Rules
Navigating the site:
Southeastern British Isles, countryside.
Ten Commandments of ecology:
Charles J. Krebs, The Message of Ecology (1988)
1: The distribution of species is limited by barriers & unfavorable environments
2: All populations increase within limits
3: Optimal and poor places exist for every species
4: Overexploited populations can collapse (fisheries, forests, livestock, and farms)
5: Communities can rebound from disturbances
6: biotic communities exist in several stable configurations
7: Keystone species may be essential for the survival of biocommunity
8: Natural systems recycle essential materials
9: as climates change the boundaries & structure of communities also change
10: Natural ecological systems are the product of evolution, selection & genetic drift
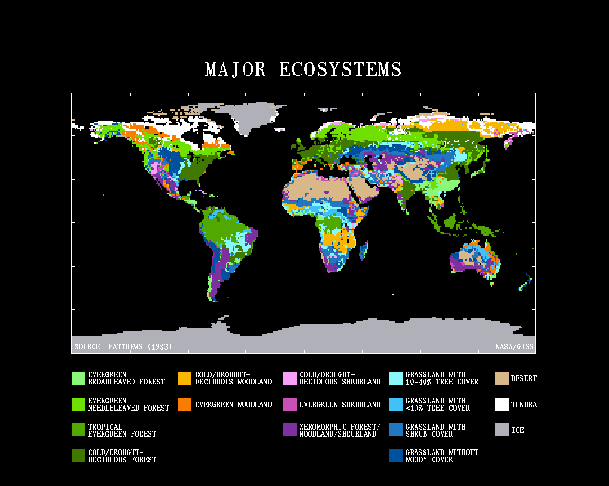
Significant extent of the principle ecological systems geographically displayed
Humans, by analogy:
1: Occupy every land biome with few restrictive barriers because of culture.
2: Have populations that rose and fell depending on food supply until c. 1700
3: The temperate coastal areas have been optimal for civilization's spread.
4: Frequent famines due to deforestation, crop failure, & desertification occur.
5: Humans have overcome adversity through culture, fire, tool use, & writing.
6: Human communities are quite diverse due to languages, customs, & beliefs.
7: Some keystone species have been essential for humans, i.e. cows & horses.
8: Economic systems alter resource flows to recycle money & wealth at great risks.
9: Climate change has influenced human food, fuel, shelter, & clothing needs.
10: Human ecological systems are the product of both natural & cultural evolution.
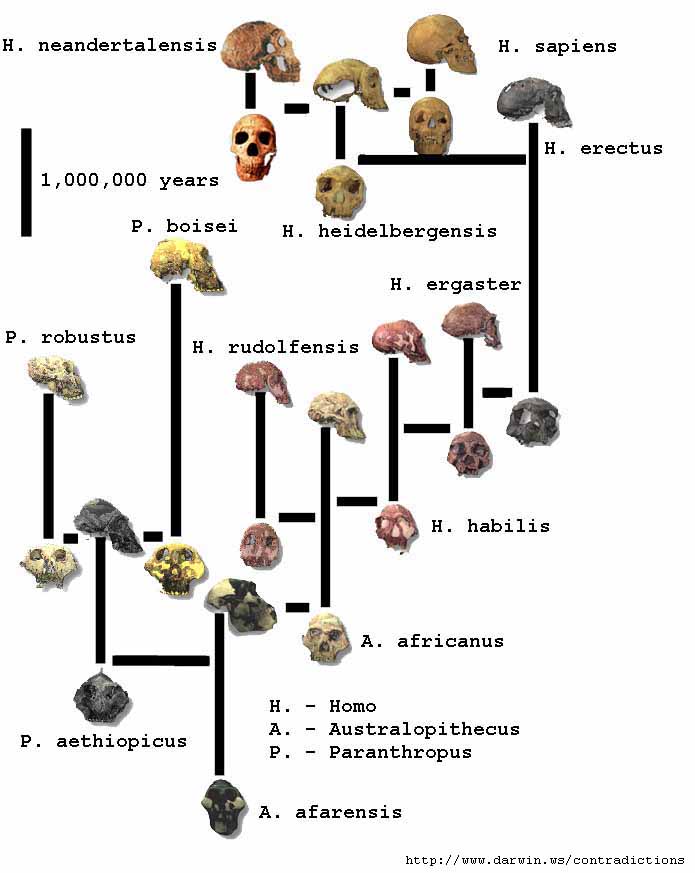
Thus: The human race, the species Homo sapiens, our ancestors and relatives are distinct from other species for many reasons, despite our being a part of nature.
a. Humans have a long gestation period (9 months) & a prolonged childhood.
b. For 98% of our evolutionary development we have lived in extended families.
c. We learned to walk upright (bipedal locomotion) over 3 million years ago.
d. Our brains have increased by three times their mass in the last .5 million years.
e. Our earliest ancestral remains are found in Africa, India, China & Indonesia.
f. The size of our heads creates a birth problem for the dimensions of the pelvic girdle.
g. Unlike our primate cousins our copulatory behavior is unrestricted by seasons.
h. Unlike our primate relatives human female's estrus cycle is visually concealed.
i. Our copulation ritual, unlike our primate relatives, is frontal: stomach to stomach.
j. Our teeth suggest that we are scavengers of roots, berries, carrion, & grains.
k. Human organs for articulate speech have lead to linguistic diversity.
l. Development of the frontal lobe enables us to plan ahead & reflect on life.
m. Humans have the capacity to create an ethical imagination to judge behavior.
n. Humans are easily deceived due to our desire to know, predict & control events.
Ecological terms | Laws of Ecology | Ecological Justice | Ecological Accounting | Ecology interpreted | Ecological systems |Eco-services | Ecological values | Land values disputed