7 Ups
and downs of Population
Prologue
“Human population growth has been so prodigious
in recent centuries that it has also become a major driver of environmental
deterioration, in the extent of pollution, consumption of natural resources,
and destruction of habitats needed by other species.”
p. 140
Outline
Overview
“the elephant in the living room” is the matter of population
size
“Population genetics
is concerned with changes through time in the composition of gene pools (all the genetic information possessed
by a population), …; population dynamics or demographics … is about changes to the
numbers of individuals and in the forces that produce these changes in a given
population.” (140)
“an input-output system.” – see formulas { 141
.
Butterfly dynamics–checkerspot butterfly life cycles { 141
.
Human dynamics – 6.859 billion people July ‘10 { 142
.
Family Planning { 144
.
Curbing the population explosion { 146
.
The arithmetic of population growth { 149
.
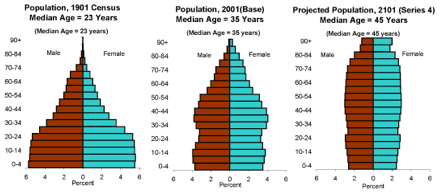
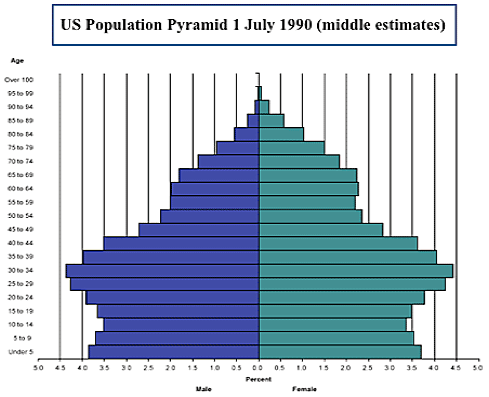
Population pyramids { 151-52
.
Population momentum { 153
.
Aging populations { 155
Vocabulary
Demography: fertility, mortality N>, rule of 70, doubling time, Fibonacci sequence, Infant death, contraception,
migration, Malthusian dilemma, exponential versus
arithmetic growth, inverse square law, correlation.
Population distribution, graphs
Formulas
Population N
– M + (Em Ī Im) = P
Fertility
minus mortally (plus or minus migration) equals population
Impact I
= P * A * T
Impact is equal to Population times Affluence time Technical capacity
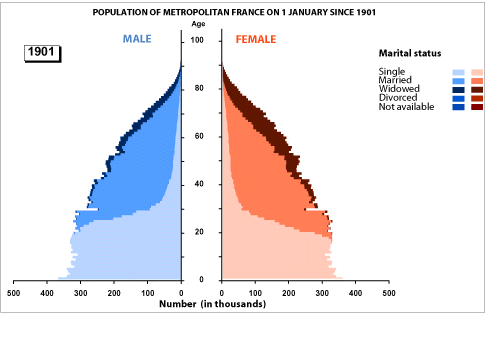
French population change 1901-2001
Doubling time
The rule of 70
% / 70 = TD
percent ÷ 70 equals doubling time [TD]
The percentage of change divided by seventy (or seventy-two) is the time it takes for a quantity to double [TD].
Summary
“ . . . the problems
that continued rapid global population growth is now bringing to the planet,
that, in the view of the vast majority of knowledgeable scientists is already
overpopulated.”
p. 157
US Bureau of the Census on line
Population
dynamics is the key to understanding the human reality
of birth, death and migration as it impacts any region.
Understanding aggregate behavior of large numbers allows us to put
cases of individuals and regional impacts into a more understandable
perspective.
These are all linked with the Golden ratio through the Fibonacci sequence, which is given by
| The differences among arithmetic, fibonacci, & exponential growth patterns. | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | one | two | three | four | five | six | seven | eight | nine | ten | eleven | twelve |
| F | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 13 | 21 | 34 | 55 | 89 | 144 |
| Ex | 1 |
2 | 4 | 8
|
16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 | 2048 |
| difference | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 24 | 51 | |||||
![]()
Merchant | Worster | Cronin | Reisner | Jackson | Siry | Leopold | Diamond | Williams | Austin | Mumford | Marx
