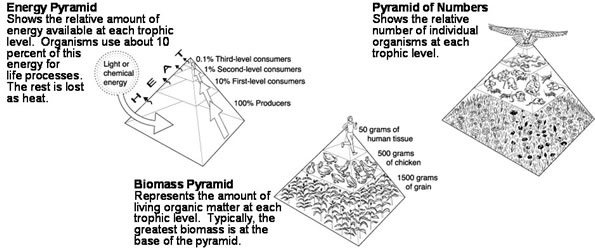
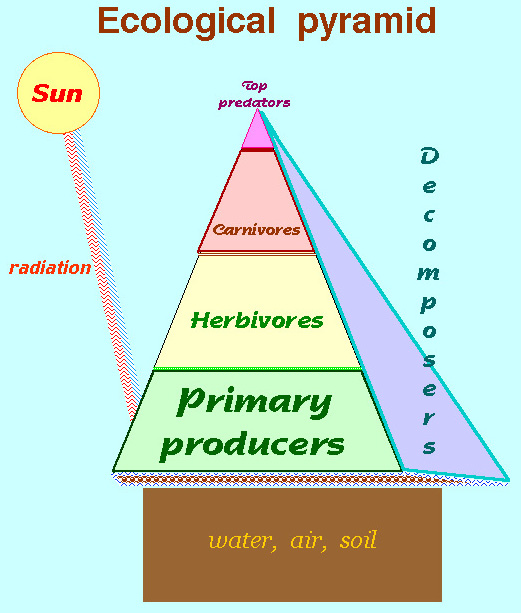
Impacts
The type of ecological effects that undermine functionally necessary structures in ecosystems.
These structurally necessary parts of an ecological system function variably to sustain a diversity of or a thriving number of species and thereby interfere with needed services because the extent of the interference diminishes the accumulation of natural capital:
√ damage
The relationship between natural capital and commercial assets over time as a graph:
Table of Consequences
" degrees of disturbance "
| # | Type | duration | remedy | strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | disruption | short-term | leave undisturbed | preservation, breeding |
| 2 | damage | long-term | conservation | adaptive management |
| 3 | destruction | nearly permanent | restoration | landscape renewal |
Because natural systems are dynamic and change with time, climate regime, geographical features and weathering, there are means to work with ecological processes to revive or restore wetlands, forests, fields, or populations of desired plants, animals, fungus or bacterial biota.
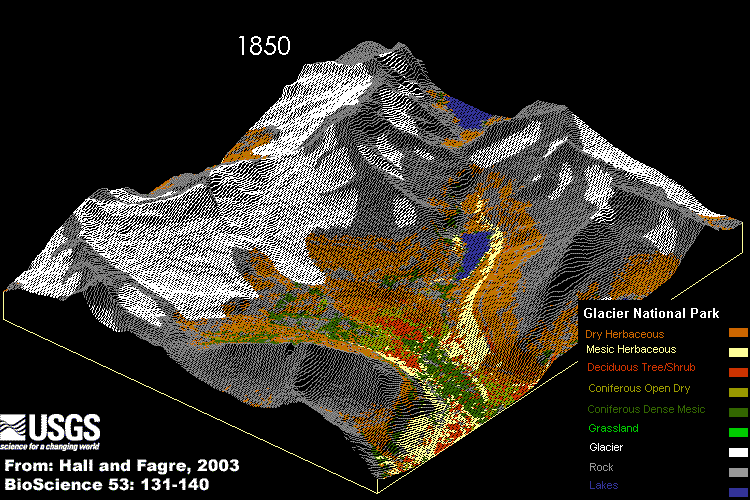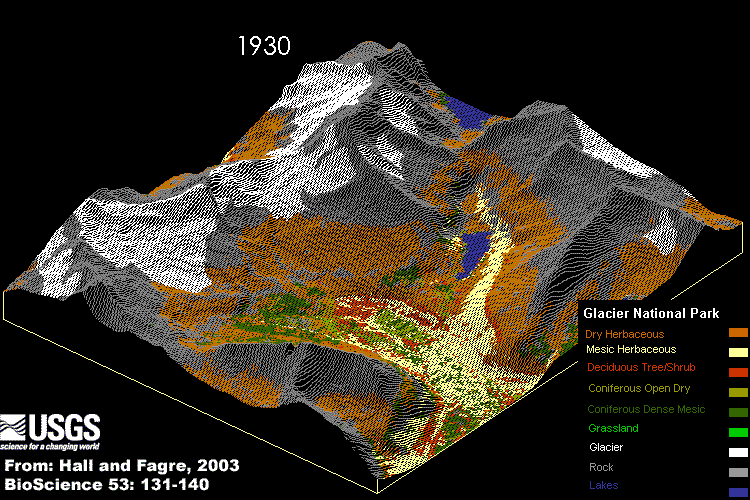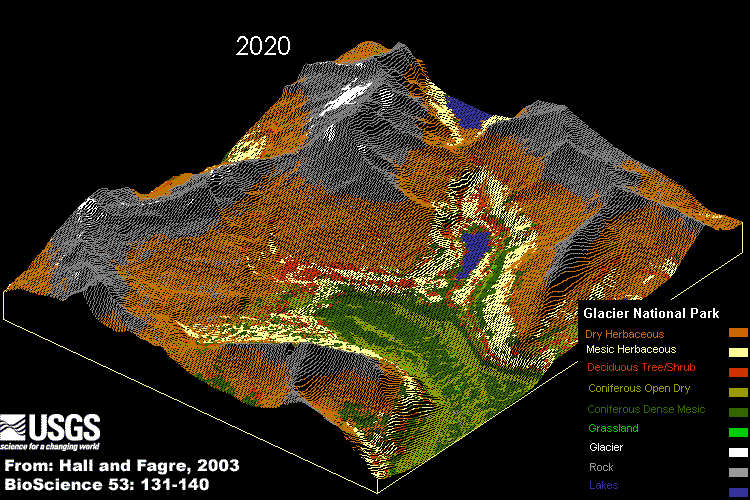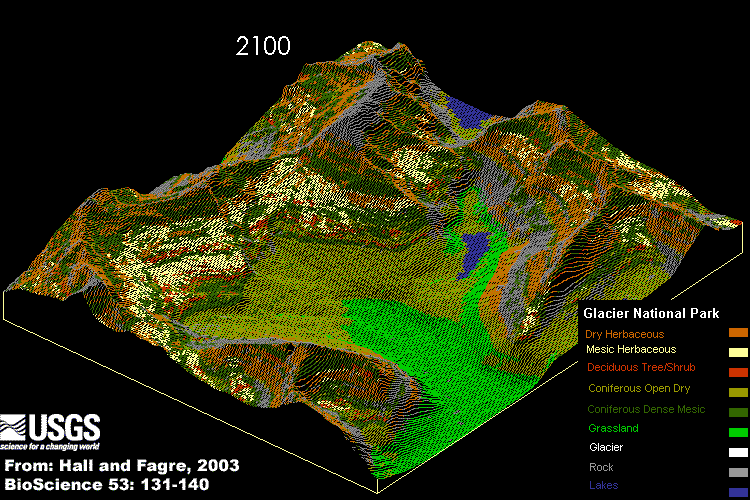
The computer simulation of the effects of abrupt climate change on part of Glacier National Park.
Facts
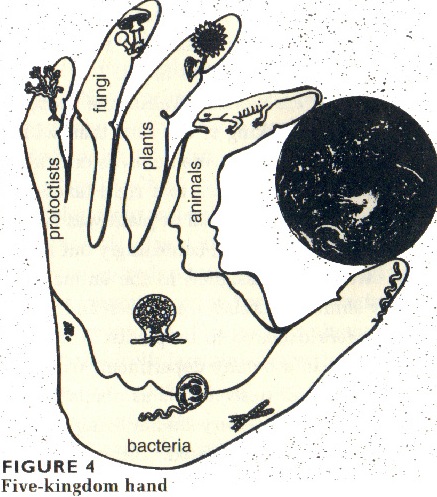
Life on earth is ancient and divisible into six huge kingdoms of thousands of related species with a common ancestral line from which all descended with differing capabilities and genetic capacities to adapt to altered conditions that favor one or another of these strategies for survival, nourishment, reproduction, and dispersal so that species are flourishing despite inherited disadvantages.
The three "D" s of ecosystem resilience and decline:
disruption | damage | destruction
Disruption, is the intermittent disturbance or enormous interference with natural systems.
- deforestation
- fire
- drainage
Damage, refers to the undermining of an ecosystem's productive potential.
- oil spill
- sewage
- dumping non-toxic but astringent chemicals
Destruction, involves the actual loss of one or more species, key physical features, or ecological ingredients that so sustain an ecological system that it ceases to exist as it was.
- toxic waste disposal
- radiation exposure
- acid rain
Habitats and biotic communities of importance:
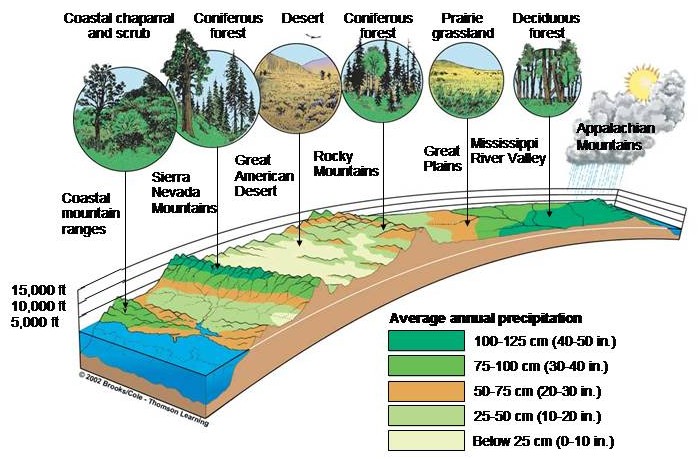
A transect of biomes along the 40th N. parallel of the central USA.

Oak Savannah woodlands thrive adaptively in periodically very dry regions such as Central California's hills.
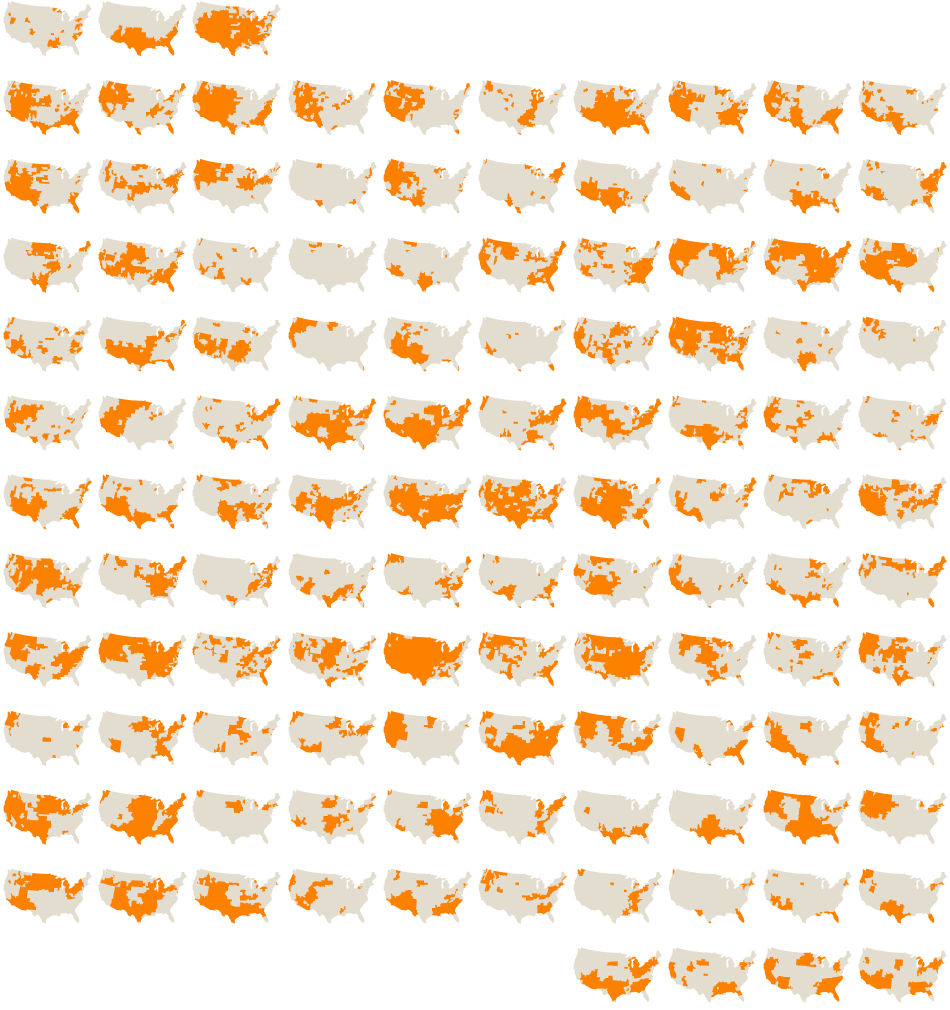
Drought patterns in the USA by county over a century from 1900-2012.
"More than half of the country was under moderate to extreme drought in June [2012], the largest area of the contiguous United States affected by such dryness in nearly 60 years. Nearly 1,300 counties across 29 states have been declared federal disaster areas. Areas under moderate to extreme drought in June of each year are shown in orange above."
New York Times: 7-20-2012
Terms to recall:
surplus.
auxiliary systems.
booster capacity.
WEAL from weald.
inflation.
conserving productivity.
investing.
seed corn.
thrift.
counter-cyclical compensation.
utility as a dead-end.
preservation and capital preservation,