


Systemic Thinking
All the parts of a coral reef are interdependent, but coral polyps are symbiotic.
"Earth centered education.... it is that quality of mind that seeks out connections."
"knowledge necessary to comprehend interrelatedness, and an attitude of care, or stewardship."
David Orr, Ecological Literacy. 92.
Beyond the dialectic in three lessons.
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|
Machinery |
Essential parts |
Earth engine |
"the world is beyond our perception . . . "
 |
Systemic Thinking, Part one: |
|---|---|
| The pyramid metaphor describing triangular relations |
All of the discernible parts contributing to the whole have a combined impact greater than the mere sum of each contributing part when taken apart analytically and assessed separately.
OR: The sum of the parts is less than all of the pieces functioning together as a unit.
This characteristic of a structure is called synergy, or the multiplier effect because the influences of the combined impacts are greater than the mere sum of the effects of the interacting parts.
Gregory Bateson, in an attempt to examine and explain systemic thinking used a metaphor of the machine where four pieces of a systemically related action bring about a combined force more powerful and directed than could be exerted by any of the four separate pieces operating singly or alone.
The four identifiable pieces are:
start-up, motion, friction, directed drive.
But is this four-piece description–a sort of working quartet–adequate to explain the maintenance of life on earth?
Each part of Bateson's model answers a "What question ...?"
See below.
What keeps the motion going?
What moderates the movement?
Bateson's model
There are four working parts or essential ingredients.
start-up or ignition,
Fuel to enable motion,
Flywheel to overcome friction,
governor or directed drive to stabilize forces.
The four essential parts of the system from Bateson's suggestion that nature is like a machine.
 Systemic
Thinking, Part two:
Systemic
Thinking, Part two:
models of functional relationships
Fuel (fusion engine of stars) and Ignition are essential ingredients in any biological or manufactured machine:
Sources or necessities of kinesthetic or explosive actions.
Electrons are the ignition that fuel the cosmos.
Solar energy and planetary thermal conditions are essential for the machinery of life on earth to function.


The transfer and movement of elemental nutrients that are in a sense an additive to the fuel.
| lithosphere | Oceans & Air | Living systems |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Ingredients, | Atmosphere | life's necessities to persist. |
Flywheel & Governor are needed to keep the process going and regulate the torque.
The flywheel perpetuates the force
and
The governor then adjusts acting as the control adding regularity to the motion.
The flywheel is gravitational attraction.
![]()
The governor.
They suggest that if you were to draw a system of related pieces that functioned as a unit, each piece must provide power, action, continuing motion and smooth performance so that the functional integrity of the process is sustained.
 |
||
Fuel
 |
 |
Flywheel
 |
 Ignition |
||
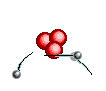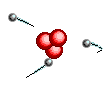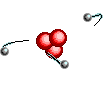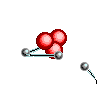
Bateson's model based on an engine's four working parts: Fuel, Ignition, Flywheel and Governor.
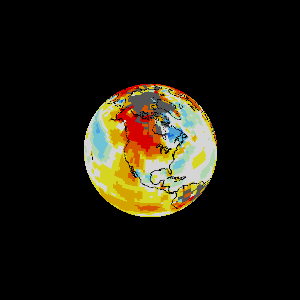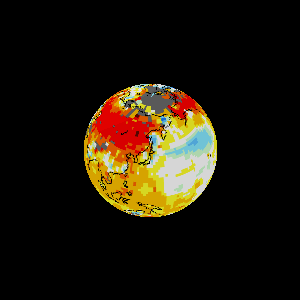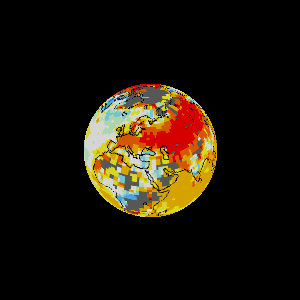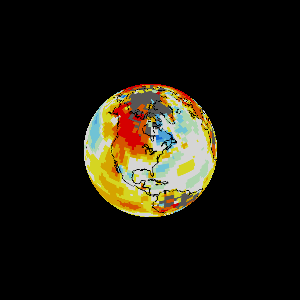
Earth as an engine.
A Governor is carbon release and capture rates.
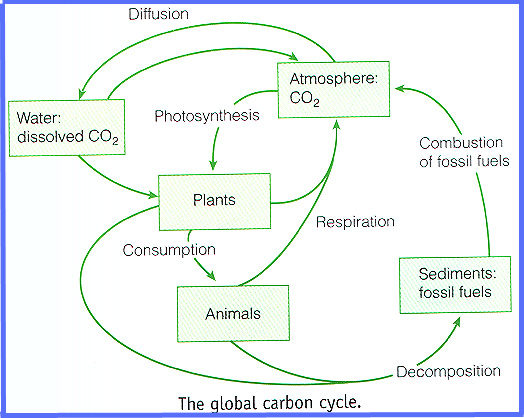
While the above model is simple in that it has only four parts what would you suggest if you were to draw a system of related pieces that functioned as a unit?
Key words:
Fuel, is the source of thrust or movement (Solar, the air's thermal insulation, and geothermal energy supply biomass for food, fuel, and fibers)
Ignition, is the combustion that burns the fuel (oxygen allows for combustion)
Flywheel, is the mechanism that continues the motion (gravity allows for constant circulation)
Governor, is a device that regularizes the thrust (nutrient cycles of carbon, nitrogen or sulfur regulate the speed of growth.)
Cycles of sulfur as a sort of governor of the ecological system, or nature in motion.
Background:
Bateson felt that a simple explanation of a machine would, by analogy, assist students in understanding how parts operate together to perform a function.
Much like the gears on the bike sulfur and carbon adjust the speeds of the abiotic drive wheel and the biotic steering wheel of the "ecological bicycle" used here to represent life adjusting to changes in conditions on earth.
Consider the role of sulfur and an analogy to the function of sugar as a fuel in any cell.
The respiration of
plants and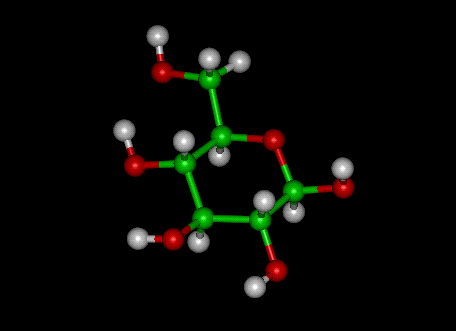 animals by consuming sugar in the form of glucose (combustion) is the origin of power.
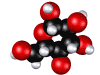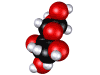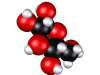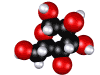
animals by consuming sugar in the form of glucose (combustion) is the origin of power.  All living beings store this chemical energy as glucose [pictured on the right].
All living beings store this chemical energy as glucose [pictured on the right].
By attaching compounds to one another in chemical bonds that are broken and released (by converting the molecule ADP > into ATP) fuel is available in a constant cycle of exchange. Work in cells is done, so long as there is fuel for these units to function.
The shape of the molecules that store energy is influenced by the precise location of sulfur atoms in the molecule. Sulfur is a trace element, needed in small amounts, to make the synthesis of ATP and ADP sufficiently effective for the health of living organisms.
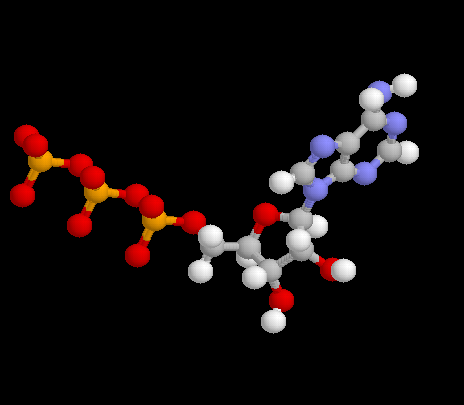
The ATP molecule (above) is a store house for later use when these molecules are broken down from ATP > into ADP to be used to accelerate the functions performed by that particular cell.
Osmotic pressure allows for sugar to enter the cell from the surrounding medium.
 Enzymes control the rate of the production of the product and by products of the breakup and storage of sugar (glucose).
Enzymes control the rate of the production of the product and by products of the breakup and storage of sugar (glucose).
Glucose molecule is a compound of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
C6 H12 O6 is the chemical formula for this vital sugar.
Already, we have more than four steps. Can you list them?

Systemic Thinking
Part three
The missing parts.

Case:
 The model's four parts ignore the mass, structure, transformation, and storage of the fuel that provides the power in addition to the
exhaust material.
The model's four parts ignore the mass, structure, transformation, and storage of the fuel that provides the power in addition to the
exhaust material.
Start
Finish
In an important context, the model needs to include the First and Second laws of thermodynamics. The laws refer to the conservation of matter as the first consideration and the increase in heat as the liquid fuel is converted into motion as the second consideration.
Second law of thermodynamics, no transformation of energy is every completely efficient and residual power escapes as heat.
New concepts:
These laws are the new elements that must be connected to old ideas, or Bateson's model .
Battery, the storage unit for excess power generated [motive (motion) power is converted into electricity and stored].
Exhaust, the excess material produced that is not needed in the process but could, as waste builds up, stop the functioning system. See the externalities discussion.
When adding these to elements the diagram, the process might look like simple intake and exhaust valves:
But there are important systemic connections that make these valves operate synchronously wit the cylinder.
|
Fuel |
|||
|
/ |
\ |
||
|
Battery |
 |
Ignition or Combustion |
|
|
| |
| |
||
|
Flywheel |
Exhaust |
||
|
\ |
/ |
||
|
Governor |
|||
Bateson's model seeks to depict the Earth as a functional system.
A model is only as revealing as its accuracy in reference to real operating conditions.
Any systemic thinking ties the pieces together as a functional whole such that impairment of any one part affects the optimal operations of some or all of the other parts.
In the revision of Bateson's machine, the Earth engine includes:
- sources,
- fuel,
- ignition,
- exhaust,
- flywheel and
- governor.

Sun to soil ratios

![]()

• sunlight affects water heating it to evaporate if excessive,
• soil moisture needs moderate temperatures or else it evaporates,
• less soil moisture means reduced water available for photosynthesis & growth,
• organic matter in soils can, without ample water, oxidize and disappear into the air,
• roots hold the soil, aerate the soil, and allow water to seep into the ground,
• without plant growth, the roots wither,
• the extent of root mass in the ground contributes to the volume of carbon held in the soil; the greater mass of carbon makes it a more organically rich growing medium for plants.

The above related phrases are an example of systemic thinking, using a "cradle" [source] to the "grave" [sink] approach to account for all the parts in a complexly functioning system.
Soil may actually be the exhaust remains of a process that when used wisely can become part of the fuel used to return the system to a functionally satisfactory equilibrium. That means the end product and by products are captures and returned to the circuit of life to renew the world.
Fritjof Capra on Prigogine, Maturana & Varela's work on living systems.