...... Ecology
...... Ecology Navigating the site:
Ecology

Three
laws of ecology are based on three laws of thermodynamics.
- You
can never merely do one thing.
So every action has an equal and opposite reaction!
- There is a paradox about free lunches; although there is no such thing as a free lunch, our earth in this universe may be the ultimate free lunch!
So, there are ecological consequences on earth that limit what people can achieve over time.
A pine forest living today is the descendent of vegetative associations that may have been selected for by the grazing habits of dinosaurs, millions of years ago [coevolution].
The three laws of thermodynamics are:
- The amount of energy in the universe (a closed system) is constant.
- Every conversion or transformation of energy (decay of order) from one form into another is always inefficient because it is accompanied by increased randomness, we call this increasing disorder, and in terms of energy that amount of random, disorder is measured as heat.
- The eventual heat death of the universe occurs because, as energy is transformed, heat accumulates until every conversion finally produces more heat or infrared radiation of such a low frequency and long waves, too disorderly to do any work.
![]()
Ecology (defined)
The study of creatures, populations, and life in relation to their surroundings or material milieu that dynamically sustains all living things.
Forest of Fontainebleau, Jean-Baptiste Camille Corot, 1846 Ecological thought, development of
Ecological values inhering in land
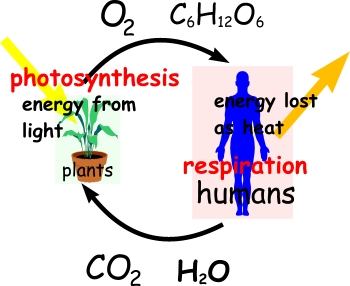
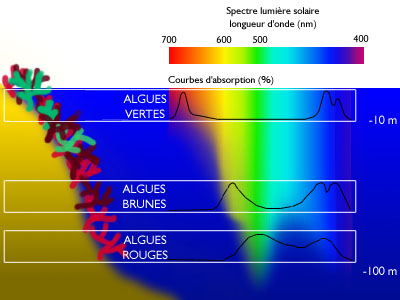
biological community is called a biocenose
natural wealth of habitats, or settings
Symbiotic associations are common.
A unifying science of the earth
English Commons
Genetics | Science Index | Social Analysis | Population Index | Global Warming Index | Nature Index | Words