Climate & Biodiversity
Climate & BiodiversityNavigating the site:
Miller, Ch. 6, 13.
Climate, Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Ozone Loss
On the wind is:
- circulation,
- nutrients,
- virus, bacteria, fungi
- dust causing red tides
- pollination
- volcanic dust (SO2)
- rivers of air afloat above an ocean of heat
There is no away, because of interconnections.... we hasten the process.
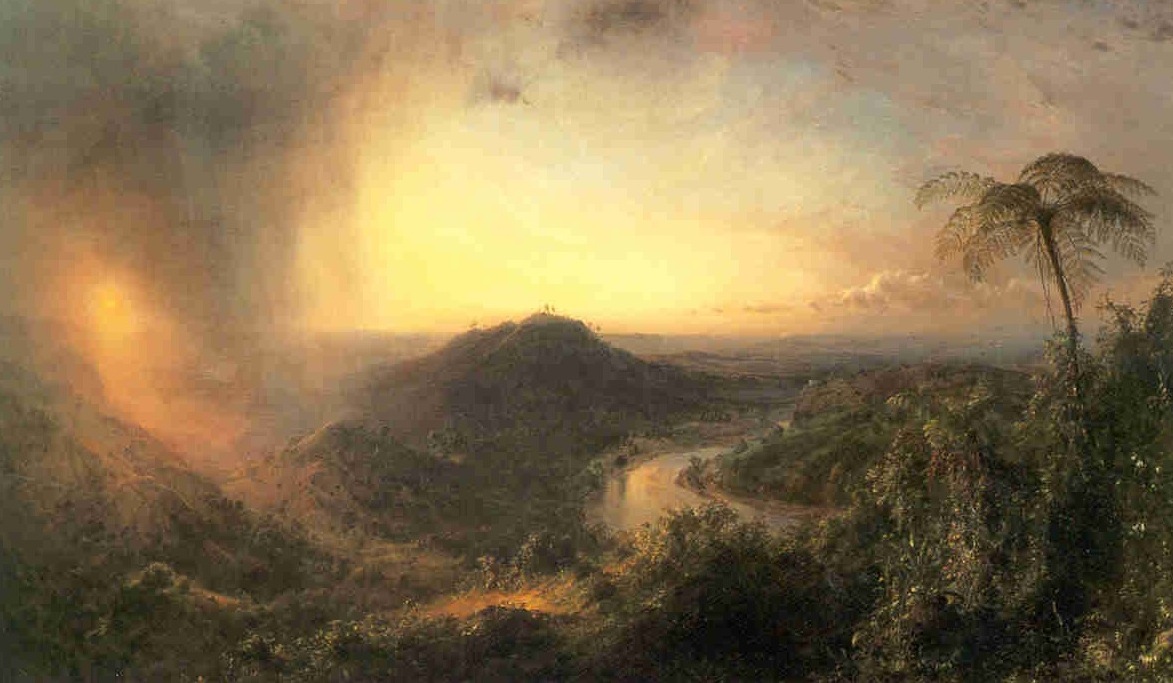
"Wind is an important factor in climate through its influence on global air circulation patterns. Climate, in turn, is crucial for determining what kinds of plant and animal life are found in the major biomes of the biosphere,..."
"How does climate determine where the earths' major biomes are found?"
p.106-107.
The day to day physical properties of the troposphere, or short-term properties are called weather. By properties we mean: temperature, pressure, density, humidity,cloud formation, wind speed and direction, and sunshine or solar radiation.
p. 107
Earth orbit
Climate and life zones are due, in part, to the Earth's inclined axis.
p. 108
El Nino and La Nina,
The cycles of seasonal variation in the transfer or suppression of heat from the Indian to the western Pacific Ocean. Part of a system known as the Southern Ocean Oscillation (ENSO).
p. 109
The Chemical make up of the atmosphere may leads to a greenhouse effect, because of the radiant energy absorbed by certain chemical bonds. Such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, CFCs and water vapor.
p. 111
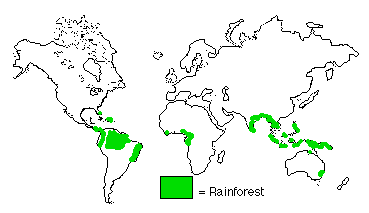
Biomes, climate and life zones on earth... (and in the seas)
p. 112
Limiting factors and biomes
- average temperature
- average precipitation
figure 6-12, p. 114.
Dialectic: terrestrial and marine ecosystems
they interact (figure 13-10, p. 288.)
Watersheds are ways the rivers affect the seas (6-42, p. 136.)
Rain shadow effect (figure 6-10, p.112.) and marine layers of air are ways oceans affect land
Three zones are examples of zonation a key ecological concept.
water flows, like air flows carving out zones of similarity and contrasts:
- Source zone
- Transition zone
- Floodplain zone
moving water, sediment, waste, debris, and detritus from higher to lower elevations.
mixing, settling and rearranging materials in a slow crescendo
Links:
Genetic adaptation: Changes in the genetic makeup of organisms of a species that allow [gene pool] the species to reproduce and gain a competitive advantage under changed environmental conditions.
genes
"units of information"
"traits passed from generation to generation"
segments of related DNA, nitrogen base pair sequences, "found on chromosomes."
differential reproduction, natural selection, mutation evolution, ecological diversity, genetic diversity, geographic isolation.
G-7
"...we find it hitched to everything else in the universe."
John Muir, co-founder of the Sierra Club, 1892
p. 137.