How do you learn?
![]() Read over and look closely at the two following diagrams [one and two] and compare your previous answer
to the question above about how you think you learn:
Read over and look closely at the two following diagrams [one and two] and compare your previous answer
to the question above about how you think you learn:
The world appears flat, but is it more than we comprehend?
Do not worry about being precisely accurate – look at the diagram below and place yourself in relation to the four axes. Arranging your behavior closer to the cross hairs if you are an even balance among the active, passive, details and big picture. Otherwise place your self on the axes farthest from the cross hairs if one or more of these behaviors is more like the skills you rely on to succeed in leaning new information. Closer to the cross is the behavior most like you to farthest from the cross is least like you with respect to processing new ideas.
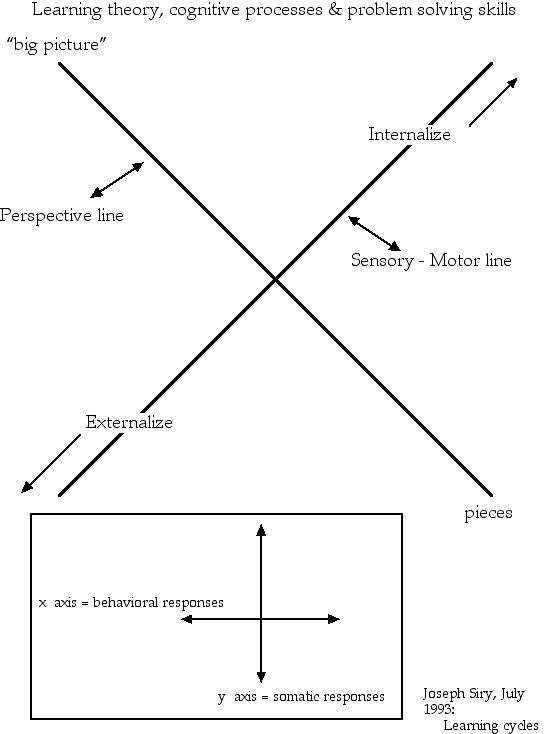
Somatic refers to any bodily activity employed when learning and behavioral refers to the expression of emotions when we learn to master something.
 Answer the question
"How would I describe the way I learn best ?"
Answer the question
"How would I describe the way I learn best ?"
Do refer to the above diagram and the following behavioral approaches to learning new information or new concepts.

When we are acquiring new skills, the manner of learning can be thought of in relation to these terms referring to four related styles:
| Learning Style |
|
|
|
|
||
|
 |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F T
|

|
|
Look at each of the above labels and compare them to the descriptions below.
Think about how you learn new information, and how you behave when starting a new subject area or are asked to perform a new task.
| Your Ranking | Most like me | More like me | Less like me | Least like me |
|
Or Behaviors |
Use a most likely to a least likely approach to this ranking. For instance put the behavior that most matches your response in the first block on the left and the behavior that is least often ever used in the last block on the right.
Rank the four different behavioral patterns according to the way most like you (that is the easiest for you to do and thus the most frequent approach you use to new material). The last behavioral pattern on your list should be the least like you (that is [i.e.] the most challenging aspect of a new task and thus the least frequent approach you employ when confronted with a new situation).
| most, | ----> | ----> | least. |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
FT |
Descriptions of learning behaviors of styles
QS means quick start; a person who sees the bigger scene from the start.
This refers to how you learn fast or catch on to things with few mistakes in a short period of time. You rapidly grasp the big picture and quickly fit the subordinate pieces together into a meaningful pattern.
FF means fact finder; someone who loves to check the details.
This behavior is indicative of people who love to make lists of what they need to know and enjoy searching out the sources of this information because the like to check the accuracy of what they know. As fact checkers for newspapers and magazines these people enjoy checking leads to assure the accuracy of the data they interpret.
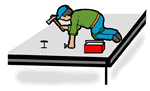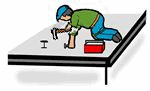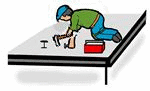
I means implementer or a hands-on learner.
This category refers to someone who enjoys being told what to do and goes ahead precisely as instructed because they like to see results and take pride in what they make, craft, or carry out. These are doers, people who claim they learn by doing. Hands-on learners.
FT means follow through; one who gets things finished.
This behavioral category is characterized by responsible actions that people perform who enjoy checking up on others or on themselves to assure that the task gets done and is done well. These folks enjoy seeing that the work they do is completed, before starting something new.
The goal of my instruction is for you to be able to make up your own mind after weighing the evidence, being asked thought provoking questions, and building a reasoned argument with convincing evidence.
Think about a learning situation where you were expected to master a set of new practices or set of instructions.
What did you do to successfully accomplish the new task or assignment?
At which of the levels did you begin at, as suggested by the above pyramid diagram?
Intelligence
How do we learn?
What does learning involve?
Learning involves a mastery.
We all learn so differently from one another.
| Go Back |
Go on |
See an organizational scheme for all my courses here: CORE
Comparing your goals with my intentions

General remarks on assignments
Writing as a practice I encourages thought.
sample annotated bibliography.
Terms | Glossary | Word webs | Basic vocabulary | Advanced Vocabulary | Antonyms | Synonyms