson, 33) according to Edward O. Wilson.
Wilson takes Smil's evidence and concludes "The constraints of the biosphere are fixed."
"We have driven atmospheric carbon dioxide to the highest level in at least 2000 years, unbalanced the nitrogen cycle, and contributed to global warming that will ultimately be bad news everywhere."E.O. Wilson (p. 23) Future of Life.
How will we know the arrival of the bad news?Protests in Bonn, Germany at international climate deliberations to protect people & species.
Wildlife as indicators of the "organic and inorganic conditions of existence" (Darwin):
Wildlife
fructus naturalis is the Latin term: public trust – ownership – access – regeneration
&
Wildlife Conservation – the protection of fisheries, birds, mammals, reptiles & amphibians
because they represent renewable sources of food, or fuel to achieve human ends.
related terms: game management, ecosystem management, endangered species protection, adaptive management.
Wildlife as indicators – living things tell us something about ecological situations.
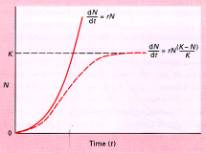
"the bottleneck through which we are passing is real. . . . , Earth's capacity to support our
species is approaching its limit." (EOW- 33)
![]()
Their existence serves to warn us.
√ guardians of a certain set of conditions
predators for whom diverse array &/or numbers of prey must exist
Their conditions tell us something.
√ annunciators of a range of tolerable conditions
steno (narrow) vs oligo (wide range)
This complexity and interdependence should alarm us.
√ any species upon which numerous adjacent species depend
keystone species allow for a varied, but vulnerable ecological system.
Life
 carbon based carbon compound molecules (organic)
carbon based carbon compound molecules (organic)
origin of life
genetic variability
Biochemical unity


51 different types of compounds account for 90% of the biomass of millions of species,
20 amino acids whose combination s make proteins are all variations of a single structure"
Cells and Organisms
"protein machines"
Universal Prerequisites
"the necessities for supporting a long-lived and hence relatively stable biosphere are obvious: ...
Quantifying these prerequisites is not that easy." (41-42)
Star Candidate & Habitable Planets (Mars and Earth) Goldilocks hypothesis
stellar mass, | planetary composition, distance, equatorial inclination
Life on the Earth "strange freight of life" Loren Eisley (anthropologist)
Formation and early evolution
Changing Atmosphere
Original highly reducing equilibrium conditions: (no free oxygen)
Oxygen crisis: made as a by-product of bacterial metabolism (bugs' waste)
ORIGIN OF LIFE
27 foot tower of life in the National Museum of Natural History
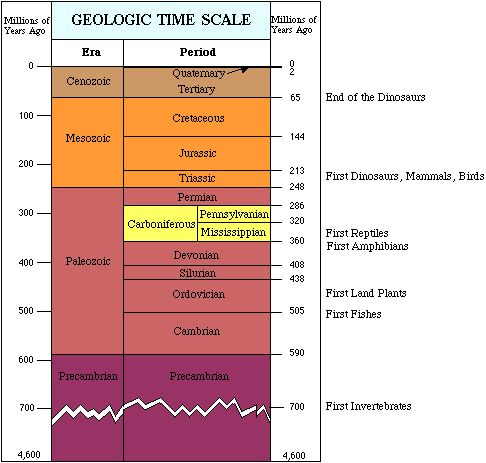
Precambrian organisms lived exclusively in oceans more than 543 million years ago (mya), and their functional importance is revealed by isotopic anomalies and stromatolites

![]()
He sets up the dichotomy (2-sided) of arguments about life's likelihood.
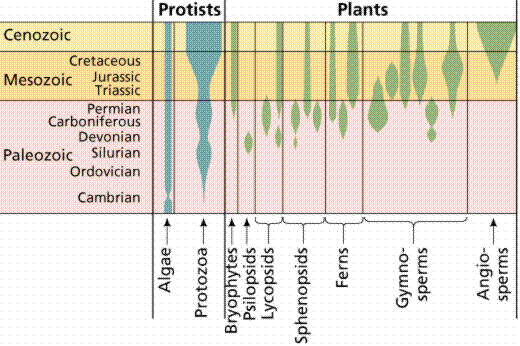
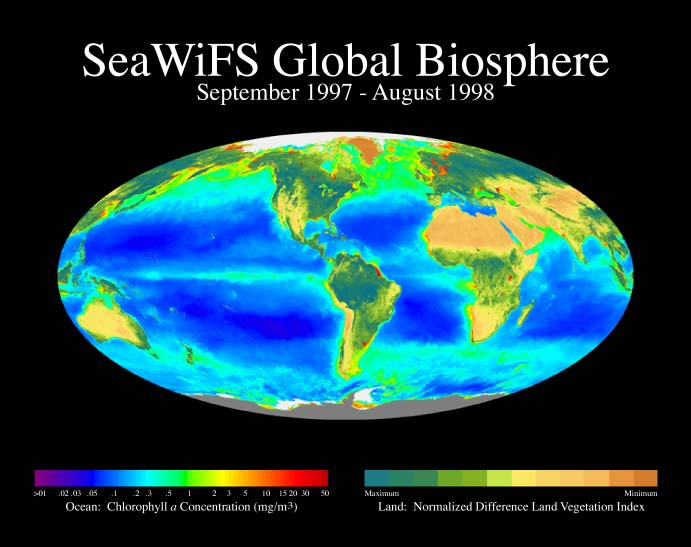
The width of the colored bands indicate the relative number of species that belonged to these types of plants and protists. The emergence of bacteria and plants that photosynthesize completely altered the Earth a billion years ago.
![]()
Two arguments about the relative abundance of life in the universe are inevitable due to matter and energy, or a rarity– if even replicable.
Inevitability argument
"Life is an obligatory manifestation of matter"
Jacques Monod, the probability of a biosphere existing is virtually zero.
( Smil, pp. 60-61)
Hoyle low probability estimate (1 in 4000 chances taking 10 billion years)
Andromeda Galaxy, one of billions, Smil's selective sieve is not the same as random shuffling.
Therefore
Descartes | Galileo | Hooke | Newton | Einstein | Tattersall | Gell-Mann
 |
||
Life | ingredients for |Origins of life | Biochemistry | Capacity | Constraint warnings | ecologic-diad | Paradoxically | Species indicate | Conclusions |
||
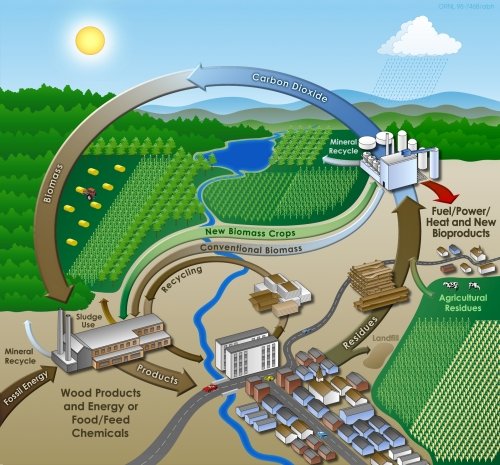
An article about Vernadsky's importance.multimedia look at Vernadsky's worknature | many meanings | nature's geometry | natural capital | role of plants | production |
||

|
||
![]()