

 |
 |
 |
|
| The living wealth of the Earth. |
![]()
Biological
diversity | What is it? | Three
kinds | Importance | Map
| Optimum | E. O. Wilson | Problem solving
![]()
Biological diversity is one measure of any area's ecological productivity as it is distributed among a variety of species or conditions; that is a measure of how much nutrition is available to living creatures from solar radiation, nutrient cycling, water and air. Biotic diversity is thus, a metric revealing how available calories from bacteria and plants are distributed among plants, bacteria, fungus, and animals.
Here is a representation done by the American Museum of Natural
History depicting the percentage of creatures by their biological affiliations
and their mass on earth.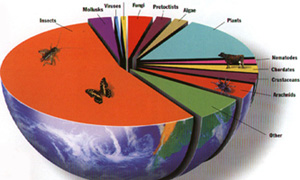
From the adjacent drawing it becomes obvious that humans are just a minor member of this living assemblage.
Consider that insects account for over half of the creatures on earth by weight and variety of species. Among insects the vast majority by weight and the most diverse group on earth are beetle's; the coleopterans.
Wildlife and global warming's impacts.
What this means is that the large animals that we associate our own species with, many among the grouping called the chordates, are utterly dependent on the far more numerousness – and often unseen– crustaceans, arachnids and insects that have been developing on Earth for the past 300 million years. Humans by comparison have descended from a family that is not much older than three to six million years.
In addition to the dependence of large obvious animals like elephants, lions and pandas on the smaller creatures, the insects, crustaceans and arachnids are dependent on fungi, algae, protoctists, plants and bacteria. The whole concept of biological diversity refers to the capacity of the worlds creatures to sustain other creatures because of their productivity. Without such diversity there would be no agriculture, no pollination of crops and groves, no civilization.
So what is biological diversity?
This flywheel that drives the productive potential of the living world?
Biological Diversity is the product
of the dynamics of energy flow and nutrient cycling in ecosystems. 
The National Science Foundation’s National Research Council finds that:
“Human beings, both individually and collectively, have always sought to transform their surroundings. But for the first time, they have begun to play a central role in altering global biogeochemical systems and the earth as a whole. . . . the loss of biological diversity is a by-product of varied human activities, including the clearing of tropical moist forests for agricultural purposes. . . .
Such human responses can alter the course of global environmental change.”[NRC (1992), p.17]
“The most widely used definition of biological diversity includes three levels: genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Deforestation reduces diversity at all three levels.” (67)
According to the United Nation’s World Conservation Strategy and the National Research Council, the loss of biological diversity is an indicator of the ecological health of the planet from which the economic development of all nations ultimately derives.
Seeing and acting on such an interdependent relation among atmospheric warming, biological diversity loss, and human social well-being is the larger goal of ecological problem solving. The method of ecological science.
"Most of the old-growth forest has been cut. Only about
17% of the original old-growth Douglas fir forest of the Pacific Northwest remains,
the bulk of this being in United States National Forests." [public land]
Seven species of evolutionarily rare species, other than the northern spotted
owl, exist because the conditions of the old-growth forests nourish their existence.
$4 billion dollars worth of timber is at stake as 3000 remaining breeding pairs
of spotted owls remain affecting 800 to 2500 hectares of habitat per pair. ($8
million per pair) Timber leases are subsidies to lumber companies since the
purchase price of the lease is less than the cost of maintaining the forest!
Any forest is like a savings account in that it earns interest at an accumulating rate. Like a bank account rivers and other natural features require an investment if one is to anticipate a withdrawal without losing the earning power of the account. The lumber that comes from particularly old forests of 80 to 180 year old trees is of higher quality than the lumber of recently planted forests. Like an older savings account the accumulation of wealth is greater in a forest as it matures.
Global hotspots where biological diversity is under assault and declining.
"This is the assembly of life that took a billion years to evolve. It has eaten the storms -- folded them into its genes and created the world that created us. It holds the world steady." (15)
the greatest bank of biological differences lies in the tropical rain forests
more than 60% of the diversity of rain forests exists in the canopy above the floor
About twenty places on earth are characterized by a rapidly growing human population in close proximity to nurseries of creatures with a high degree of species richness, or extremely varied habitats, or sources of genetic variability. These genetic hearths are where we derived many of our domesticated crops and animals.
There are three kinds of biological diversity:
Biodiversity is due to: 1) habitat differences, 2) species richness, 3) genetic variety
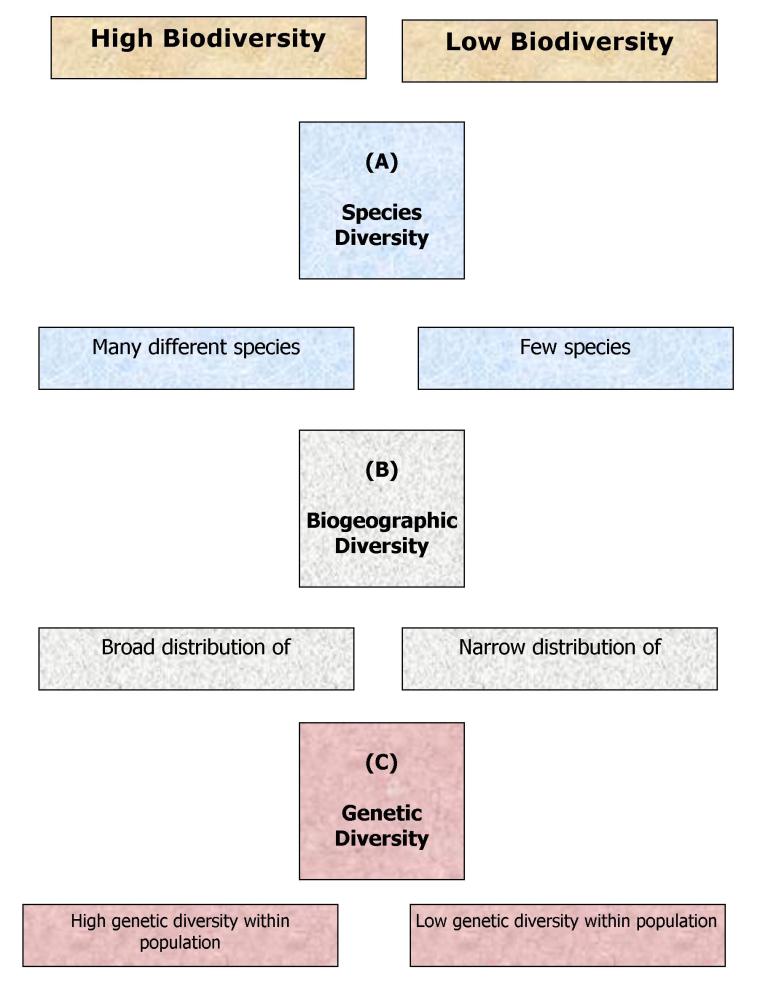
Genetic diversity,
Genetically specialized plants and bacteria capture solar energy or reduce minerals from the earth's heated waters transferring this energy, fuel, or fiber along food chains to all other living organisms. The genetic viability of all life ultimately depends on bacteria and plants that form webs of biotic communities where fungi breakdown material to make nutrients readily attainable by plants and animals.
Species diversity,
The relative abundance of species may be influenced by availability of resources, or competitive interaction.
Sometimes called "species richness."
Three measures of diversity:
"This failure to understand the production and maintenance of species numbers suggests that ecologists might phrase the problem of diversity better in terms of the factors that influence speciation, competitive ability, and degree of specialization which, after all, determine the number of species that can coexist in a community."
"Observed species abundance distributions apparently stem from the complex structure of natural communities which causes their organization to assume a superficial element of randomness" [ Ricklefs, p. 740]
Habitat diversity, (or biogeographic diversity)
"The most wonderful mystery of life may well be the means by which it created so much diversity from so little physical matter. The biosphere, all organisms combined, makes up only about one part in ten billion of the earth's mass. … Yet life has divided into millions of species, the fundamental units, each playing a unique role in relation to the whole."
(35)
An ecosystem is a collection of biotic communities (organic features of a place) +
collection of habitats (inorganic features of a place)
existing dynamically over time due to the reuse of scarce nutrients & materials by either:cooperating – symbiotic or,
competing – rival organisms (creatures, life, beings).Area is required for diversity to increase & not decrease over time:
640 acres = 1 square mile or 250 hectares
100 hectares = 1 square kilometer
Importance of biotic diversity:
Edward O. Wilson, Harvard University, biologist
The Diversity of Life: (1992)
“Great biological diversity takes long stretches of geological time and the accumulation of large reservoirs of unique genes. The richest ecosystems build slowly, over millions of years. It is further true that by chance alone only a few new species are poised to move into novel adaptive zones, to create something spectacular and stretch the limits of diversity. A panda or sequoia represents a magnitude of evolution that comes along only rarely. It takes a stroke of luck and a long period of probing, experimentation, and failure. Such a creation is part of deep history, and the planet does not have the means nor the time to see it repeated.”
(74)
“I can not imagine a scientific problem of greater importance for humanity.” than the loss of biodiversity.
(254)
Biodiversity is our most valuable but least understood and most under appreciated asset.
"Its potential is brilliantly illustrated by the maize species Zea diploperennis, a wild relative of corn discovered in the 1970s by a Mexican College student in the west central state of Jalisco, south or Guadalajara."
The new species is resistant to diseases and unique among living forms of maize in possessing perennial growth.
"The Jalisco maize was found just in time, however. Occupying no more than 10 hectares (25 acres) of mountain land, it was only a week away from extinction by machete and fire."
A balance – or optimum range of disturbance –
must be struck to assure biotic diversity in maintained.
"The problem of collective meaning and purpose is both urgent and immediate because, if for no other reason, it determines the environmental ethic. Few will doubt that humankind has created a planet-sized problem for itself."
"we are the first species to become a geophysical force, altering the earth's
climate…"
303
"The global population is precariously large, and will become much more so before peaking sometime before 2050."
306
"eating up the planet's capital, including natural resources and biological diversity millions of years old. Homo sapiens is approaching the limit of its food and water supply. Unlike any species that lived before, it is also changing the world's atmosphere and climate lowering and polluting water tables, shrinking forests and spreading deserts."
307
Problem solving is an opportunity to use critical thinking
that is necessary to understand effective means to forestall loss of biotic
diversity. Critical thinking and problem solving should in the end instill in
its users an “ecological imagination” in which one solution brings
into being another solution and so on in an interlocking array of “mutual
dependencies.”
One outcome of ecological problem solving is to imagine several opportunities to enhance complementary values in a single solution to a perplexing situation where conflict would otherwise destroy the viability of essential ecological services.
The most biodiverse nations in variety of life.
biology and dynamic conditions | The "game" of life | ten ecological commandments | ecological problem solving | The Double Helix | Origin of Species
Back | Population data | Contents of Site
![]()