 |
|
| Richard Dawkins, | |
| The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution. | |
| New York: Free Press, 2009. | |
Dawkins, p. 8.
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
“Evolution is a fact, and this book will demonstrate it. ”
"It is plain truth that we are cousins of chimpanzees, somewhat more distant cousins of monkeys, more distant cousins still of aardvarks and manatees . . . ."
"we do know this because a rising flood of evidence supports it."
Dawkins, pp. 8-9.
The varieties of evidence for evolution:
cladistic trees | crania | variety | neoteny | gene inheritance | geology
 Satirist's view of Darwin (1850s).
Satirist's view of Darwin (1850s).
"Darwin had first-hand experience of power of artificial selection and he gave it pride of place in Chapter 1 of On the Origin of Species. . . .of his great insight, the power of natural selection. If human breeders could transform a wolf into a Pekinese, or a wild cabbage into a cauliflower in just a few centuries or millennia, why shouldn't the non-random survival of wild plants and animals do the same thing over millions of years?"
Dawkins, p. 42.
“The main point I want to draw out of domestication is its astonishing power to change the shape and behavior of wild animals, and the speed with which it does so."
Dawkins, p. 28.
The American zoologist Raymond Coppinger makes the point that puppies of different breeds are much more similar to each other than adult dogs are. . . . the technical term for this is neoteny, . . ."
Dawkins, pp. 35-36.
...thoughtful and rational churchmen and women accept the evidence for evolution.”
Dawkins, p. 6.
A map of the power "deniers" have in blocking the teaching of evolution and Darwin's concepts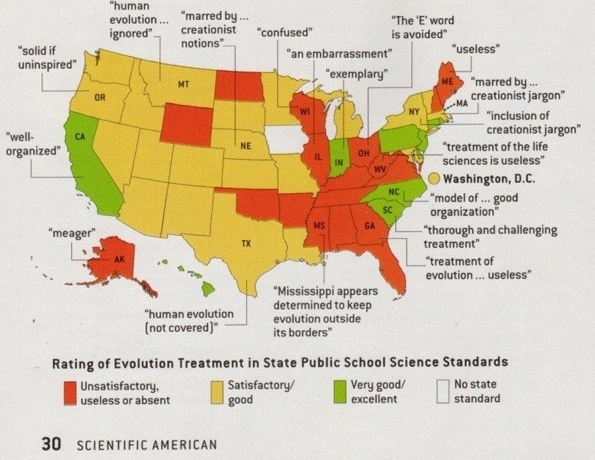
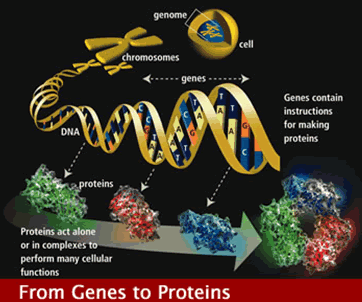 "A Mendelian gene is an all-or-nothing entity. "
"A Mendelian gene is an all-or-nothing entity. "
"Nowadays we know that genes are lengths of DNA code, not physically separate like cards, but the principle remains valid. Genes don't blend; they shuffle. You could say they are shuffled badly, with groups of cards sticking together for several generations of shuffling before chance happens to split them."
He defines evolution as changes in the gene pool frequency.
Dawkins, pp. 27-29, 33-34.
"The concept of a gene pool has meaning only in light of Mendel's law of the independent assortment of hereditary particles."
" Darwin never knew Mendel's laws. . ."
"Mendel showed . . . he didn't used the word 'gene,' which wasn't coined until 1909 . . . it is not like blending paints."
Dawkins, p. 29.
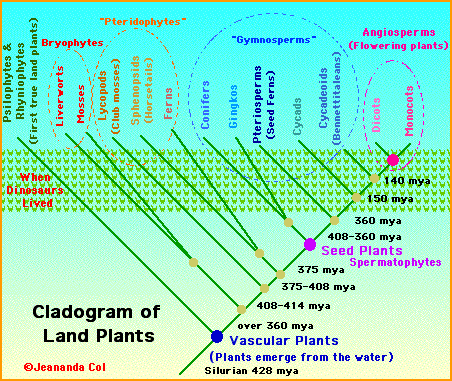
“we don’t need fossils in order to demonstrate evolution as a fact”
145
“There is one more type of evolutionary clock, the molecular clock. . . “
107
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions
“Indeed a species can be defined as a set of animals that engage in gene transfer among themselves.”
Except for
- Rotifers (sexless)
- Nematode worms &
- fruit flies
303
The bilateral complementarity of decapods and vertebrates
exoskeleton – endoskeleton
“the bat hand and the human hand are homologous.”
p. 312.
![]() “Just as the vertebrate skeleton is invariant across all
vertebrates while the individual bones differ, and just as the crustacean
exoskeleton is invariant across all crustaceans while the individual tubes
vary, so the DNA code is invariant across all living creatures, while the
individual genes, themselves vary.”
“Just as the vertebrate skeleton is invariant across all
vertebrates while the individual bones differ, and just as the crustacean
exoskeleton is invariant across all crustaceans while the individual tubes
vary, so the DNA code is invariant across all living creatures, while the
individual genes, themselves vary.”
“This is truly an astounding fact, which shows more clearly than anything else that all living creatures are descended from a single ancestor.”
p. 315.
“we find the same kind of hierarchical tree of resemblance.”
p. 315.
“The antibodies present in the rabbit constitute a history of the natural shocks to which its flesh has been heir–including artificially injected proteins.”
Like vaccines in humans
p. 316.
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions |
Genetics and descent from common ancestors
“Humans and chimpanzees share 98 percent of their genes.”
This common ancestry among Orangutans, Gorillas and Chimpanzees, our distant cousins, is due to the method of DNA hybridization.
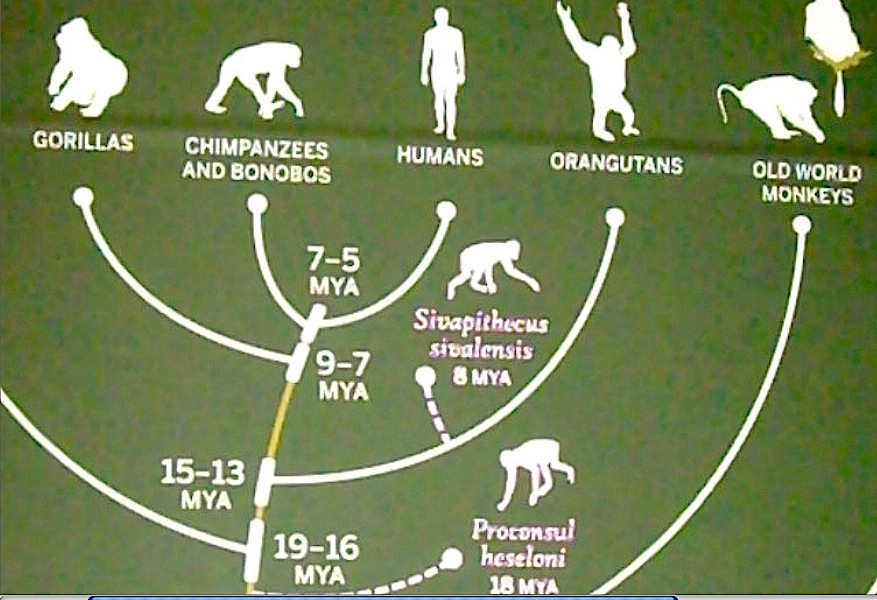
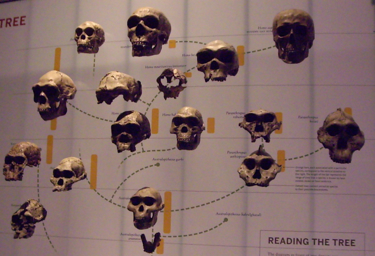
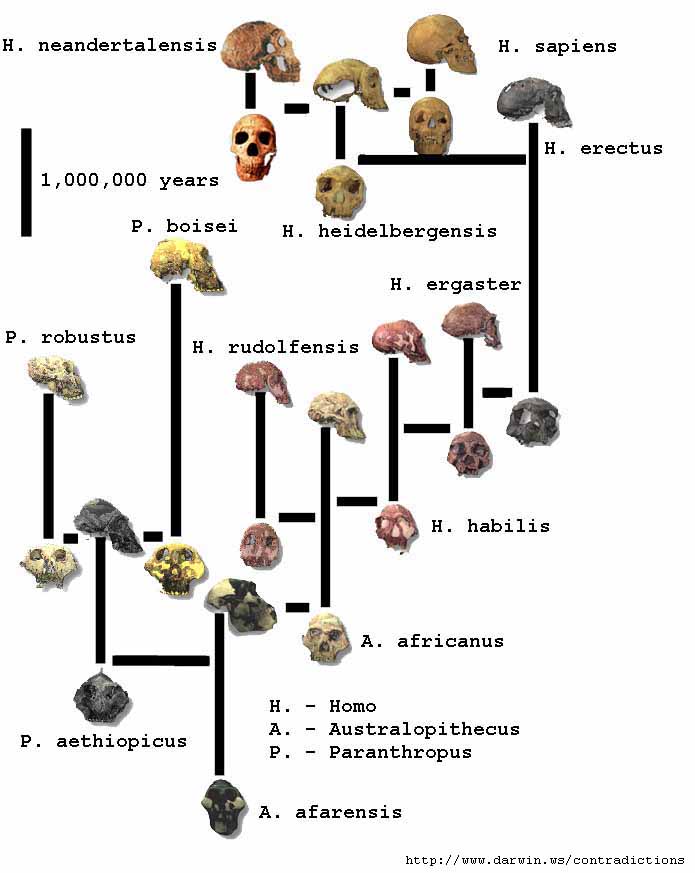
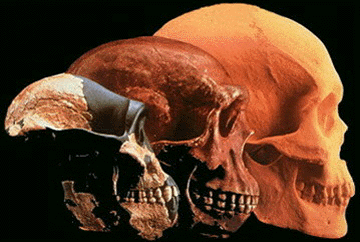
| The ancestral relations among the genus Homo and its antecedents: | ||
 |
 |
|
| Human ancestry is actually more complicated than the schematic on the right suggests. | ||
"Slightly older than the Taung Child, one of the most beautifully preserved skulls we have, although lacking a lower jaw, is called 'Mrs. Ples'."
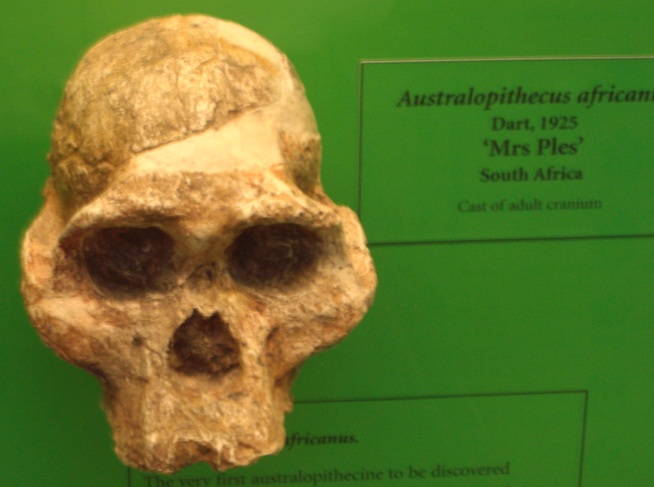

". . . she was originally classified in the genus Plesianthropus. This means nearly human', which is a better name than 'southern ape'. One might have hoped. . . "
He then argues that these so named "Southern ape" [Australopithecus] are better named "half-human" but names matter in cladistics and the first to name is often more important than an accurate nomenclature.
p. 391.
There are three means of relating DNA lines
1. antibodies
2. melting point of genetic strands
3. direct sequencing matching
320
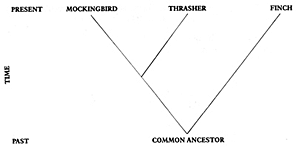
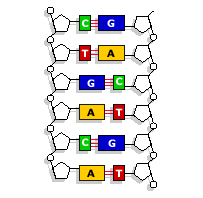
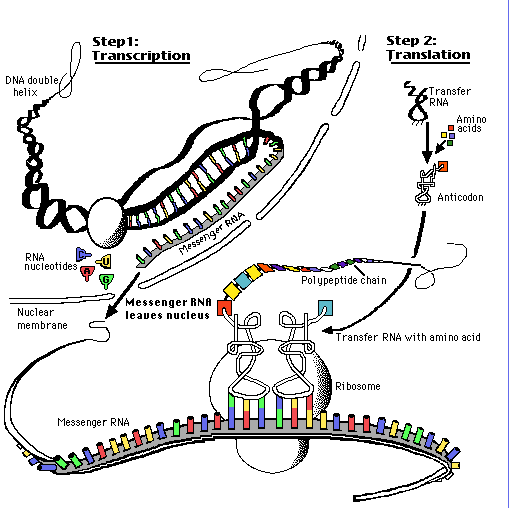
“Comparative DNA (or protein) evidence can be used to decide–on the evolutionary assumption–which pairs of animals are closer cousins than which others.”
p. 321.
“What turns this into extremely powerful evidence for evolution is that you can construct a tree of genetic resemblances separately for each gene in turn.”
pp. 321-322.
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
“And the important result is that every gene delivers approximately the same tree of life.”
Different versions of the descendents that form a tree of life based on common genetic strand analysis.
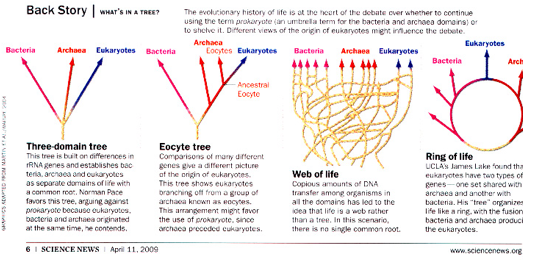
Though these trees differ, we can suffice to say that life is impossible without bacteria.
322
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
Dawkins uses taxonomic trees to determine ancestral relations.
Dr. David Penny, of New Zealand took 11 species and compared five genes.
the “Penny” tree search for common ancestry and cousins (-) relationships among eleven mammalian species
kangaroo |
rabbit to rat ą rhesus monkey - chimpanzee - human |
dog - horse - pig ą sheep - cow
“The sum total of the genetic sequence data now available puts the matter beyond all conceivable doubt.”
322.
He describes the ancestral relations among Penny’s eleven species:
A kangaroo is from a marsupial-mammalian ancestor
- Ż rabbit-
- rat
- Ż rhesus monkey-
- chimpanzee-
- human
- Ż dog-
- horse-
- pig
- sheep-
- cow
p. 322.
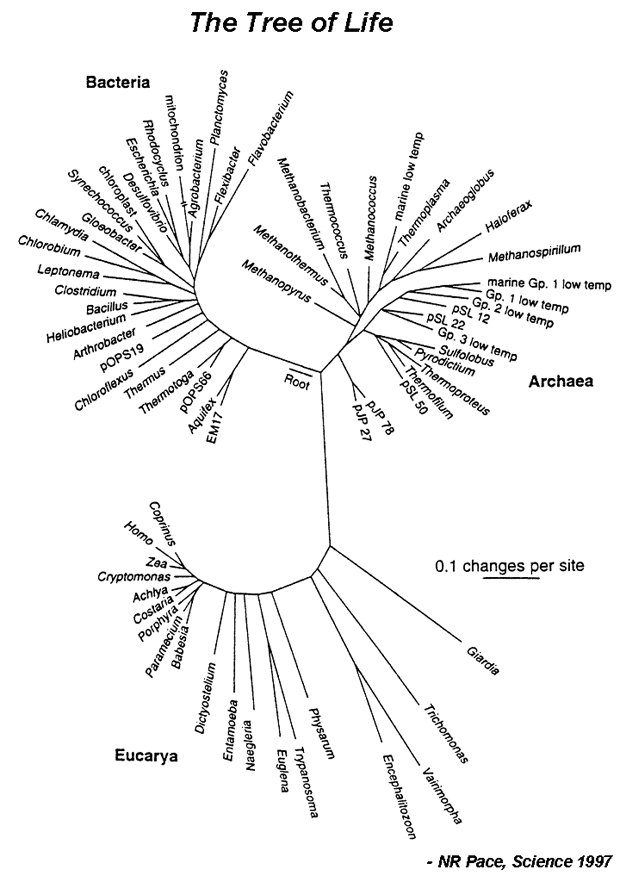
Hillis’ plot of relations: He and his team plotted three thousand species to the same depth of inheritance.
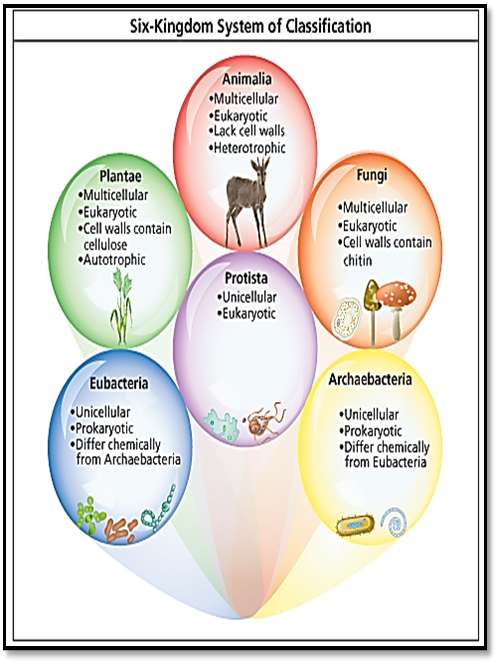
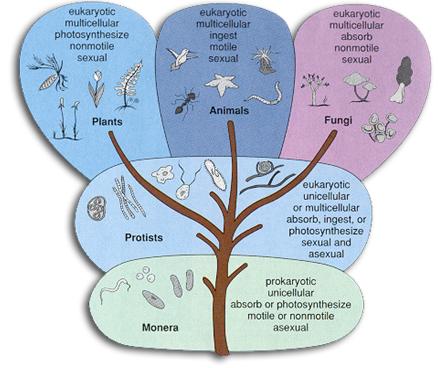
Archaea Bacteria Protists Plants Animals (4) Fungi
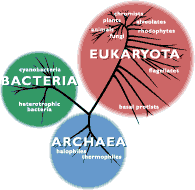


pp. 328-329.
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
ten million species are plotted on the tree (conservative estimate)
330
“so the molecular clock assumes that there are certain aspects of evolution itself that proceed at a fixed rate.”
“Indeed, much evidence suggests that evolutionary rates are highly variable.”
p. 330.
“The majority of genetic change at the molecular level is neutral, and can therefore be expected to proceed at a rate that is independent of usefulness and might even be approximately constant within any one gene.”
pp. 331-332.
“Leaving pseudogenes aside, it is a remarkable fact that the greater part (95 percent in humans) of the genome might as well not be there, for all the difference that it makes.”
“the remaining five percent—the genes that are read and used.”
p. 333.
There are neutral variants of genes that are essential to the body that have no affect on how the gene is expressed.
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
There are two processes that are essential, but happening simultaneously in the geological record that affect how genes are expressed:
1) The actual patterns of land and sea change gradually over time due to plate tectonics,
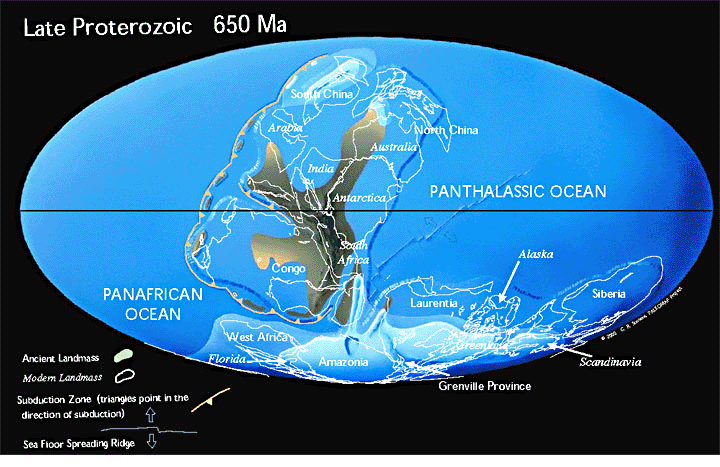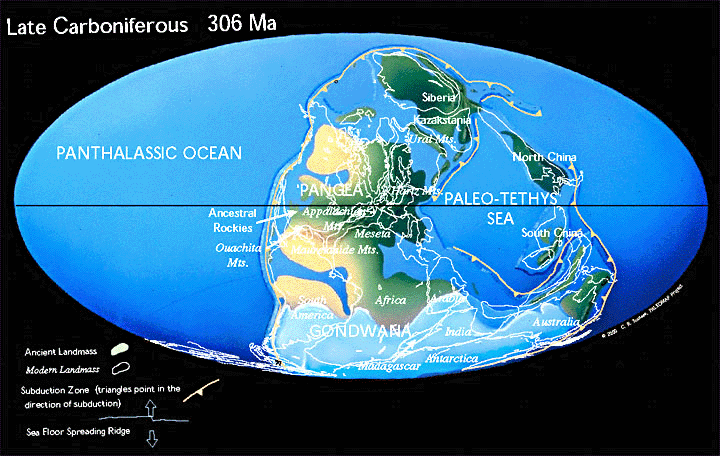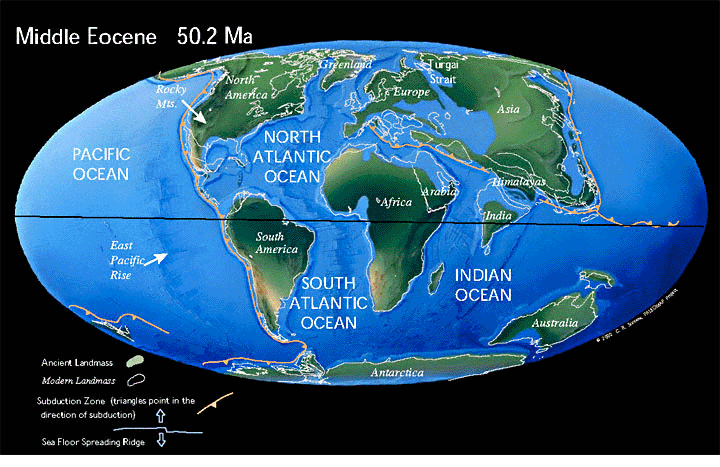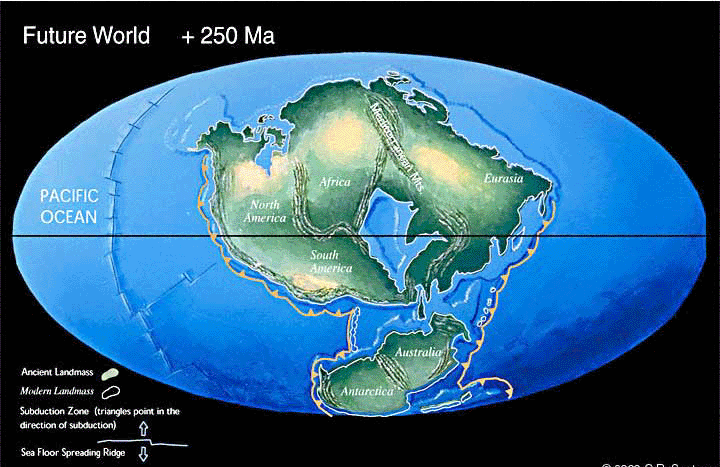
2) Climate, moisture and temperature are not constant over short and long time periods.
 "The fossil record, like the spy camera in the murder story, is a bonus, something that we had no right to expect as a matter of entitlement. There is already more than enough evidence to convict, . . . . more than enough evidence for the fact that evolution in the comparative study of modern species and their geographical distribution. . . . We are lucky to have fossils at all."
"The fossil record, like the spy camera in the murder story, is a bonus, something that we had no right to expect as a matter of entitlement. There is already more than enough evidence to convict, . . . . more than enough evidence for the fact that evolution in the comparative study of modern species and their geographical distribution. . . . We are lucky to have fossils at all."
p. 146.
“It is a fact that the immediately surrounding reptiles, birds' close neighbors on the tree of life, happen to be extinct, while the birds alone of their kind, marched on. The closes relatives of birds are all to be found among the long extinct dinosaurs. If a wide variety of dinosaur lineages had survived, birds would not stand out: . . ."
p. 160.
"As geological time goes by the genome is subjected to a rain if attrition in the form of mutations. In that small portion of the genome where the mutations really matter for survival, natural selection soon gets rid of bad ones and favours the good ones.”
334
“The very existence of pseudogenes–useless untranscribed genes that bear a marked resemblance to useful genes [protein forming]–is a perfect example of the way in which plants and animals have their history written all over them.”
336
“Living bodies, too, have their history written all over them.”
339
 The dolphin has lungs – not gills and thus its history as a mammal, land dwelling mammal is
evident in its anatomy, physiology, and genetic endowments.
The dolphin has lungs – not gills and thus its history as a mammal, land dwelling mammal is
evident in its anatomy, physiology, and genetic endowments.
340-41
“…we shall continuously find examples of evolution correcting an initial ‘mistake or historical relic by post hoc compensation or tweaking, rather than by going back to the drawing board as a real designer would.”
341
He discusses the blow hole in the dolphin’s head as an example of such compensatory or supplemental re-engineering done sub-optimally by natural selection
341
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms s | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions
He mentions Helmholtz’s belief that the eye is a flawed optical instrument
351-52
“So what the eye lacks in optics the brain makes up for with its sophisticated image-simulating software. But I haven’t mentioned the most glaring example of imperfection in optics. The retina is back to front.”
353
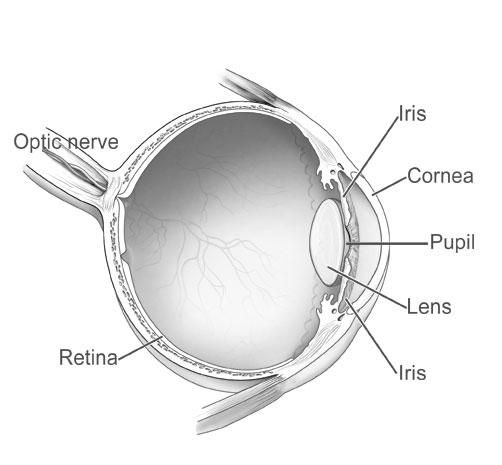
even a major design flaw “can be corrected by subsequent tinkering.”
355
“Human embryos also have blood vessels supplying their ‘gills’ which are very similar to those of a fish.”
359
“Eyes and nerves, sperm tubes, sinuses and backs are all poorly designed from the point of view of individual welfare, but the imperfections make perfect sense in light of evolution.”
375
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
“The natural economy is solar powered.”
“…or a green leaf which is nature’s solar panel. Plants use solar energy to drive ‘uphill’ chemical syntheses, manufacturing organic fuels primarily sugars. ‘Uphill’ means that the synthesis of sugar needs energy to drive it; by the same token, the sugar can later be burned in a ‘downhill’ reaction that releases the energy (a fraction of) again to do useful work.”
375
“If the planet were not in orbit around a star at all. Life would be completely impossible.”
412
‘there is a finite zone bathed in heat and light, where the evolution of life is possible.”
“The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that, although energy can be neither created nor destroyed, it can–must in a closed system become more impotent to do useful work: that is what it means to say that ‘entropy’ increases.”
413
But while the universe as a whole is hurtling downhill towards its inevitable heat death, there is scope for small quantities of energy to drive little local systems in the opposite direction.” [like ours ]
414
“energy from the sun powers life,”
415
Reasons | Common Descent | DNA's role | Kingdoms | Homo | Tree of life | Geology | Dolphins | Eye | Conclusions | Source
 Richard Dawkins,
The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution.
Richard Dawkins,
The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution.
New York: Free Press, 2009.
Darwin | | Keller | | Lewontin | | Margulis | | Mayr | | Tattersall | | Thomas

 "Evolution is a fact."
"Evolution is a fact."