Cosmos
Cosmos 

Navigating the site:
Physical reality
We are faced with distinguishing the actual condition from the appearances.
To do so is difficult, to say the least. Albert Einstein had an interesting comment about the hidden reality we do not perceive directly without technical and imaginative assistance. Students after Einstein and Kaluza have insisted that we are only now becoming aware of the enormous size and relatively large number of unseen --nevertheless real-- dimensions masked by the atoms and their subatomic particles. The neutrons, protons, electrons and numerous other particles persist in actual dimensions of space too tiny for us to perceive at the core of matter from whence three powerful forces emerge.
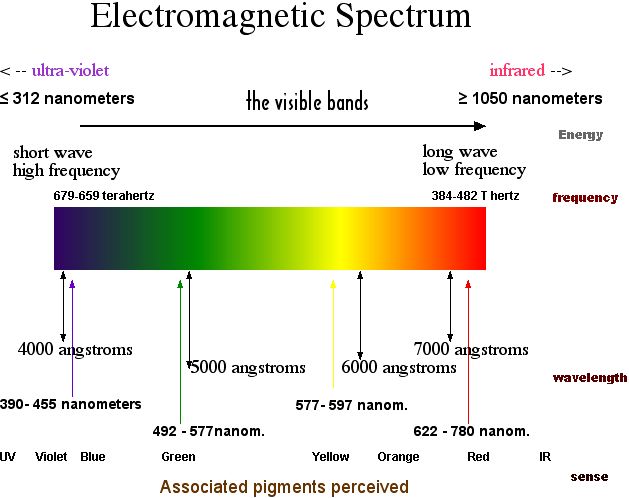
Fundamental universal forces | electromagnetism | spacetime | gravitational shapes | etymology of physical
These fundamental forces are the reason we have electromagnetic energy. That is the force holding atoms in compounds together that shapes and lends form to molecules that enable life.
Two of the three forces found in the atom's nuclei are:
1. Strong nuclear force, that accounts for the binding of protons and atomic nuclei.
2. Weak nuclear force that accounts for radiation and fission.
3. Electromagnetic force that accounts for the movement of electrons, light, radiation and attraction.
Gravity may be understood as the latent force of mass that these above three forces bring into existence.
All of space is permeated by things that we cannot see, let alone hear, smell, taste or touch.
| greater frequency | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
high energy |
|
lower energy |
||
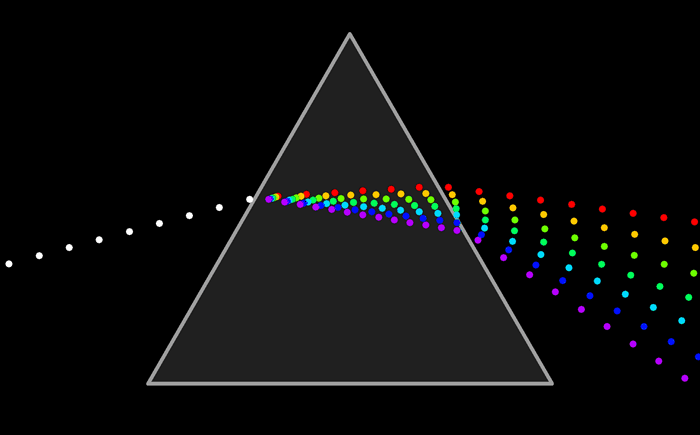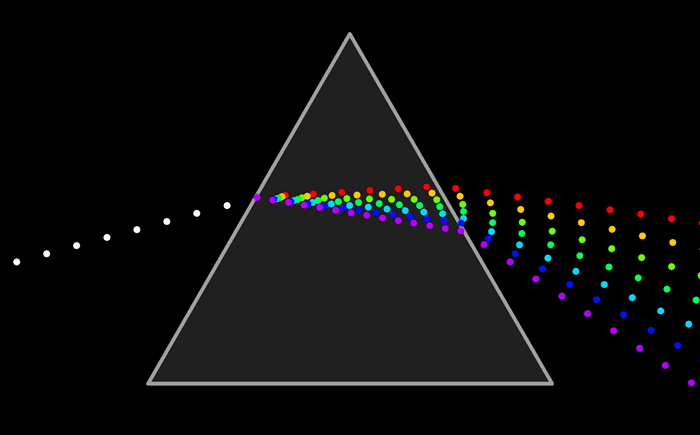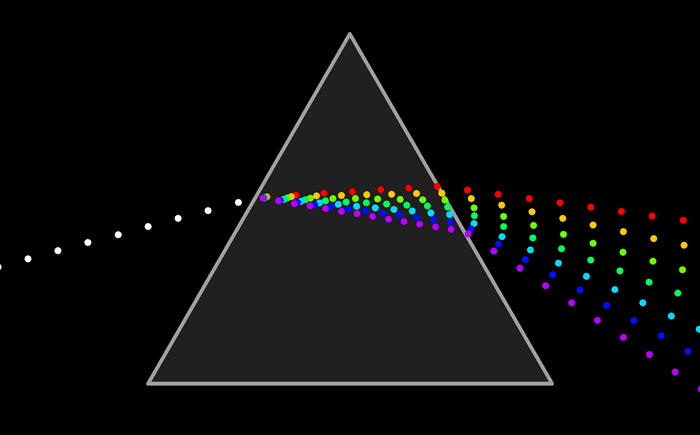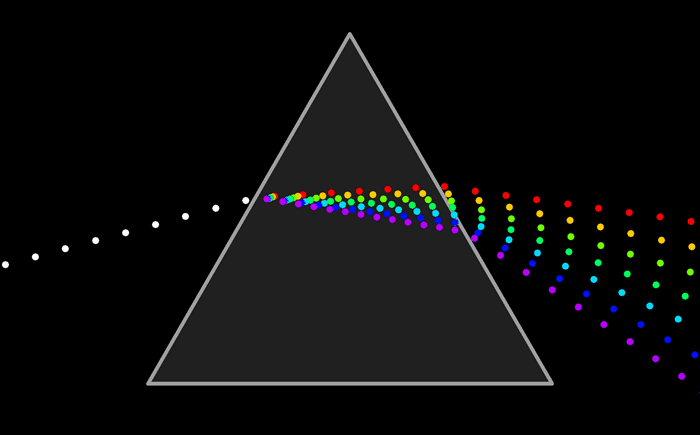
Fundamental universal forces | electromagnetism | spacetime | gravitational shapes | etymology of physical
Gravity as the warp of spacetime.
Take for example when you look at the night sky. First realize the sun's light take 8 minutes to reach the Earth's surface; that is how far away the sun -- our star– is from the Earth and our moon. The moon would still appear in our sky in the evening eight minutes after the sun were to disappear (an unlikely event).
Once
the sun has appeared to set and the darkened sky  reveals
the omnipresent stars, one can begin to recognize an orderly arrangement
in the celestial motion due to the earth's rotation on its axis. Looking
at the evening sky at the stars and the galaxies that stretch before
you, you are really looking into the past. Light traveling from distant
parts of the universe to our Milky Way Galaxy and our star cluster takes
millions of years to traverse space.
reveals
the omnipresent stars, one can begin to recognize an orderly arrangement
in the celestial motion due to the earth's rotation on its axis. Looking
at the evening sky at the stars and the galaxies that stretch before
you, you are really looking into the past. Light traveling from distant
parts of the universe to our Milky Way Galaxy and our star cluster takes
millions of years to traverse space.
The constant velocity of the earth rotating on its axis, inclined as it is at a slight angle of incidence to the plane in which we observe the planets in their annual transit of the solar system, give to the celestial object the appearance of a regular movement "Like the sun and the moon, stars always rise in the east and set in the west. Distant stars shed their light years, even thousands of years before the day you observe them. Those stars at or near the center of our own Milky Way Galaxy disperse light in all directions and 30,000 years after that light is emitted we see the electromagnetic emanations here on earth. As Carl Sagan reminds us "Space travel and time travel are connected." (Cosmos, p. 207) Because we perceive time as separated from space, to our appearances the spacetime of Einstein's imaginative discovery is but a metaphor.
Light travels at 300,000 meters per second, so you can deduce that the outer space that you see on a starry night is quite large, indeed.
Fundamental universal forces | electromagnetism | spacetime | gravitational shapes | etymology of physical
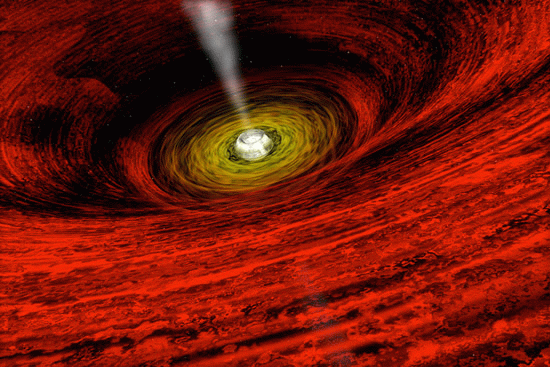
A light ray bends as it passes a dense object.
Artists rendering of an x-ray emission from the vortex of a black hole (a very dense object) in interstellar, deep space.
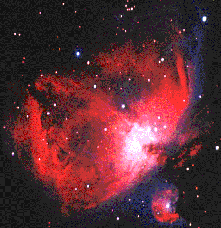
Orion Nebula
from the Hubble Space telescope.
Fundamental universal forces | electromagnetism | spacetime | gravitational shapes | etymology of physical
Physical is from the Greek root word –physis– for the material conditions of existence. It conveys the ideas of form and function of the objects and things we see, feel, touch, smell, taste, and measure or otherwise: if not directly observed, then encountered around us.
For example the air or atmosphere.
Beyond Einstein by M. Kaku | Wilczek | Hawking | Gell-Mann | Feynman | Einstein | Thomas | Galileo | Hooke | Newton | Kaku
Quantum mechanics | quantum behavior | atomic science | chemical elements | energy
Words | Science Index | Social Analysis | Population Index | Global Warming Index | Nature Index