Concept maps reveal simple to complex descriptions.
| Compounds |
subatomic parts |
the world we inhabit |
 |
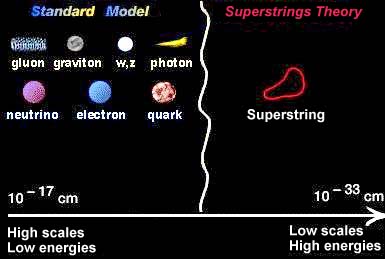 |
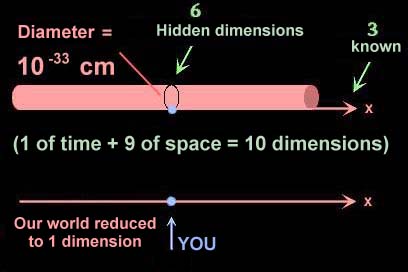 |
| |
|
|
| Atomic theory |
String Theory |
Reveals we live in many unseen dimensions |
The above concept map is an example of the idea of reductionism when moving from left to right, or of emergent properties when reversing directions and moving right to left.
|
The term reductionism means that as we break material down into ever smaller parts [Atoms, sub-atomic particles, and superstrings] one conclusion is that this process also (by implication) reduces the importance of human will, or personal volition.
|
|
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
A concept map is a graphical display of any deliberate relationship that is explained between two existing or among more than two basic notions, ideas or thoughts that evoke an image or graphic display of significant associations.
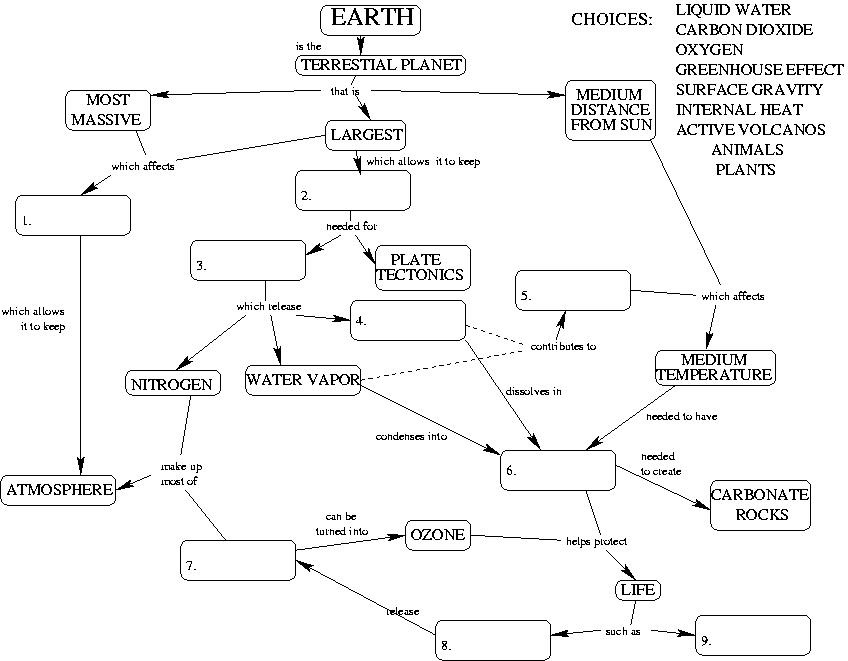
There are nine steps in the diagram below – meaning different ways to describe relations among concepts to describe the Earth – in getting from simple linear associations of related concepts to more complicated ways of diagramming causes and effects.
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
When arranged in a discernible pattern a concept map represents a simplified model of the systematic relations among important single conceptions that come together to form a larger, coherent whole.
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
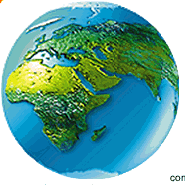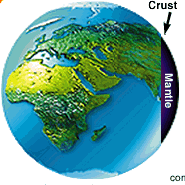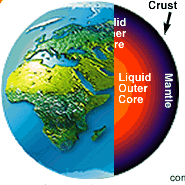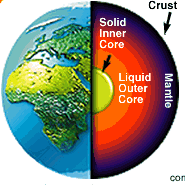
An intricate description of the Earth as a system of relations.
Earth here can be thought of as land, the natural features of any terrain for commercial purposes.
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
The mapping of ideas and their relations starts simply; called a linear formula displaying a sequential relation among variable concepts:
Consider a linear relation or formula for the creation of wealth; how is wealth created?

With linear relations among land, labor and wealth thinkers for five hundred years have used these categories to explain the "Labor Theory of Value."
| Land |
Labor |
Wealth |
| natural resources |
human resources |
valued outcomes |
| landscape |
agriculture |
food |
| minerals |
mining |
metals |
| water |
irrigation |
hygiene |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Nature |
when mixed with |
Human work |
creates |
Capital |
|
|
|
|

|
| |
X
|
|
=
|

|

|
Times
|
.gif)
|
Equals
|
|

|
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Means of learning
A linear concept map is but the start of a more complicated association among the many factors needed to describe actual conditions we find, say in a fishery.
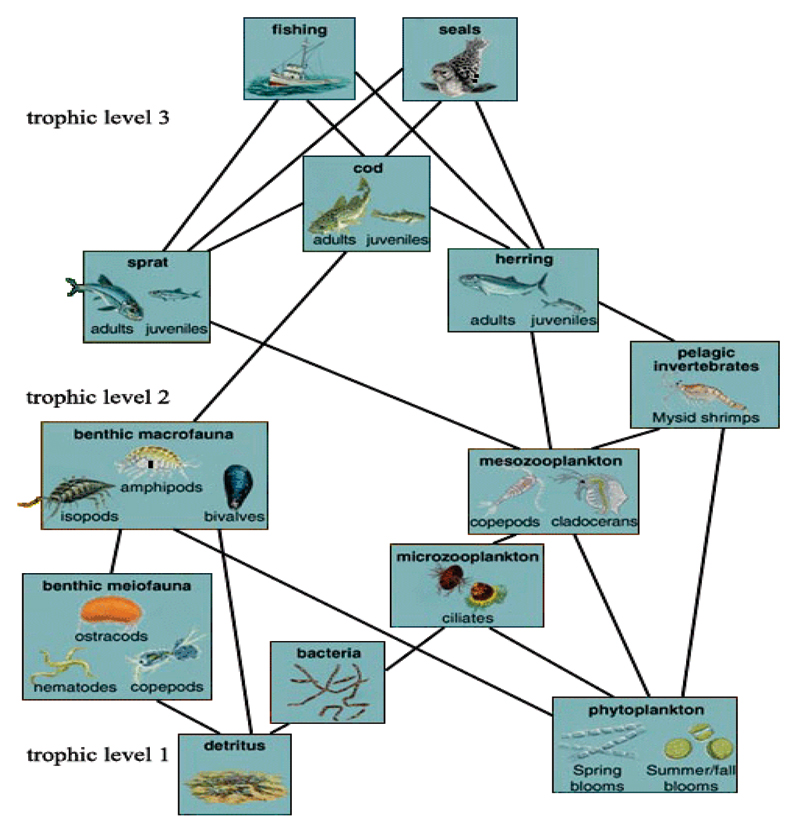
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
Frequently ideas and their relations are drawn as pyramids or a triangle to represent three equally significant relationships.

Sugar is an example of wealth from land and labor creating a durable commodity; the importance of sugar as a commodity is not to be exaggerated.
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
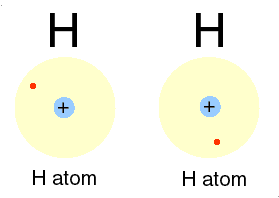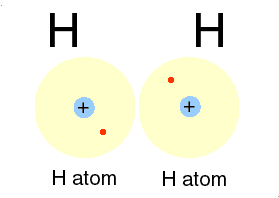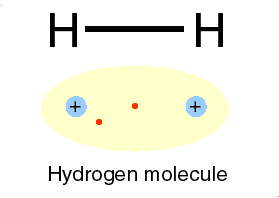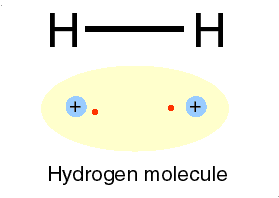
Or circular diagrams are used to depict a recurrent and recursive relationships among the four sectors:
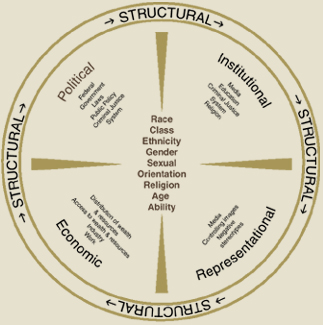
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
Even in diagrams, such as this steam engine, certain ideas and their relations are expressed and as a model can generate a concept map.
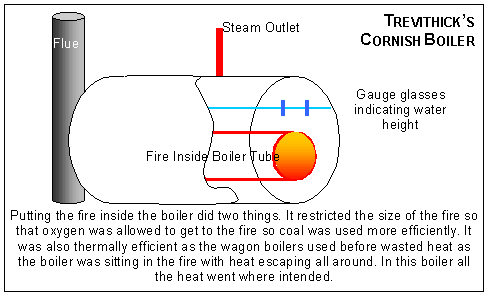
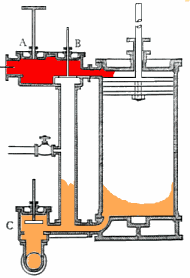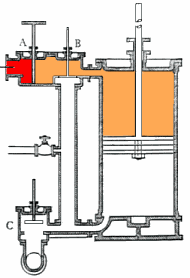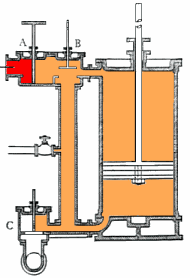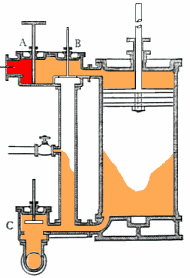
Even with a diagram of the concept, complex relationships may still require verbal explanations.
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Trees | Means of learning
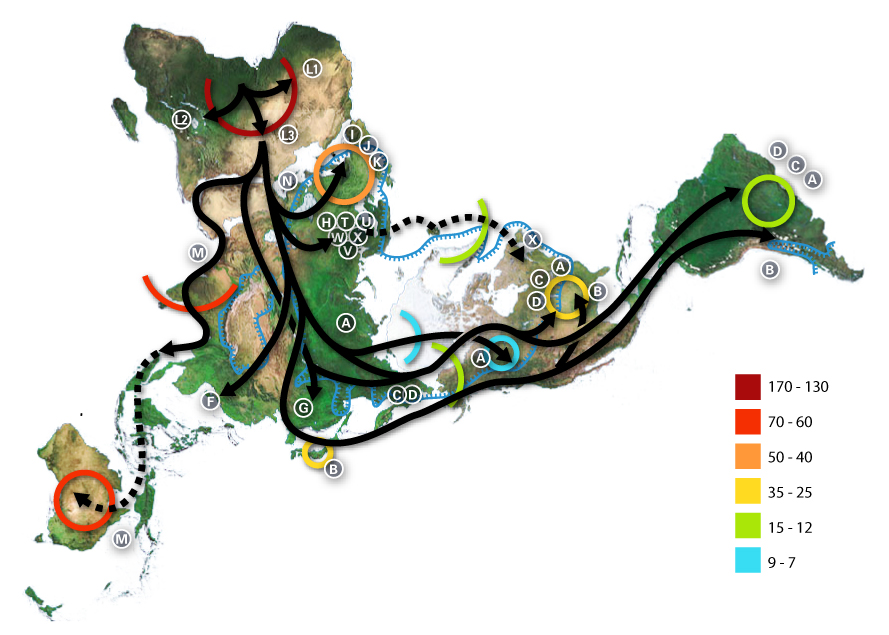
Humans are found on the family tree – a concept map for evolutionary relationships – that means over time, historical change is best understood as a tree conceptually.
The relation among current living things are like so many branches on a tree that exists in time.
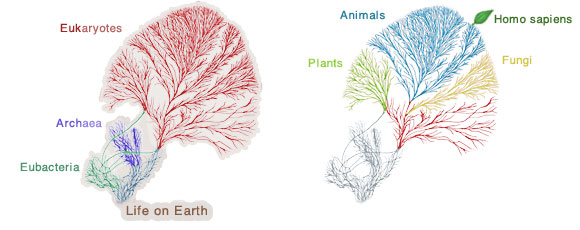
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
Means of learning details in the sense of communicating what we know.
Waves | A whole earth complex | Linear approach | Food chain | Triangular or pyramids | Circular | Text assisted | Trees | Means of learning
Contrasting concepts









.gif)