![]() echnology disturbs
echnology disturbs

|
Reflect | |
 |
||
Technology alters what we experience because tools reinforce and often refabricate new views about nature, the world and the universe because the way we use tools influences how we can choose to live.
Reflecting | metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Science contrasted with technology | Amusing ourselves | Words | technical change | metaphors
Activity: compare and contrast settings to understand C O R E.
Contrast this painting of an urban New York City in the 1930s –spotting  the orderly composition of structures, especially structures that are out in front of the residential buildings and the role of the wall in the foreground–with the medieval town of Carcasonne restored in southern France. In both of these settings the divergent tool complexes and the technological facets of each civilization become more recognizable as both obstacles and adaptations each society made given the tools that were widely used at those times.
the orderly composition of structures, especially structures that are out in front of the residential buildings and the role of the wall in the foreground–with the medieval town of Carcasonne restored in southern France. In both of these settings the divergent tool complexes and the technological facets of each civilization become more recognizable as both obstacles and adaptations each society made given the tools that were widely used at those times.
One of several medieval walled bastides, shown above is Carcasonne, in southern France.
Carcassone, France was a medieval walled bastide (or fortress town) that has been rebuilt to indicate life during the middle ages in a fortified city. The concept of a defensive enclosure impervious to attack was a response of technological capabilities to the Huns, Tartars, Turks, Vikings, and Moors who at one time or another from 400 Ad to 1400 Ad attacked various parts of Europe. The walls were eventually no match for growing populations, merchants with a commercial desire to expand contacts, and the siege weapons from Asia, including Arabic numerals from India, algebra, gunpowder, cannons, and "greek fire" or naptha. Together the siege engineering of artillery as an effective weapon brought metallurgy and ballistics together with a strategy that literally broke down the walls that protected rich little enclaves such as these bastides that the French had placed on the frontier to withstand the invasion of Saracens or Moors for Spain and North Africa.
Clarification:
 Six related ways of defining Technology
[ etymology, Greek
]
Six related ways of defining Technology
[ etymology, Greek
]

metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
How technology alters our language, imagery, and descriptions.
Several metaphors reveal the deeper significance of historical changes in the manufacture of material culture.
In addition to "voracious vehicles":
Human origins -- navel of security
Human identity as it is revealed in tool making and reflected in architecture.Ancient -- maze of ingenuity
The Chinese invention, dispersal and European uses of the clock in the middle ages.Modern -- machine in the garden
Mining, mechanics, and the influence of mechanization in preindustrial Europe.Post-modern -- engines of control
The transition of industrial technology in Europe & America to the "electronic village."metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Time

ancient Egypt Clepsydras or water clock
Hindu use of the "0" or zero in ciphers.
ancient Greece Antikithera device
Mediaeval China Su Sung's Astronomical clock 1079
Baghdad & Muslim clockworks
625-1125 Toledo Spain
1280 weights to run a clock mechanism
1450-60 fusee & spring drive for watches
1603 Hans Lippershey telescope
1680 Christian Huygens & pendulum clocks
Navigation & time
Textiles & timing
Electricity and wave frequency
Automobiles & timing
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Culture
 Human culture
adapts to changes in value depending on how people measure & think about
time.
Human culture
adapts to changes in value depending on how people measure & think about
time.
In agrarian societies people measure value in respect to seasonal cycles (few members of those societies even had sundials, but they followed the apparent passage of the sun through the sky as it changed daily and monthly).
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
 Labor Theory of Value
• The time it takes to combine ones labor skills with land and natural
resources determines the cost of a product.
Labor Theory of Value
• The time it takes to combine ones labor skills with land and natural
resources determines the cost of a product.
Inventions have worth in respect to how much of an investment in time anyone makes to produce something.
1) "Sociological, value placed on invention, level of
inventiveness, native ingenuity, educational system, openness to novelties, character of entrepreneurs, extent to which inventive faculties are diverted into industrial production."
2) "Volume of capital accumulation; the absolute amount of new investment, rather than the rate of increase, though, . . . the faster the better."
3) "bottlenecks in the supply of labor, natural resources or finance . . . both induced the early adoption of spontaneous inventions & stimulated the discovery of new methods."
H. J. Habakkuk, American & British technology in the nineteenth century; the search for labor-saving devices. [Cambridge, 1962], 1-2.
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
"Means of production" as a key to understand the categories or types of material culture. Foraging, fuel, food, fiber, & shelter, hunt organization differs from agrarian labor sex specific chores & non sexually specific tasks done at harvests, barn raising, defense, and preparation.
The purpose and division of labor
"Work its structure, organization, & concepts must in turn powerfully affect the tools and techniques and their development."
"The extent of the market is limited by the degree of the division of labor."
Labor is the activity associated with birth, the creation, or the investment of time, talent, and purpose at work.
"Technological change appears to be accelerating."
Family as a unit of labor was replaced by machinery, but the derivations reveal the original relation of family surnames and occupations: potters, sowers & weavers, revealed in surnames:
Baker, Butler, Smith, Goldsmith, Tailor (Taylor), Carpenter, Cook, Cooper, Mason, Chandler, Coulter, Croft, Fuller, Joiner, Shepard, Potter, Weaver, Wright, Miller, Tanner,
etc.
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
![]()
PACEY:
Worldwide changes hinge on certain dialogues involving the accumulation and application of knowledge to craft.
Certain basic or cornerstone tools and techniques have the power to alter people's behavior labor patterns & social institutions. Some examples of transformative tools are fire, agriculture, steam engines, electricity, or computers.
Inventions, engineering, or techniques alone, are not technology.
rice growing
spinning wheel
paperpipe organs, calliope or musical instrument with pipes and key board.
gunpowder
transistors
technology requires:
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
3 aspects or facets are different qualities of technical inventions or tool complexes that reveal how techniques must be adapted to every feature of the tool complexes that form the basis of "different but related inventions."
1 Material - the function, purpose and applications to which technology is directed
2 Cultural or literary - metaphorical power (ideological)
3 Social or Organizational or institutional constraints affecting the social behavior of people including personal or communal relations.
In order to accommodate the resources, power, energy flows, fuels, products, solvents, wastes, capital costs, financing, marketing, design and regulation changes that accompany any drastic revolution in technology, the craft or labor of workers must adjust to new conditions. The replacement of craft guilds & skilled union movements by industrial unionism is an example of such a radical shift in control over wealth and resources due to changes in the institutional relations of labor and ownership of tools, factories and machinery.
When related to ownership in the factory system that was established in textiles, the weavers and skilled workers destroyed the newly invented machinery as to save their jobs. These people were called Luddites because their leader was Ned Ludd, a weaver whose livelihood was threatened by the textile manufacturing business' introduction of mechanical looms. (Industrial revolution)
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
![]()
The role of religious orders in promoting the use of new tools and emerging technologies
Taoist acolytes were taught the mastery of fire, smelting, astronomy , fumigation, macrobiotic diets, and geomancy.
Buddhist Monks practiced tantric yoga, cultivated vegetarian diets, wrote scriptures in the world's first books, cast prayer bells, & built enormous prayer wheels-the forerunner of "flywheels"
Augustinian's kept the 7 sacred gospels that became the text of the New Testament , they conveyed eastern agricultural advances from Africa to Europe, Luther was trained as an Augustinian and left; & later sparked a Reformation.
Franciscans rediscovered nature as God's creation and the influence of the four elements on people and society, they carried Vitruvius book --based on Airs, Waters, and Places of the ancient Greeks-- on design to America which influenced the mission building and town (puebla) layout of the Spanish colonists.
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Technology has a lasting influence because as artifacts some more essential tools' outweigh others in their cultural, political, or literary influences. Such influences reverberate throughout in our postindustrial
or "information / atomic" age. We can see some of this influence in either the metaphors or the agrarian terminology used to measure the performance of modern machinery.
Revealing phrases such as:
A horsepower is a unit of power equal to 550 foot-pounds per second (745.7 watts).
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
![]()
The importance of hydraulics as a formative role in shaping society.
 Wittfogel's
hypothesis: social order is imposed by the technological requirements of dams
& canals.
Wittfogel's
hypothesis: social order is imposed by the technological requirements of dams
& canals.
Water as an elemental piece of technology;
There is a geographical determinism and land realism that suggests that nature dictates cultural changes. In dry or arid regions of the earth people have always shaped their societies around the making and maintenance of those arts that relate to the search for, recovery and continued use of water resources.
One example of this realism and determinism is that "water is the driver" of the nutrient cycles and needed hygiene that nourish communities as it is the basis of the hydraulic civilization. Water even sustains the fossil fuel civilization created by western democracies in this century because water is needed for steam and making steam is needed to turn the turbines that attached to a dynamo, generates electricity. Water and electricity are mutually interdependent in that you cannot have one without the other.
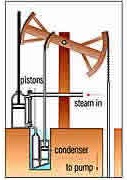 What coal was to the last century, and oil is as a strategic
fuel now, water once was to the earliest machines because water wheel supplied mills with power to grind grain or saw timber. To remove water from mines, as the deeper shafts and tunnels filled with water seepage, the steam engine (shown to the left) was invented by Thomas Savery and Thomas Newcomen.
What coal was to the last century, and oil is as a strategic
fuel now, water once was to the earliest machines because water wheel supplied mills with power to grind grain or saw timber. To remove water from mines, as the deeper shafts and tunnels filled with water seepage, the steam engine (shown to the left) was invented by Thomas Savery and Thomas Newcomen.
"Fuel economy was the purpose of Watts' first improvement to Newcomen's engine (1769), and continued to be the motive behind developments in the steam engine from Watts' separate condenser down to the compound engine."
"It was first adopted in areas and industries where power was
dear and its supply 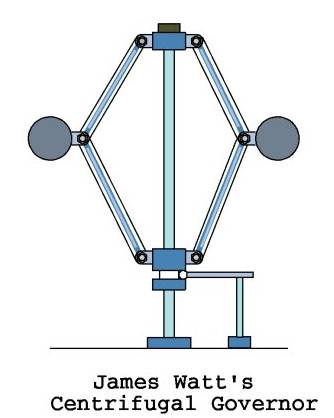 inelastic, for example where supplies of waterpower were
small and irregular."
inelastic, for example where supplies of waterpower were
small and irregular."
"The inelasticity of raw materials and food stuffs directly stimulated innovation in transport."
"Thus a moderate range of innovations of English origin can be attributed to natural-resource scarcity in England, . . ." [158 159]
Because it regulated the speed of the drive shaft to an optimal range of torque to most effectively utilize the power of the steam engine, James Watt's "twin ball device" was called a "governor." This centrifugal governor compensated for the effects of overheating of the steam engine or friction on the drive shaft. Since overheating might speed up the motion of the main shaft and friction might slow it down, the "ball governor" was introduced to maximize output with a minimum of wear on the operating parts of the steam engine's machinery.
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Railway transportation revolutionized space and time
1680-1880 Resource related Land-use conflicts:
Guns, railroads, empires, & control
Chartism: 1830s was a  revolutionary
age: Liberalism & Laissez faire,
revolutionary
age: Liberalism & Laissez faire,
the abolition of British Slavery, & Chartist movement 1838-1848.
Faust 1832 Goethe's who created an epic story of this fable died in that year.
Antislavery movement: Quakers, Abolitionists, War (Thoreau)
triumph of industrial labor with the formation of Labor Unions
Britain, France, USA, Russia, Germany, Austro-Hungarian Empires
1860s Japan -- China -- India -- Italy -- emerge as world leaders
Mechanization becomes industrially linked to complex "tightly coupled systems:"
electricity -- railroads -- urbanization -- suburbanization -- natural resources & engineering -- all working in synergy together to produce a marked change in the organization of labor around "scientific management" promoted by Frederick Winslow Taylor. These ideas were adopted by Henry Ford as "Taylorism."
Taylorism, was the organizational triumph of the mechanical perspective on work.
Kinetiscopes, the early use of sequential still photos to provide observers with the illusion of movement.
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Media wars: Sepoy Mutiny, Boer War, Spanish American War were to a very great degree wars kept alive, if not instigated by the newspapers and magazines.
Innovative inventions: of dynamos, bicycles, automobiles, radios and airplanes based on breakthroughs in material's science, propulsion, and exaptation of older design elements into a new technological web.
P: 8-9, K: 13, 14, LM: 5
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Electricity
Science & Technology where handmaidens
in the discovery and development of the electromagnetic spectrum
1791 Luigi Galvani & chance discovery of conductivity
Joseph Henry & Humphrey Davey observe & Maxwell interprets
1833-37 German & British Telegraph; US 1843; Wash. - Baltimore.
1866 the Transatlantic Cable linked Britain & America
1878 electrification of street-lighting in London
1965 first Television broadcast in Saudi Arabia
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
 Electricity
extended civilization around the world and penetrated deeply into the wilderness of every continent.
Electricity
extended civilization around the world and penetrated deeply into the wilderness of every continent.
Electrification delivered cheap, clean, affordable power to people that revolutionized the way they lived, worked and traveled.
Electrical inventions including dynamos or generators, direct and alternating current, various size motors, railway traction engines, and batteries all came together and engendered – that means "helped to create" – the basis of an automated, automatic, automotive culture.
The photograph here of the nuclear powered cyclotron at U.C. Berkeley is just one example of the uses --in this case atomic research-- to which energy can be employed.
science as a story
| defining science | contrasting technology
and science
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Evaluation and Examination of the influences of technology
![]()
The consequences of technological autism
Both media & culture together generate the web of technical relations: when they interpret the explain the way in which new techniques supplant older traditional ways of doing something or achieving a purpose.
Any web of technical relations explain how resources, water, energy fuels, materials and tools combine to
reinforce one another to sustain  another whole tool complex. Examples of this web maintaining new tools such as electricity and automotive engineering, are just one of several influences that tools and techniques possess in shaping our response to their power to transform our lives and the lives of others in our society.
another whole tool complex. Examples of this web maintaining new tools such as electricity and automotive engineering, are just one of several influences that tools and techniques possess in shaping our response to their power to transform our lives and the lives of others in our society.
The billboard from the Sacramento airport ably renders the "web of technical relations among cornerstone inventions, automated switching devices, electronic appliances and remote control tools that when linked together under gird, support or sustain our security, hygiene, consumption, and comfort.
Our identity becomes lost among the gadgetry as the power of technology becomes
more widespread and pervasive as an extension of our senses, organs, or muscularity.
Two examples of unseen and under appreciated – yet widespread influences – because of the discovery and uses of electricity are automotive and refrigeration engineering.
Readings P: 10, K: 16 & 17, LM: 5 11.
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Automotive engineering
Changes in values, redefining resources, demanding observant behavior, precise production, enormously expensive finance, industrial labor patterns, & the unintended consequences of congestion, disabilities, and nitrous oxide emissions.
Internal combustion engine
1860-1876, prototype development by N. Otto
1885, Daimler & K. Maybach automobile engine
1913, Henry Ford's assembly-line
1931, oil discovered in Saudi Arabia when searching for water
1935, Aramco founded: Mobil, Standard oil, Texaco (Arab-American Oil Company)
Highways as public investment date from 1915 on the federal, or national level.
1 in every 5 jobs in automotive
fuel is oil, coal, wood
German "autobahn" & American "freeway"
A nation on wheels -- "MOTOWN"
Morbidity & mortality rate changes
Travel as tourism to more far-flung places.
Transport of goods at greater distances from the place of origin
Automatons important as robotics is widely used in the auto assembly industry.
![]()
metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Refrigeration
ORIGINS in evaporative cooling & condensation
"Air conditioning created the 'sunbelt' in the South."
This electrically dependent, refrigerated air was adapted to buildings, homes, & cars
chlorofluorocarbons --CFCs-- replaced toxic material --ammonia in refrigeration-- when exapted then was used to form both of the thin coating substances we call Teflon™ and Goretex™
CFCs were found to be not so inert in that they were interfering with the formation of oxygen molecules composed of three oxygen atoms.
That molecule is ozone -- made by three oxygen atoms and it insulated the Earth from ultraviolet radiation.
So concerned were scientists, technicians and corporation executives that produce the CFCs that they met together with international lawyers and representatives from all countries and agreed to limit, and then phase out production of harmful chemicals that destroy the ozone layer in the air.
That agreement is the Montreal Protocol on Upper Atmospheric Ozone Protection.
![]()
Reflecting | metaphors | time | culture | work| Cornerstone tools | Three aspects | Religion | Hydraulics | Railroads | Electricity | Refrigeration
Science contrasted with technology | Amusing ourselves | Technical change
 |
||
|---|---|---|
| Tools of Toil: what to read. | ||
| Tools are historical building blocks of technology. | ||
Pursell | Pacey–World | Postman | Head | Tenner |Pacey–meaning| Eberhart | Snow | Kaku | Boulding | Delillo | Kranzberg
| Postman–Tech | Postman–Television |
Technology index ![]() landscape index
landscape index ![]() words index
words index ![]() photograph index
photograph index