9 Cycles
of Life
Stability, in the face of inequity and scarcity, is what it is all about.
JVS
| The physical transport of coastal water . | The physical movement of ocean winds. |
|---|---|
 |
 |
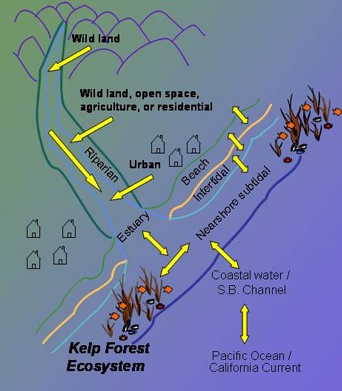
| Kelp forests affected by runoff from landuse. | Krumholz forest affected by salt spray. |
The conditions of physical, chemical and biological existence.
terms | outline | method | summary
Outline
- 1, Living resources are actually the wealth of the world
- 2, Energy, food is among our least understood sources of energy
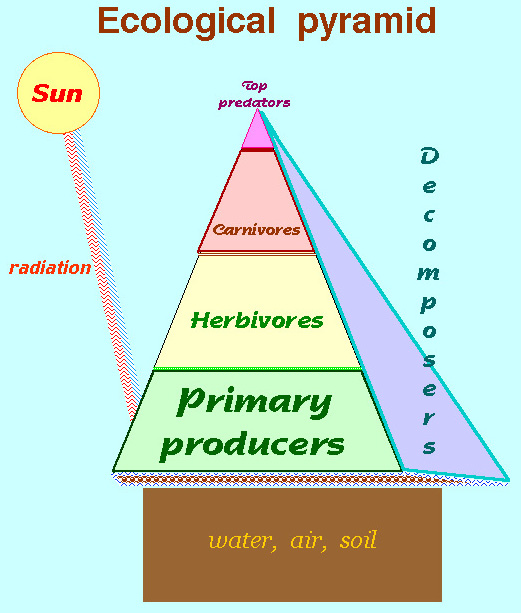
- 3, Food webs or levels of feeding are called trophic structures tied to cycles
- 4, Soils represent the crucial six inches that stand between feast and famine
- 5, Climate or the average conditions of weather over time is shifting abruptly
- 6, Gaia refers to the titanic qualities of the earth as a self-regulating entity
- 7, Complexity is an adaptive response to the tensions creating a milieu
Vocabulary
ecology has three and nature has four definitions to comprehend complexity.
| visual | Ecology | Nature |
|---|---|---|
 |
born urge |
|
| noun | character | |
|
|
original | |
| adverb | real | |
| universal | ||
| of course | ||
| Humans as natural agents | alter or disturb, | but can restore. |
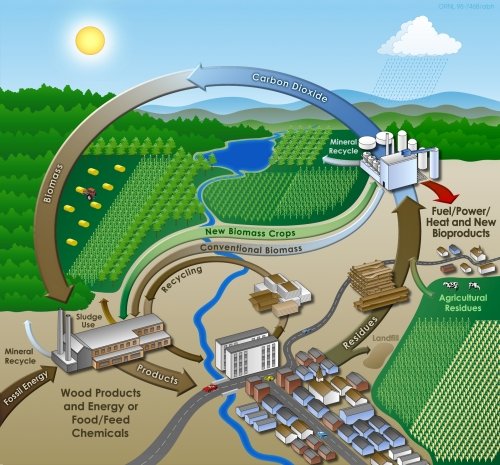
ecological vs. chemical cycles,
biogeochemical nutrient cycles, laws of the minimum and optimum, thermodynamics
& entropy, ecosystems, biosphere, loss, rates, biomass, net vs. gross primary production, radiant
vs. geothermal energy, capacity.
Dividing the world in two in order to analyze and know its three part-harmonics.
habitat + biotic community = ecological system
Why study ecology?
The habitatĐor geographical setting of any place that has a defined areaĐis the foundation of any measure of the influence of inorganic factors on the eventual quality of living conditions:
The A , B , Cs of habitats. Acid and alkaline, Bearings for bearing, Conservation. Such a study can protect you, redirect you, and motivate you to act.
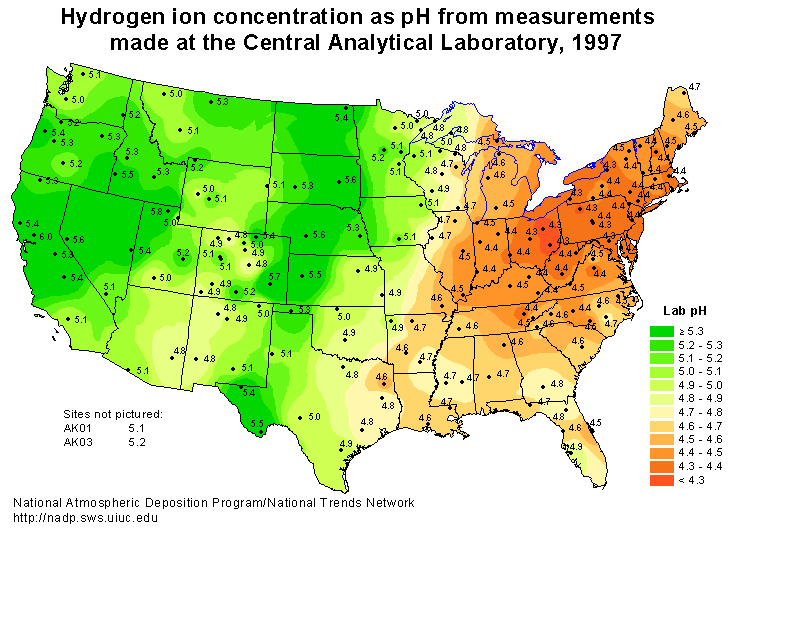
Acid rain, fog and snow physically affects east & west, United States.
Bearing means 1) the direction 2) the relation 3) the content of places; an essential alignment among points that are directly connected, or tangential to one's destination.
̉the uneven distribution of mineral
resources.Ó P. 172
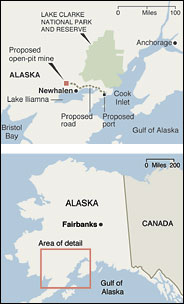
Bristol Bay Alaska where a mining development conflicts with habitats that facilitate five kinds of salmon migration, feeding & serves as a gateway to spawning grounds.
The initial condition of effective development is conservation of resources for continuing future use.
diagram | terms | outline | method | summary | acid rain map
Note:
important illustrations are displayed in italics.
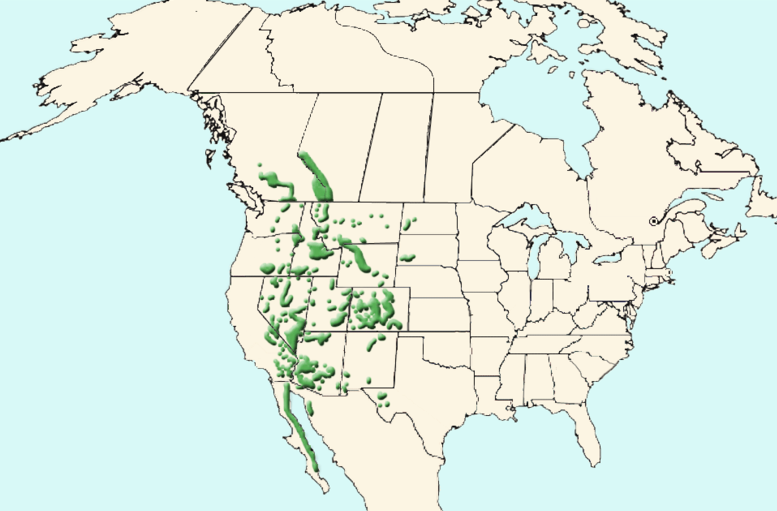
Big Horn sheep distribution in N. A.
All living resources are affected by life adapting to physical and biological situations.

2.
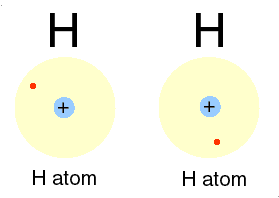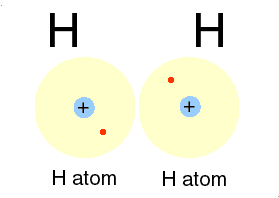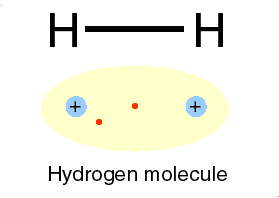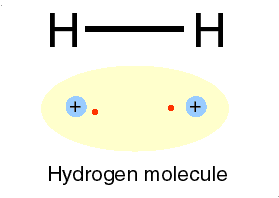
Energy { 176 Laws of ecology
3.
Food chains and material cycles ( 177
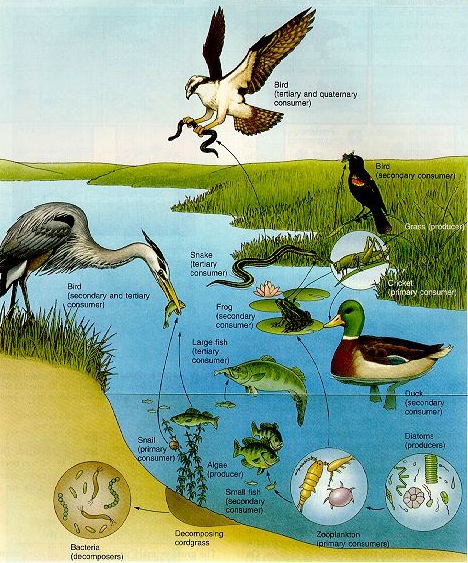
| a. Food web { p. 179 |  |
|---|---|
 |
|
Raptor
|
|
red winged Blackbird |
|
Great blue heron
|
|
Ducks & fish
|
|
plankton
|
|
| microbes | |
| A marshland is a slice of life. | dominance requires support. |
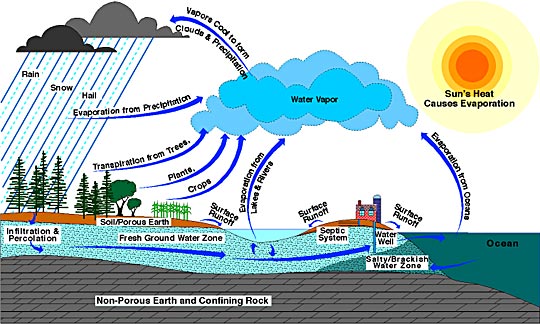
b. Hydrological cycle {180
c.
Three global nutrient
cycles { 181-183
i. Trace elements: carbon, nitrogen & phosphorus
ii. Essential elements: magnesium, iron and calcium
4. Soils and sediments { 186
All of the depositional soils seen here tinted according to their elevation above sea level have been carried as sediment by the Mississippi River and dumped in the river's delta or what is now New Orleans and its suburbs.
5.
The climate connection { 187
a.
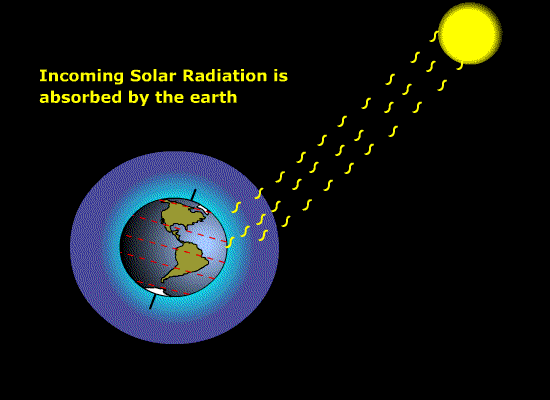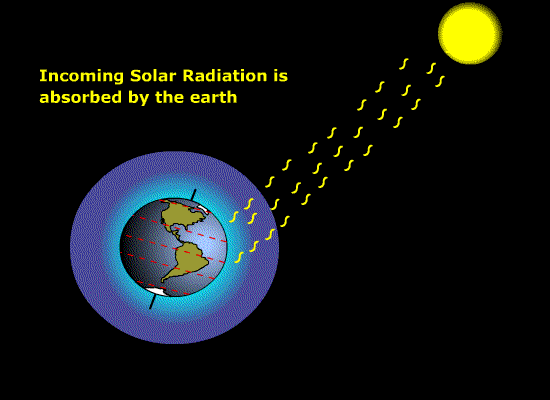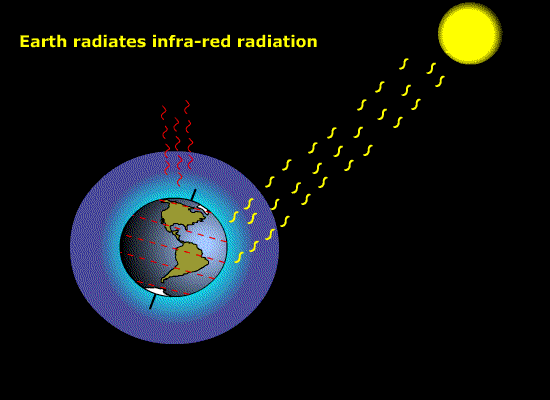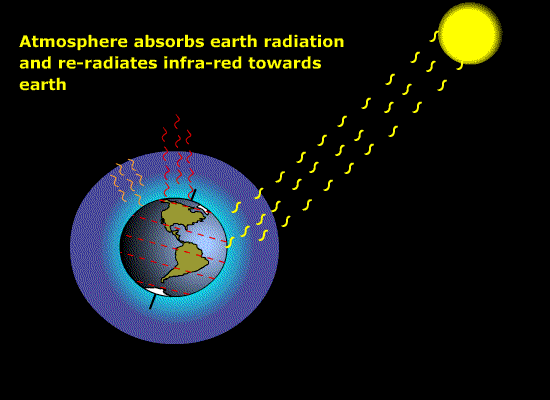
Solar radiation [Figure 9.1] { 188
b.
Source of radiant energy for photosynthesis
6.
The Gaia concept { 190
7.
The complexity of the biosphere { 191
 |
Action
|
|
| upper | ||
| Optimality | ||
| lower | ||
| Reaction |
diagram | terms | outline | method | summary | acid rain map
Dialectic:
As a method the dialectical means
can be used to analyze the complexity of ecological systems and human input and output as impact.
| Qualities | Tensions
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 2 | sources
|
radiant vs. geothermal energy |
|
functions | |
| 20 | elements
|
|
| ° | outcomes
|
net vs. gross primary productivity |
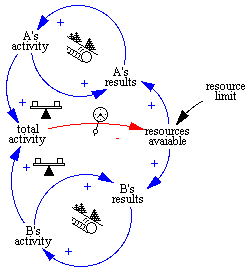
Ecosystems are functional necessities of all life, dominance rests precariously on the capacity of ecological systems to operate while recovering from intrusions.
diagram | terms | outline | method | summary | acid rain map
A study of limits:
̉relatively stable
ecosystem functioning depends on a vast diversity of organisms [and functional
living units or guilds] , and that human beings are unlikely to be capable of
assembling reasonably stable
large-scale ecosystems –especially ones able to adjust to
constantly changing conditions.Ó
p.
192.
diagram | terms | outline | method | summary | acid rain map | words with many meanings