“Natural Areas as Necessary Components of Man’s Total Environment”
by
Eugene P. Odum & Howard T. Odum
Odum on film | Ecology defined | Carbon dioxide | Carbon as a measure | Nitrogen problem | Assimilative capacity
C is the amount of public service needed to sustain private growth:
| N (N-1) | N 2 | ||||
| C = | ------------ | or approximately | C = | ------------- | |
| 2 | 2 | ||||
| services equal | Which is to say that: | N squared over two | |||
C is the network of services ( sidewalks, roads, sewers, fire, police, schools, hospitals, lakes, parks, wildernesses, forests, rivers, estuaries, beaches & oceans.)
N is the number of units in the network of services (or consider, N = natural areas' extent.)
Explanation:
“Our theme is that natural environment is an essential part of man’s total environment. Preservation of a substantial portion of the biosphere in a natural state, while not a panacea for all the ills of humankind, is, nonetheless, a necessity if we base the carrying capacity of the earth on the quality of human life.
Eugene Odum in first of six parts describes ecosystems and their importance:
Ecosystems and functional logic.
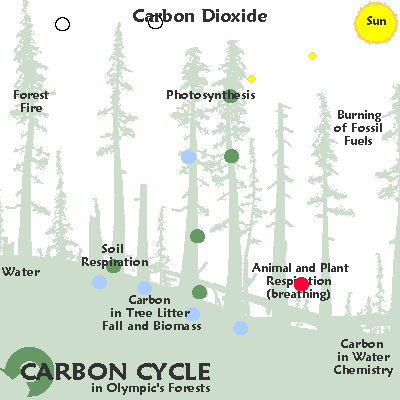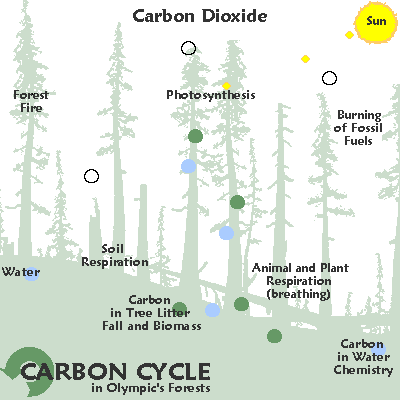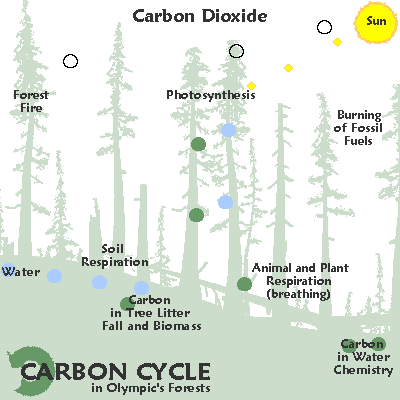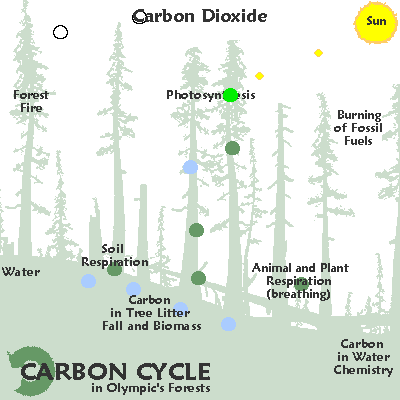
Any ecological system is called an ecosystem.
Key to comprehending any ecological system is the carbon cycle. The element carbon [ C ] "formed in a star whenever three helium nuclei collide at one spot within less than a million millionth of a second. Every carbon atom in every living creature has been formed by such a wildly improbable collision."Jacob Bronowski, Ascent of Man.
Natural areas are assets | Theme as opposed to thesis | Methodology | Ecosystem services | Ecology defined