
Nano-world • 
Nanotechnology |
 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
rendering of a Carbon atom
|
|||
Nanotechnology refers to human engineered devices that are smaller than we can see or visually identify without the aid of microscopes.
|
|||
Scale is sub cellular. A size limitation in nanotechnology currently exists in the 1nm -100 nm --or nanometer-- range. Less than one nanometer is this range in length encounters size-dependant quantum effects. Another important criteria for the definition of nanotechnology is the requirement that the nano-structure is man-made. Otherwise you would have to include every naturally formed biomolecule and material particle, in effect redefining much of chemistry and molecular biology as 'nanotechnology.' The most important requirement for the nanotechnology definition is that the nano-structure has special properties that are exclusively due to its nanoscale proportions. |
|||
| scale | |||
examples of structures |
nanometers | objects | |
carbon tubules and "buckyballs" … |
1 | atoms | |
width of the DNA molecule … |
2 | Cellular nucleus | |
| 4 | |||
MEMS … |
10 | ||
large proteins … |
100 | ||
| 1000 | |||
| 10,000 | |||
width of a human hair… |
100,000 | Tissues | |
human hair with carbon tubules in background. |
|||
A nanometer is a one billionth part of a meter; if a meter (about one yard) were 15,783 miles--or more than half way around the earth-- a nanometer would be about one inch long. |
Micron (µm) 0.000001 Nanometer 0.000000001 |
||
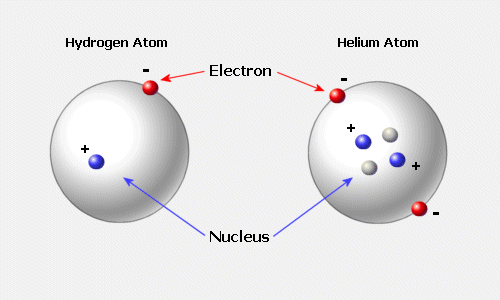 |
At the atomic nuclear and subatomic levels a new measure of scale is introduced because atoms are really small. The carbon atom, for example is .1 or a tenth of a nanometer in diameter.
|
||
 |
||
|---|---|---|
| Tools of Toil: what to read. | ||
| Tools are historical building blocks of technology. | ||