
High veldt, South Africa.
Before & after 19th century emergence of biology to replace natural history.
Environment shapes organic life as living creatures affect the conditions of water, energy air and land as the surrounding environment.

High veldt, South Africa.
"Darwinism...we mean evolution by (means of) natural selection"
Darwin replaced earlier belief with at least five theories the last of which is natural selection.
pp. 36-37.
| previous ideas in Natural History | replacement by Darwinians | general term | |
| 1 | static world of no extinctions | dynamic with extinctions normal | "evolution" |
| 2 | common special creation | common descent from parent species | speciation |
| 3 | fixity of species (never change) | multiplication of species | adaptive radiation |
| 4 | catastrophist | gradualism | uniformitarian |
| 5 | creative selection | natural selection | survival of the fittest |
Examples:
1 fossils of trilobites
2 finches (mocking birds) , tortoises, pines
3 manatees, sea turtles, mangrove forests
4 Mt. St. Helens, White Pine Forest succession to beech & maple hardwoods
5 bacterial and insect resistance
One step vs. two-step process
1) -- abundant genetic variation every generation;
2) -- limited survival of the offspring who reproduce.
"mechanism of adaptive change"
harmony and adaptability of the organic world 68
Is it "an essentially mechanical explanation." ?
"Yes, in that it is a material
and physical examination of natural change and variation and is not metaphysical.
He accounts for variation
in terms of "survival of the fortunate."
Darwin's ideas about ethology, ecology, & evolution form the heart of the modern biological synthesis that he derived in part from Paley, Lyell, and Malthus.
| Evolution | Genetics | modern synthesis |
| by means of natural selection | cellular and molecular biology | combine to form |
| naturalists | Mendelian | biology |
Differentiation of characteristics in breeding populations and their offspring arises from:
All individuals convey variation +
reproductive success to selection from among the survivors
+
abundant offspring not all variants are "hardy"
in that they reproduce =
New generations with variations about the norms that are evident in the parent organisms.
p. 69.
Population thinking: is the capacity to think about fungus, animals, bacteria, and plants as not types of fixed (unchanging) kinds of creatures, but as a set of potentially breeding individuals such that interbreeding or even asexual reproduction conveys dvantages and disadvantages on the subsequent descendents of a breeding pair or reproductive individual. Thus fertility replaces the belief that like produces like as a focal point of comprehending how living organisms convey traits from parents to children and grand children.
Analog to animal and plant breeders is:
| key elements | meaning | examples |
|---|---|---|
| ethology, | animal behavior | learning, instinct & mating |
| ecology, & | animal or plant interdependency | who & what eat one another |
| evolution | animal, fungus, or plant descent | common ancestry |
 |
||
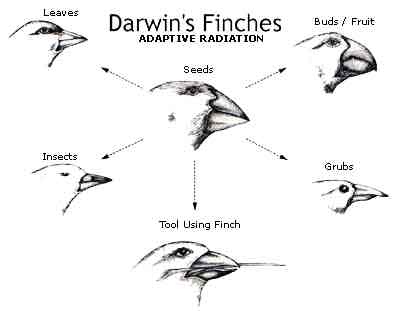
Environs shape life: |
The mouth parts of adapted creatures are selected for by surviving on widely available food sources. |
|
|
Literate
|
||
 |
There is no definitive answer to whether or not Darwin was externally influenced by his times (zeitgeist) and what he read, or was he influenced internally by his method of evaluating evidence he collected by contrasting and comparing his findings with practitioners and writers. 69. After 1833-36 voyage he was, with some help of ornithologist
John Gould in 1837, a determined "evolutionist" .... Gould upon reviewing
the mocking birds Darwin had gathered from different islands in the Galapagos
concluded that there were three different species where Darwin had originally
conjectured there were only one species with three varieties. What this meant was he had altered the status of human beings in the worldview of creation, natural history and biological thought. July, 1837, in Darwin's worldview nature and human order were altered:
Ernst Mayr One Long Argument (1991) Cambridge: Harvard U. Press. pages: 36. 37. 54-60. 69. |
|
| Photo-home | Books | Assignments | Calendar | Research | Government | Themes |
Last Updated on 3/20/03 | 6-8-2011.