 Revolutions
Revolutions
Navigating the site:
of ecological revolutions that
conceptualizes the relations among coexisting and coequal facets of natural and social forces that together shape the outcome of landscape alterations, air pollution, or water consumption.
ecological core is | model of wealth & worldviews | ecosystems are? | landscapes change
AIR
LAND  WATER
WATER
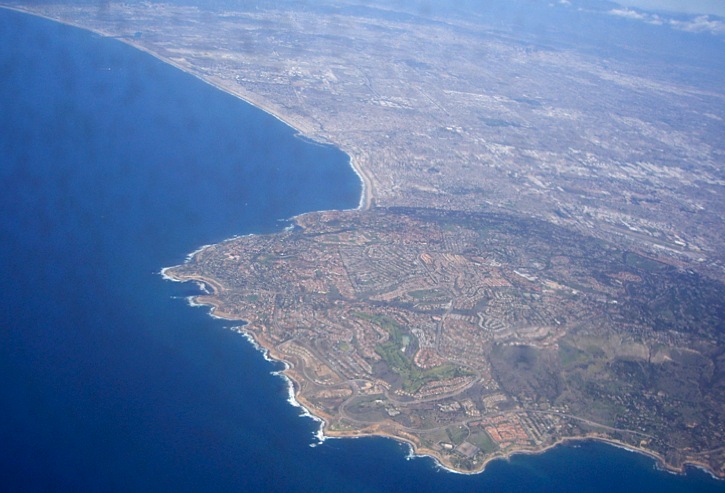
Does she adequately depict how landscape changes occur?
Land is an ecological system of living and non-living actors.
The relation of humans to nature is reciprocal.
Human dynamic natural fluctuations
landscape
|
polycheate worm reef is an amassing of indviduals. |
The ecological core is the focal point of ecological and environmental history so Merchant places it at the center of her concentric circular model of the dynamic conditions of existence.
Simple three concentric sphere model
ecological core is | model of wealth & worldviews | ecosystems are? | landscapes change

 Merchant's
model
Merchant's
model


