Energy
How
can we know if the earth's life support systems are functioning well,
or poorly?
Energy is like pieces of a puzzle | complexity beneath appearances | four fundamentals | integrity | forces
This image graphically displays the concept of ecological tithe.
Energy and the environment are very much like movable pieces of a puzzle [Rubik's Cube]. The three dimensional cube defines a reasonably good means to comprehend energy for two reasons.
1.1, There exists three basic universal forces creating environmental resistance that we refer to as energy–the ultimate sources of energy.
1.2, Another way to think about energy as Rubik's cube is because for every facet of energy you understand there is a corresponding facet such that to change one characteristic of energy, the other two facets are altered simultaneously.
These complementary facets create complexity that requires functional integrity for any condition where energy is a factor in the outcome of a situation. 
Rubik's Cube is a three dimensional puzzle where you can never merely change one side.
Three fundamental universal forces are analogous to each side of the cube in that changes in one affect the other sides very differently:
- gravity "It means that, figuratively speaking, gravity is the square of the strong subnuclear interaction."
- strong force, fusion–the force propelling our sun as it does in all stars.
- electro-weak force, radiation, chemical bonding.
 Electromagnetic fields or radiant energy pervade the universe, the earth, life and animate our bodies.
Electromagnetic fields or radiant energy pervade the universe, the earth, life and animate our bodies.
2. A Foundation: forestry, arboreta, & diversity; the problem of sustainability in Amazon rain forest is a microcosm of the world's dilemma.
3. The complex of energy, forces, flows and feedback: Gregory Bateson and the model of reality.
4. One problem of energy lies in the western origins of attitudes about Nature.
The materials which make-up nature, as Aristotle defined, were the dialectical creation of four elements.
But as we have seen all forms of energy has physical, ecological and social facets.
 Energy
is the ability to do work, alter an existing condition, or the capacity
to regenerate spent fuel to
overcome resistance.
Energy
is the ability to do work, alter an existing condition, or the capacity
to regenerate spent fuel to
overcome resistance.
Systemic qualities in any situation where energy changes from one form to another means that there are characteristic functions that tie all the parts to a whole thereby creating an interdependent structure.
We know nature by disturbing the surrounding universe.
Disturbance: the deliberate or unintended influence of a single activity, or multiple activities on a larger pre-existing condition, or entire situation.
Law of the Conservation of matter
matter can neither be created nor destroyed – what you start out with in any reaction, you end up with even if it appears differently form the original form of matter.
Laws of Thermodynamics
1st Law: energy is neither created nor destroyed – but remains constant over time.
2d Law: energy is constantly degrading –every conversion of energy from one form to another is less than completely efficient–thus the energy is more random, less useful and we measure that as increasing heat.
3d Law: energy conversion form one form to another produces heat and in the final conversion all energy in the system, or universe is turned to heat–the heat-death of the universe.
Growth in the final analysis produces heat; but in all living things is constrained and limited by the ingredient or nutrient needed in the least amount. Thus the essential nutrient present in the smallest amount restricts the rate of growth. Justus von Liebig discovered in 1840 this anomaly in production states that yield is determined by the scarcest resources.
Three laws of motion: inertia, gravity, and reciprocity.
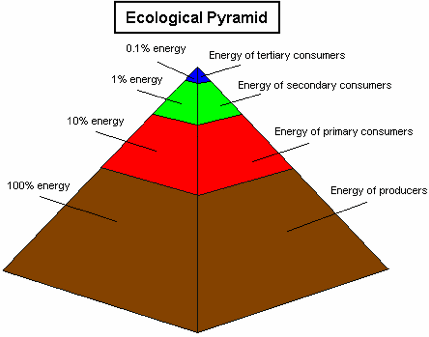
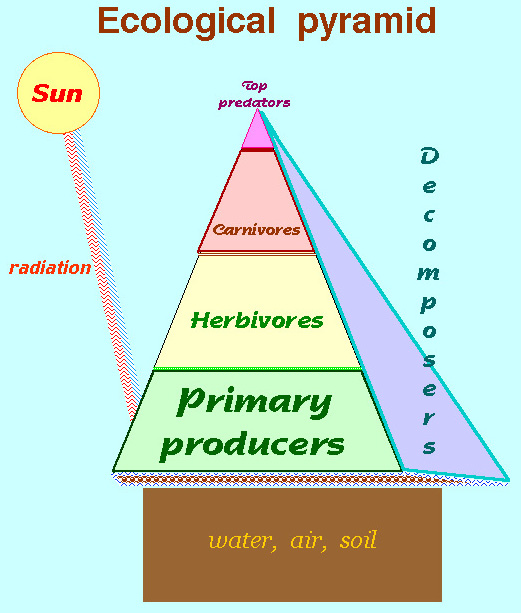
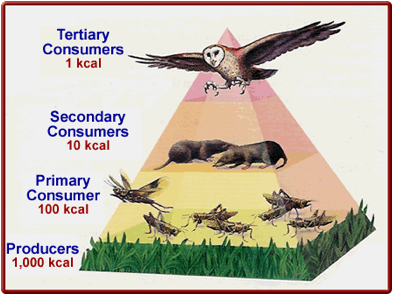
The ecological pyramid is based on the laws of thermodynamics, whose limitations influence the tapering shape of the design because less and less usable energy is available at each subsequent level of consumption.
Given the laws of ecology that constrain all systems, a combination of two underlying classes of existence: abiotic or inorganic and biotic or the organic facets of existence cyclically combine due to available energy to form the complexity of ecological systems.
oxygen
air
water
Abiotic food
fiber
Biotic
The complexity of nature
1. distinguish inorganic habitat's parts:

radiation is a limiting factor
area's size, extent geology, & geographical setting
water, energy, air & land form a resource base
2. recognize the biotic communities' essential features
vegetation is the cornerstone of natural productivity
keystone species and the web of numbers
stress functions, rates of turnover, & renewable cycles.
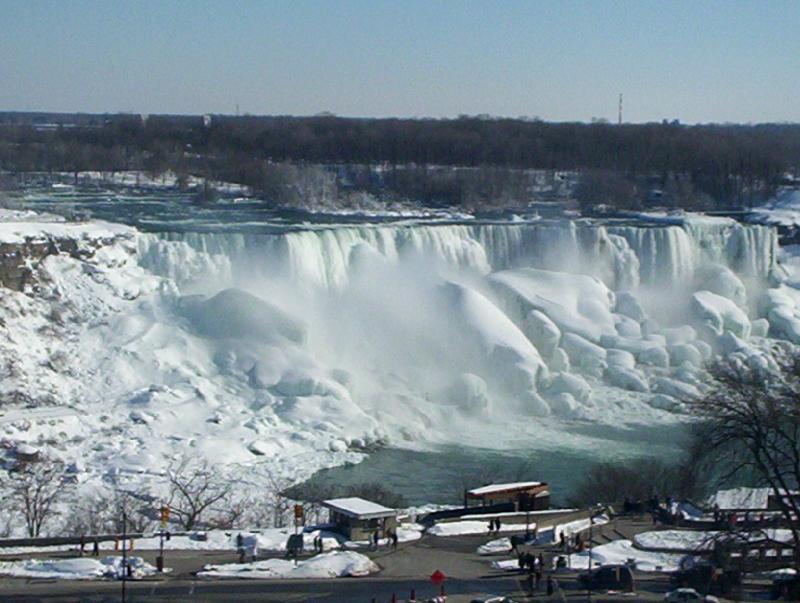
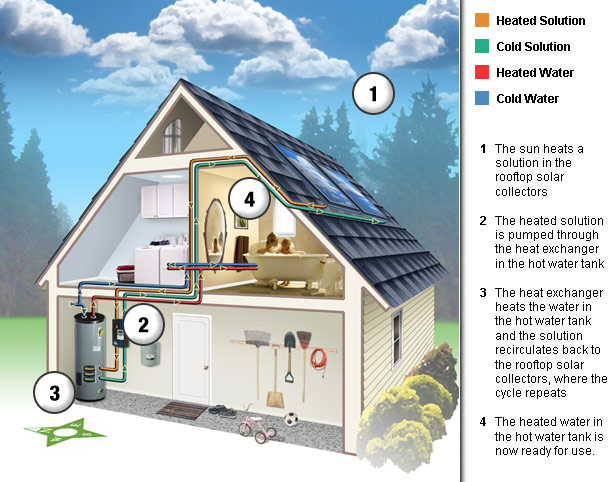
Gravity relentlessly pulling water even through the ice buildup of Niagara falls moves mass from the upper level of the Canadian shield down to the lower elevation.
The pressure from the force of moving water can be made to turn a turbine. In so doing the turbine or dynamo spins an iron electromagnet in a magnetic field inducing an electrical current to flow.
Electricity is inherent in the very structure of the atomic elements and compounds, such as water. Electrical forces inhere in the electrons and protons comprising the atoms which compose all that we see in the universe. 
Bacteria are more complicated and important than ever thought.
Three basic Scientific Laws of matter and thermodynamics
Systems and feedback loops are a means to understand ecosystems
Sustainable Earth, low-throughput or low-waste society (Miller; pp. 12, 50-51,60-63)
Population, energy and resource ratios:
Population, [P] times energy [E] & divided by resources [R-E] squared
P * E / R-E (squared)
The result of the equation is net useful energy [ Miller, 89.]
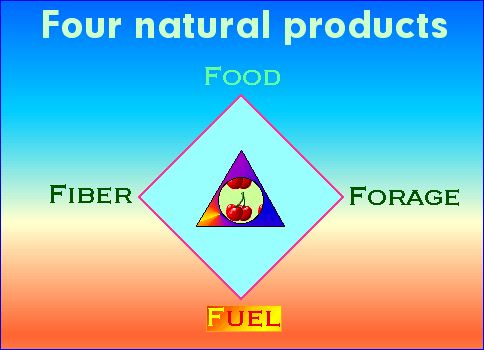
The magic of the number is four when considering the products of energy and the ways western civilization, influenced by the Greeks have thought about matter and energy.
Land Realism & geographical regeneration together may be thought of as ways to understand how four natural products of the landscape require, air, water and energy.
4 Fs: fuel, food, fiber, & forage are the four outcomes of human uses of ecological capacity.
fuel, plant and seed oils, petrol, coal, wood, etc.
food, calories from lipids, fats, proteins.
fiber, cotton, sisal, hemp, wool, thatch, etc.
forage -- a function, fodder, feed or for animals
Biological integrity & species richness rest on the idea that the terrain or habitat is sufficient to nourish the keystone species of any biological community.
Habitat as WEAL:
Water - Energy - Air - Land
4 Rs:
Schooling: reading 'ritin' 'rithmetic reason Ecology: reduce reuse recycle restore In ecology, the four R's of grammar school have their own equivalent to better examine how the world works such that students can explain the limitations imposed on all creatures and ecosystems due to the laws of the conservation of matter and energy.
functional integrity
The Earth as a system and ecosystems as subsystems of the Earth must have sufficient energy to move nutrients, rearrange materials, and remove wastes in sufficient amount and over adequate time-periods to not diminish new life from being nourished. This process functions with integrity based on the assimilative capacity of the water and air, and the carrying capacity of the land to nourish emerging life.
Ecological integrity is hidden, removed from our experience, but it is only too obvious when it is not functioning, as in the case of "waldsturben" or the destruction of forests by acid precipitation.
Six concurrent crises today hamper our scientific understanding of ourselves in the world.
Identity -- do we know who and what we are?
economy & society of narcissism
biological diversity is being lost
ecological life support system decay
spirit -- have we lost our souls in succeeding?
perception is confusing the real and the ideal
![]() Interpreting
the order we perceive in the world, leaves us with
Interpreting
the order we perceive in the world, leaves us with
different understanding
today from the beliefs of our ancient ancestors.
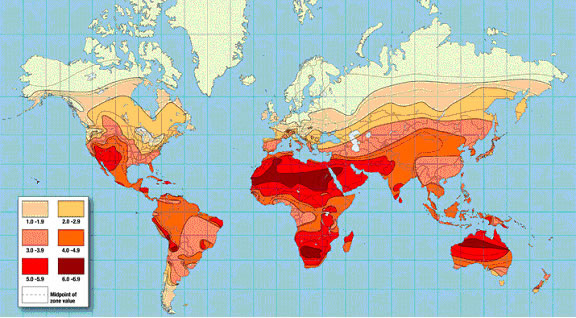
dichotomy Ancient Elements vs. Modern Forces Earth Gravity Air Electromagnetism Fire Fission – weak Water Fusion – strong Four forces, or are we able to unify electromagnetism with the weak force and explain the universe as the product of three forces?
Three forces, not four, are what some unification theorists suggest:
- Strong, hydrogen fusion into helium fuels the stars.
- Electro-weak, radioactive decay emits three forms of radiation.
- Gravitational, space is warped by mass.
The search for fundamental explanations of complex relations is one job of science.
1. Overview, pieces of a puzzle [Rubric's Cube]
2. foundation a problem of sustainability in the Amazon rain forest
3. Energy, systems and forces In our own back yard.
4. Western origins of NatureRubik's "magic" cube is a 3-D combination puzzle invented in 1974 by Hungarian sculptor and professor of architecture Ernö Rubik.