I=PAT is the impact formula for how human behavior affects nature. 1
Quotation | Formula | Meaning | Map | Importance | Web links | Terms | Table | Title | author sources
"The more we come to study the major problems of our time, the more we come to realize they cannot be understood in isolation. They are systematic problems, which means they are interconnected and interdependent."
"environmental concerns have become of paramount importance."
"For example, stabilizing world population will be possible only when poverty is reduced worldwide."
Fritjof Capra, (1996) , p. 3.
Quotation | Formula | Meaning | Map | Importance | Web page links | Terms | Table | Title | author sources
I = P * A *
T
“The
magnitude of the effects of human actions on our life-support systems and the goods
and services they supply can be
visualized as the products of three factors, summarized in the I = PAT identity.”
Ehrlich & Ehrlich, p. 205.
Quotation | Formula | Meaning | Map | Importance | Web page links | Terms | Table | Title | author sources
Meaning
I (impact) is
the product of P X
A X
T
Where:
I stands for
“impacts” or aggregate effects of
humans on the natural capital accumulation of the biosphere in different areas
and in different periods.
P is equal to population, especially population density
A is equal to affluence (per capita wealth)
or income inequity &
T
is equal to technology, or technological capability (electricity-use)
Quotation | Formula | Meaning | Map | Importance | Web page links | Terms | Table | Title | author sources
Importance
The I=PAT formula is a short-hand method or way of determining a relative means of measuring the differences in demands between very varied societies of nations, or states, or cities. It is not an accurate measure to the extent that the PQLI or Physical Quality of Life Index is a measure used by international aid organizations for understanding the social, economic and political conditions of a nation or region in relation to its neighbors and other countries.
Quotation | Formula | Meaning | Map | Importance | Web page links | Terms | Table | Title | author sources
An explanation
of the IPAT formulation is
at – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/ipat.html
The ABCs of
impacts are:
Accounting,
see – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/accounting_fo_Env_Assets.html
Biodiversity,
see – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/biodiverse.html
Conservation,
An essay about, see – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/conserv.html
What is being impacted? See – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/weal.htm
On the importance of choosing correct words, see – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/warwick.html
Terms to know, use, and examine:
ecosystems, food webs, fragmentation, total
fertility rate, population dynamics, density, PQL or the physical quality of
life, feedback (both positive and negative), non-genetic information, genotype,
population distribution of phenotypes, misuse of phenotypes, cultural
stickiness, “rational,” norms, “fallacy
of misplaced concreteness,” externalities.
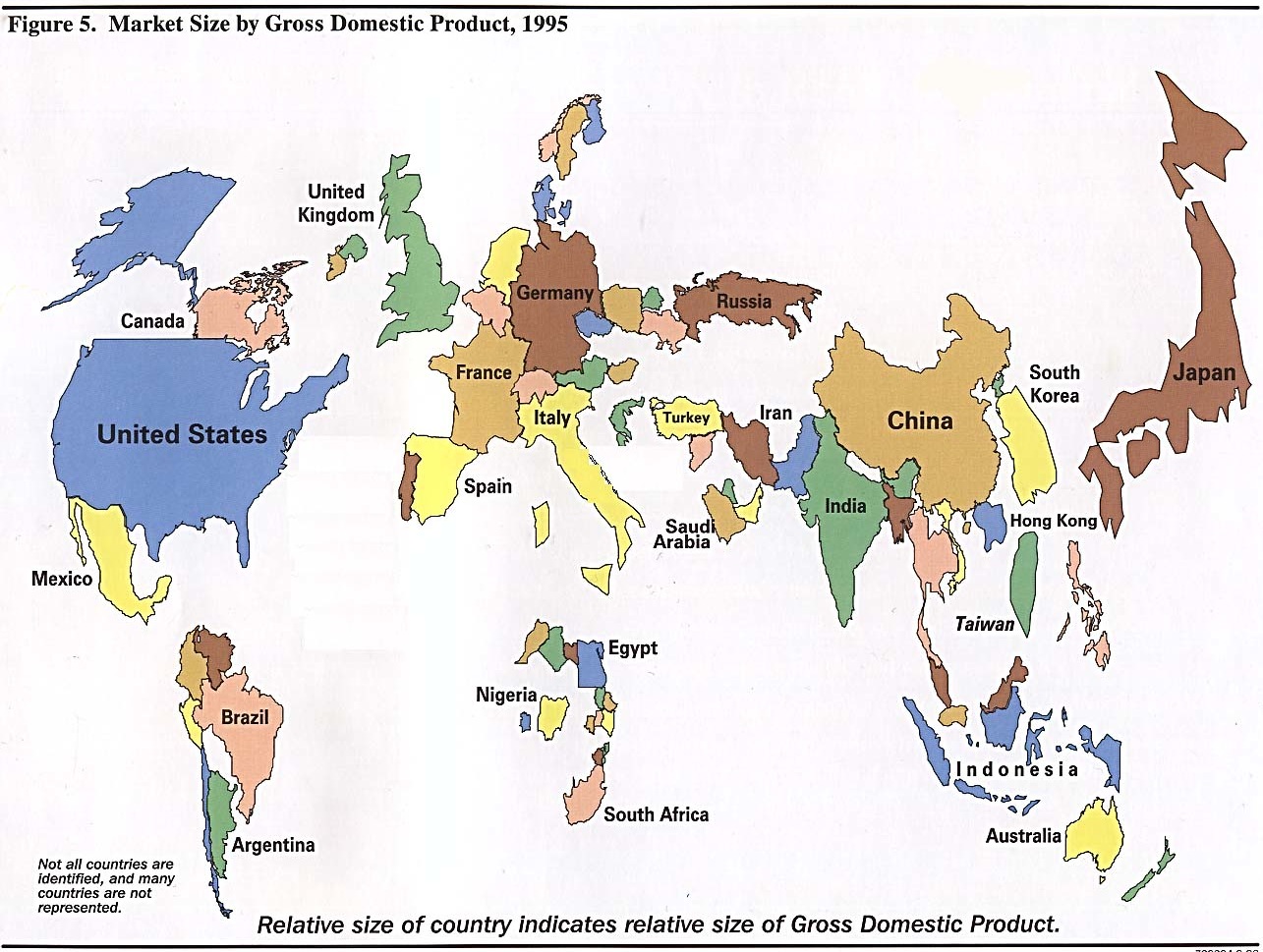
| Spectrum of degrees of intrusions | |||
 |
|||
| Types | |||
| or disturbs | or damages | or destroys | |
| affects, | |||
| alters, | |||
| adjusts, | |||
Do you have a thesis?
See here – http://myweb.rollins.edu/jsiry/ThesThem.htm
The impact formula reveals how human behavior affects, alters, or adjusts to nature.
-
Capra, The Web of Life.
-
Hardin, The Ostrich Factor.
Quotation | Formula | Meaning | Map | Importance | Web page links | Terms | Table | Title | author sources