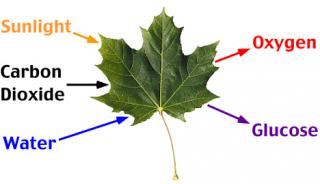
Ecolacy is the demonstrated comprehension that ecology is a synthetic science.
 Hardin, pp. 1-25. Garrett Hardin, Filters
Against Folly, How to Survive..,New York: Penguin Books, 1987.
Hardin, pp. 1-25. Garrett Hardin, Filters
Against Folly, How to Survive..,New York: Penguin Books, 1987.
“The essential orientation of ecology is all-inclusive, global: investigators try to account for all the factors at the same time . . . .it encounters grave difficulties.”
pp. 55-56.
“Predictable or not, these possibilities are part of the total ecological system.”
p. 56.
| Two different approaches: | A. | Not A. |
|---|---|---|
| divide up | combine | |
| discrete parts | put together | |
| analyze | synthesize | |
| Graphic # 1. | 
|
|
| linear | gestalt | |
| Meanings: | Sequential & separated | Combined & fused |
“The world is too remote from ordinary experience to be merely imagined.”
Ways to authentically imagine the enduring world
"There has been a deep change in the temper of science in the last twenty years: the focus of attention has shifted from the physical to the life sciences. As a result science is drawn more and more. . . . But the interested spectator is hardly aware of how far reaching the effect is in changing the image of man that science moulds."
Jacob Bronowski, The Ascent of Man, p. 15.
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
Syn, means to put together, + thesis meaning placing from the Greek: Suntinthenai to place together.
| Grammar | prefix | suffix |
|---|---|---|
| Greek | syn | thesis |
| meaning | "with" or "joined" | " to place" |
| synonym | combined | "to set" or "position" |
| antonym | separated | disarray, disordered |
conjoin or fuse, the process by which different parts are combined or placed together to form a more coherent or lasting whole.
as opposed to dissect or pull apart (analysis), parts can be analyzed but need to be joined, see three ways.
1) The emergent biosphere | 2) an ecosystemic approach | 3) our ties to nature
What is the environment to Hardin and other specialists?
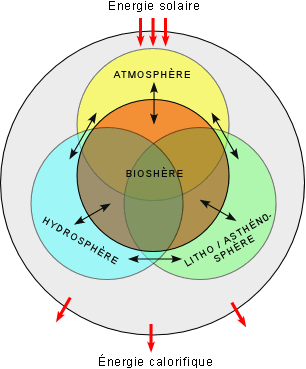
Properly conceived the biosphere or living world emerges from the physical constraints in any habitat.
As the environment is a composite of this biosphere it is critical to evaluate the way ecological systems in the biosphere ties together communities and the economy.
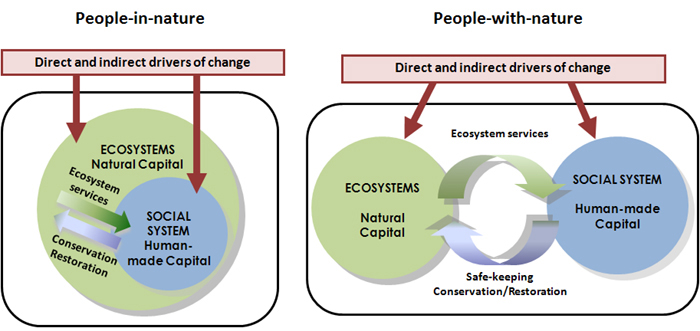
Two types of transformation in thinking that should occur soon:
1) from traditional to ecological,
and
2) from with to within nature (ecosystems).
Means to see how the pieces fit into a coherent whole:
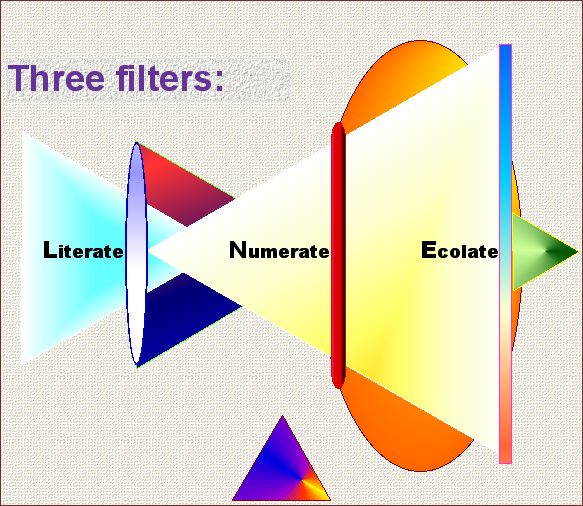
Hardin argues that thinking today must employ three analytical filters:
Ecology is the result of the two previous filters, literate and numerate.
| Ecology is the study of relations | ||
|---|---|---|
| filters | Literate | Numerate |
| able to read and write; knowledgeable | to understand and work effectively with numbers | |
| etymology | ORIGIN 1400s from late Middle English: from Latin literatus, from littera. See note. | ORIGIN 1950s: from Latin numerus ‘a number,’ on the pattern of literate. |
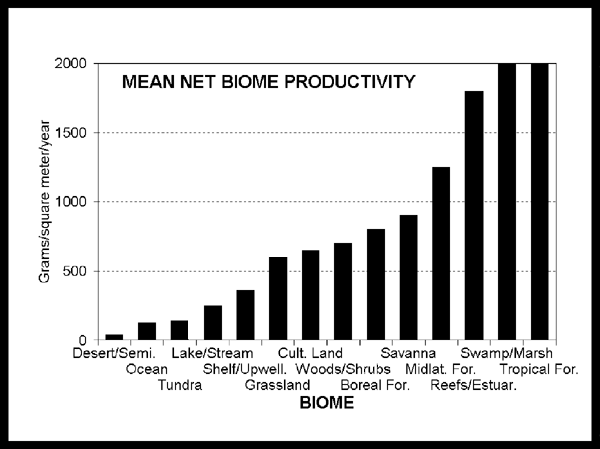
Productivity is measured by the amount of sunlight converted by plants per area over time.
Some places called biomes where photosynthesis is more productive than others:
Biomes are not all equally fruitful.
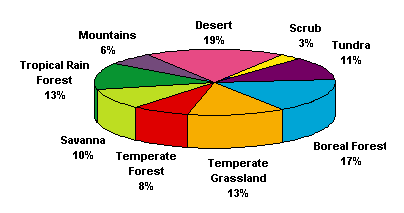
Percent of the world's terrain divided into dominant biomes.
![]()
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
Oikos – Greek, household
calc – to count, number, enumerate
Oikios topos meant the optimal setting for a plant
logos – ration, or comparative ratio
Oikumene is the ancient Greek term meaning the settled landscape from which human households (oikios) derive an enduring sustenance.
Three examples from India, the Alta Plano or Peru, and lastly from Andalucia in Spain.
In all three cases the plants, meager though they may appear, are the basis of the oikumene.
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
Oikumene was the word ancient Greek writers used for a crafted land, any landscape altered by human intent and settlement.
The Tuscan landscape of northern Italy is a vine, wheat, & olive culture, the oil from which was used in Roman times for lighting in these oil lamps.
Garrett Hardin, Filters Against Folly, (pp. 4-5).
Measure by expressing in numbers
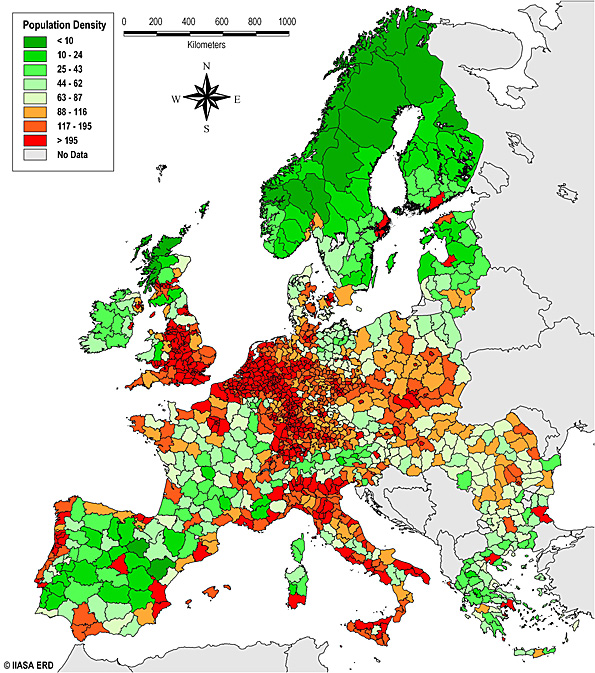
Population density is among the most important numerate expression of the relation between people and land-use.
Wealth from commerce:
.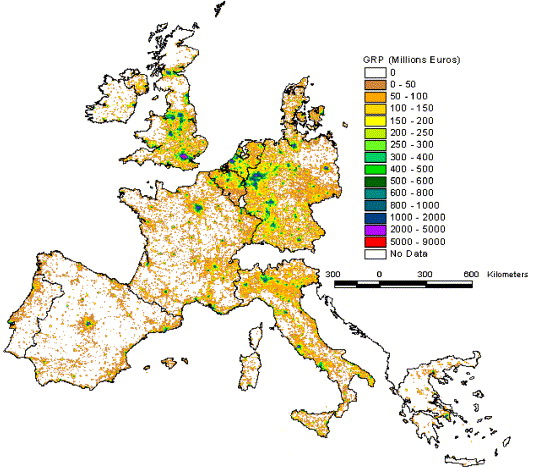
Economic wealth created by commercial activity.
“more than measurement”
(p. 40).
“The numerate temperament is one that habitually looks for approximate dimensions, ratios. proportions, and rates of change in trying to grasp what is going on in the world.”
(p. 41).
The probability of an event is an equally important numerate expression with respect to the relation of human populations to land-use and technological capabilities.
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
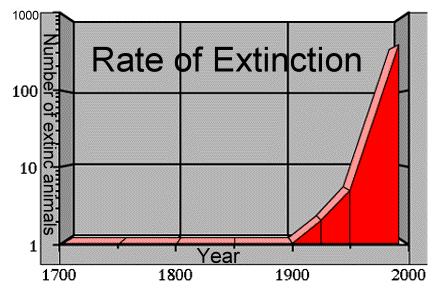
Forests in an ecolate sense are indispensable.
Forests are able to withstand drought due to fungus and nutrient loss due to lichens and bacteria.
One thing is dependent upon many another.
Top level predators rely on smallest of creatures.
Side effects are consequences of any action.
Therefore we put findings from each literate and numerate and ecolate sources together to form a new concept called ecolacy.
Ecolate filter: all side effects are really consequences (unforeseen) and thus real effects.
In ecology you may never do merely one thing & there is no "away" to throw out wastes.
“one of the functions of language is to prevent thought…”
Garrett Hardin, Filters Against Folly, (p. 53).
“The essential orientation of ecology is all-inclusive, global: investigators try to account for all the factors at the same time….it encounters grave difficulties.”
pp. 55-56.
“Predictable or not, these possibilities are part of the total ecological system.”
p. 56.
![]()
“We can never do merely one thing.”
First Law of Ecology.
p. 57.
Ecolacy, Boundaries & Limits as “filters”
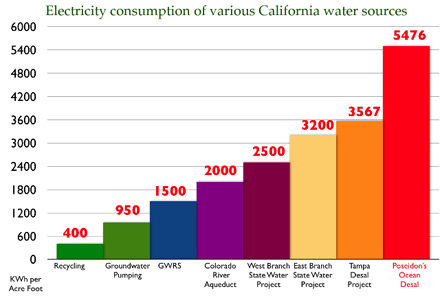
An unseen limit are the twin related boundaries: Water and electricity
"Energy production requires a reliable, abundant, and predictable source of water, a resource that is already in short supply throughout the United States and the world."
"Exploring the Energy-Water Nexus," United States Department of Energy: National Renewable Energy Lab NREL.
The water it takes for us to live uses electricity for us to have the water!
![]()
Synthesis practically speaking means that we learn to put essentials together:
"Proposed restrictions on the use of water for power generation to protect fish and other aquatic organisms could result in increased costs of electricity or potential energy shortages.
Because the energy required for treatment and delivery of water accounts for as much as 80% of its cost, an insufficient supply of affordable energy will have a negative impact on the price and availability of water.
The interdependency between the water and carbon cycles could lead to shifts in water distribution that are difficult to predict. That is, increases in electricity production – and use – may lead to higher levels of atmospheric carbon, which can impact the availability of water to electricity producers in certain regions.
In summary, the link between clean, affordable energy and clean, affordable water is crystal clear. There cannot be one without the other.
For additional resources and reference material, please access these online resources that discuss this topic @
NREL, Water-Connect Workshop's findings
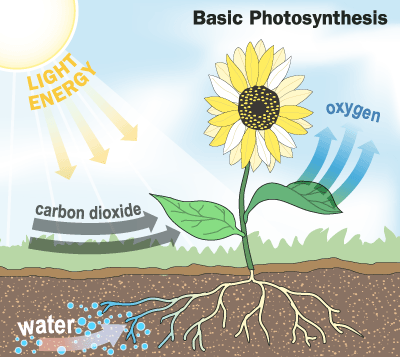
Water is also needed for photosynthesis:
“The ecolate filter is a mental filter. We can be ruined if ecology is turned into a religion.”p. 67.
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
Ecolacy means putting ideas together ecologically and is more than mere semantics:
1. Waste is a mental construct
2. There are no side effects
3. There is no away to throw to
4. All so-called pesticides are "biocides;” antibiotic characteristic.
Garrett Hardin, Filters Against Folly, p. 67-68.
Ecolacy alters the literate and numerate filters with an emergent context of the situation in
which descriptions and measurements of the past or present are seen as preludes
to some future condition.
Ecolacy requires a practical synthesis; what is synthesis?
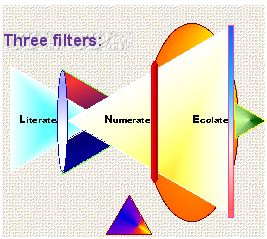 The Threefold Way
The Threefold Way
Filters
Literate -- can you read intelligently?
Numerate -- can you count accurately?
Ecolate-- can you act appropriately?
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
"Not humans apart. . . "
Brazilian coastal tribal peoples depend on preserving forested lands.
The First Law of Ecology is : “We can never do merely one thing.”
“Abusus non tollit usum.” “The abuse of a thing does not bar its use.”
“Prudence
dictates that we compare the advantages and disadvantages of all proposed
courses of action [and inaction], choosing the one that, on the balance is
quantitatively best.”
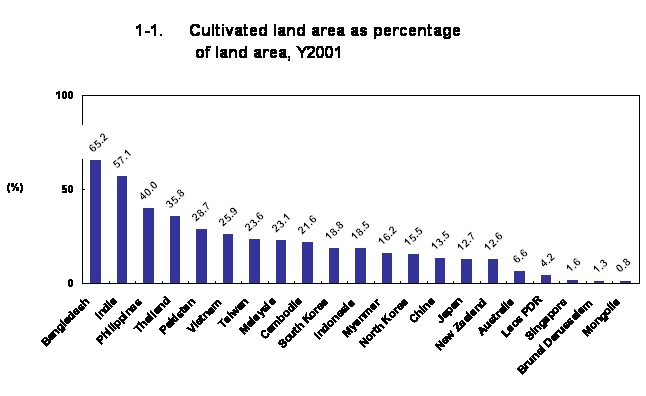
The amount of cultivated land as a percentage of all area in a nation?
(65)
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
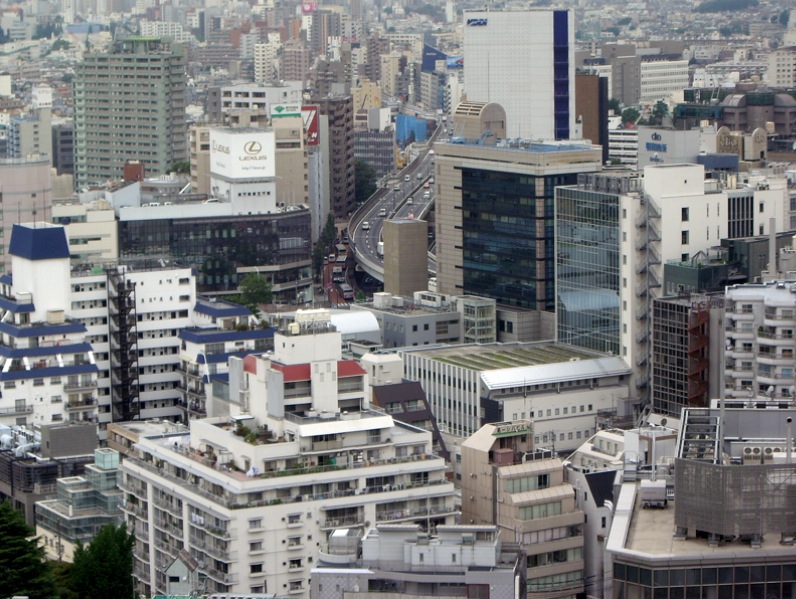

The density of living in Tokyo, Japan.
The folly of mistaking material for
mental progress 
“Nature has assigned no limit to the perfecting of the human faculties . . . the perfectibility of man is truly indefinite.”
Marquis de Condorcet (1789)
“Anything we can dream of, we can invent. Anything we can invent, we are required to use.”
“Quis custodiet ipsos custodes?” Who will watch those people who watch over us?
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
“Traditional language often throws a smokescreen over problems:
1) Waste, like weeds, is a mental construct, not an objective reality.
2) Objectively speaking, there are no side effects.
3) There is no away to throw to, since the law of the conservation of matter dictates that what you start our with you end up with–although in different forms. Matter can neither be created, nor destroyed.
4) All so-called ‘pesticides’ are similar to antibiotics in function and –in reality these biocides– are widespread substances that kill life. That is because, like bacterial antibiotic resistance to drugs, the bugs that survive pesticides pass on their immune resistance to their off-spring. Bacteria, however, are more capable than insects can share their immunity with sister bacteria in ways the insects cannot.
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
Interventions always need to be audited & evaluated
Significant interventions in the world are always interventions in systems, of which three kinds can be usefully distinguished:
Organisms: a fantastically complicated system of cells, tissues, organs. . . .
Systems of organisms: our well-being depends on the survival in good health of many other kinds of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Political systems: preservation, conservation, allocation, or political economy proposes that our well-being depends on our own resources.
“Even with the ecological focus on man (as it is in “human biology”), the bearing of other living things on the welfare of human beings is not neglected (as it all too often is in economics).”
“At high rates of interest the present value of the distant future effectively vanishes.”
74.
“A culture of poverty is one in which the future is discounted–at a very high rate.”
78.
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
Three filters and two lenses through which to get a more robust view of reality.
 |
Literacy | Numeracy | Ecolacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecology | now | population growth | keystone species |
|
|
| + |  |
 |
|---|
|
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Evolution | ancestry | surviving healthy offspring | carrying capacity |
|
 |
||
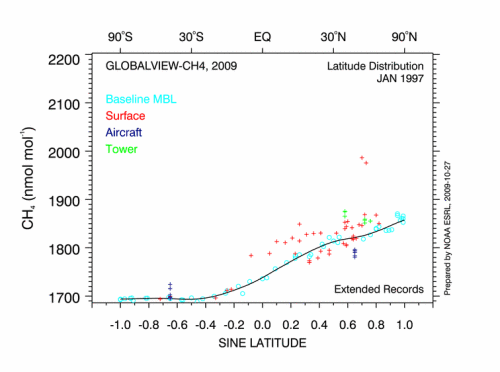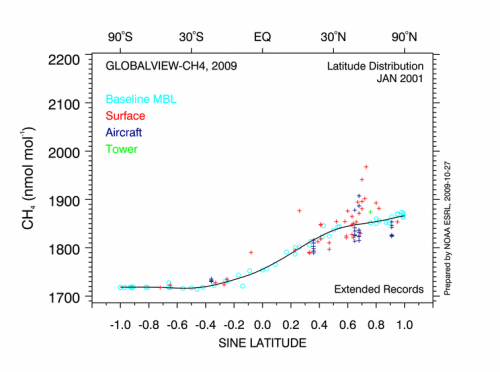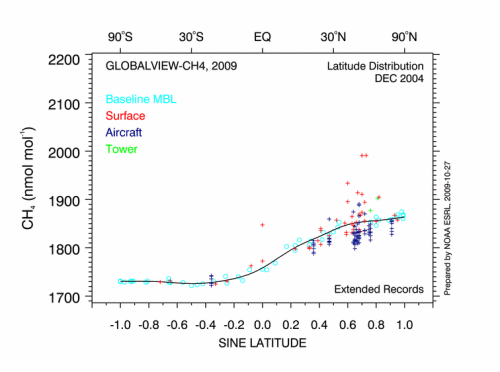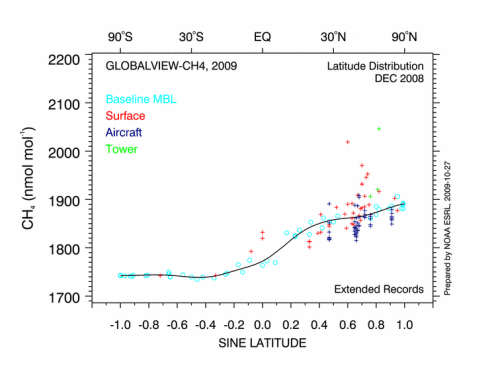
The understanding of nature is divided into analyzing current conditions as ecology and comprehending changes over time or evolution.

Changes in the life zones and changes in the physio-chemistry (carbon dioxide levels) of the world.
Environment to Hardin is divided
In two (dialectically):
p. 12.
1 nonhuman or non-living factors of existence
• physical
• biological
• geological
2 internal, or human factors
√ economics
√ politics
√ ethics
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
E. O. Wilson divides the study of nature into four parts:
- environmental policy
- ethics
- social science
- biology
“The world is too remote from ordinary experience to be merely imagined.”
Edward O. Wilson (NYC: Vintage, 1999). pages:, p. 49.
Wilson suggests that we “Think of two intersecting lines forming a cross, and picture the four quadrants thus created. Label one quadrant environmental policy, the next ethics, the next biology, and the final one social science.”
p. 9.
environmental science is needed for: policy
V V V V ethics biology
“We already intuitively think of these four domains as closely connected, so that rational inquiry in one informs reasoning in the other three. Yet undeniably each stands apart in the contemporary academic mind. Each has its own practitioners, language, modes of analysis, and standards of validation. The result is confusion, and confusion was correctly identified by Francis Bacon four centuries ago as the most fatal of errors, which ‘occurs wherever argument or interference passes from one world of experience to another’.”
Wilson, p. 9-10.
How does the definition of ecology alter the literate and numerate filters?
Matrix:
environmental policy |
ethics |
social science |
biology |
Earth as household | numeracy | ecolacy | first law | semantics | 3-fold way | culture | folly | problems | interventions | Wilson's ideas
![]()
Francis Bacon on the four idols
Garrett Hardin, Filters Against Folly, How to Survive.., New York: Penguin Books, 1987.
E. O. Wilson, Consilience, New York: Vintage Books, 1999.
Charles J. Krebs, The Message of Ecology (1988).
Ecological integrity