What characterizes science?
What characterizes science? Navigating the site:
Focus of scientific study:
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | forces | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
![]()
Key adherents who are mentioned below represent a commitment to basic axioms or postulates in science.
The examples mentioned here reveal how numbers or measurement create reliable information whose accuracy can be subjected to doubt, carefully tested and then either reinforced, modified, or discarded.
measurement by numbers is an idea shared by Pythagoras & Galileo with contemporary scientists.
rational: logos of Heraclitus vs. logic of Aristotle
- mathematical geometry, Plato and later Kepler.
- rational from ratio, Descartes' x&y coordinate system.
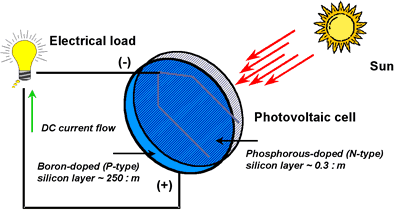
- radiation from the sun is electromagnetic; therefore electricity can be generated from light, especially ultraviolet radiation.
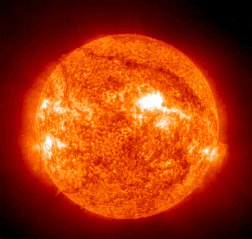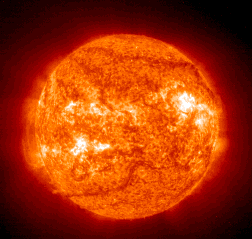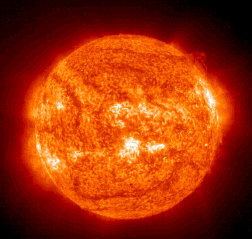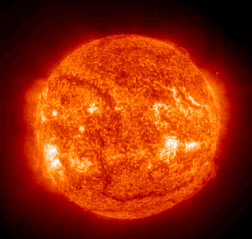

The light of a wavelength shorter than the violet frequency will trigger a flow of electrons in some compounds.
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | forces | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
![]()
repeatable: gravity and acceleration are indistinguishable [the same] said Einstein.
reliable: helical molecules of heredity
resolved by Wilkins, Franklin, Watson & Crick.
"… the world is beyond our comprehension. . . ."
John D. Erickson, Truth Versus Reality, 2004.
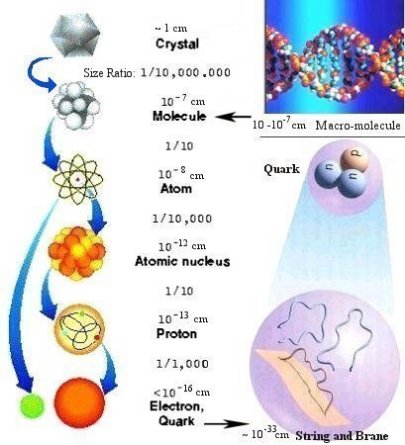
Levels of cosmic organization
scalar size 
Planck Scale
Atomic nuclei scale
Molecular scale
Human scale
Planetary scale
Scientific experimentation has revealed divergent discontinuities of sizes that exist.
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | forces | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
accurate: precise, observations of mocking birds, finches, turtles and lizards by Darwin.
trustworthy: biological heritage is a process where species are evolving together to maintain the world, Wilson – because it has a degree of knowing with recognized uncertainty.
We know that the Earth is the third planet from the Sun in a sister grouping of other mostly larger planets.
unseen forces: Frank Wilzeck, MIT lecture on particle physics.
The electro-weak and strong nuclear forces were not understood in the 17th and 18th centuries. The strong force that holds the insides of atomic nuclei together was not even imaginable in the 19th century. Only with the discovery of the neutron in the 1930s did a richer and more integrated comprehension of unseen forces emerge from the study of particle physics and the harnessing of fission. Fission is the atomic decay process for which we rely upon for electricity from nuclear power generation.
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | forces | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
fungible: in that one kind of characteristic can be thought of as another with different–even contrary– attributes. For example matter may be a form of energy, or genes are not what they seem according to Keller.
revolutionary: the idea that concepts and facts are always replaced by new findings that are more theoretically reasonable descriptions or more testable narratives. Doubt plays a significant role in the overthrow of prevailing postulates. That is to say the reform of widely accepted ideas is possible and encouraged by discovery.
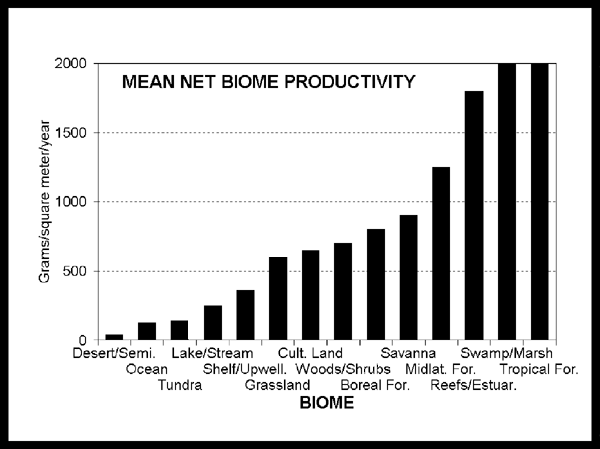
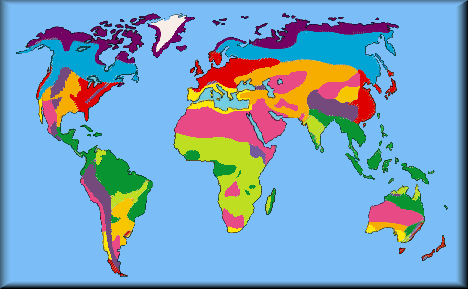
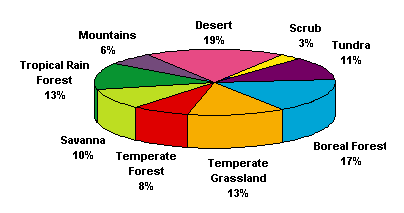
Biomass is the product of sunlight, water, carbon dioxide and nutrients that plants and bacteria enable as by-products of their metabolism. The measure of the amount of living matter is done in grams per square meter (or hectare) over the course of the year. The graph above reveals the relative efficiency of different plant, fungal and bacterial associations in creating living matter which is called biomass by ecologists. These associations are called biomes
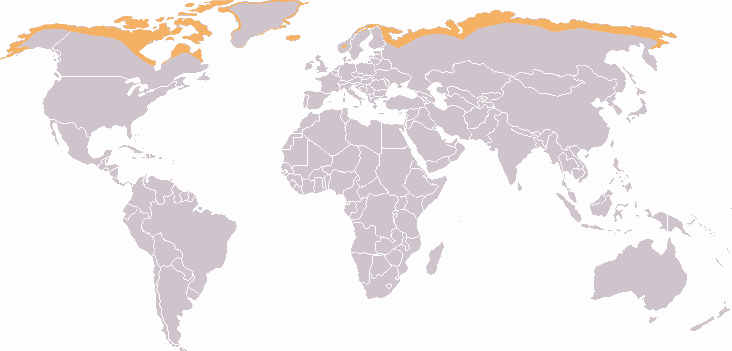
Biomes are large, naturally existing associations of plants, animals, fungus and bacteria that extend over vast regions of the landscape such as tundra, which is depicted above, and the adjacent taiga forests in the "frigid" areas of the polar zones. Biomes of temperate and "torrid" areas of the tropical zones are often associated with rain forests, grasslands or savannas, and deserts.
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | forces | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
method as opposed to a body of knowledge
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | forces | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
axioms refer to given information, for example: assumptions that are rarely, if ever disputed, such as the belief that nature is intelligible. That is to say people can understand nature and describe it with some degree of certainty.
postulates are statements that one derives from proofs about material conditions based on experiment, explanations, theories and heuristics, or discoverable properties of things. That is certain numerical constant's represent actual decipherable relations in nature that can be expressed in numbers, For instance the neutrons and protons have a density just less than 2000 times that of the electrons and that the neutrons and protons move about nucleus at 40,000 miles a second.
accuracy as precision, how precise is scientific information?
Some things in life are certain, like gravity, the increase of atmospheric pressure, or the mass of atoms and molecules.
A mole is the quantity of anything that has the same number of particles found in 12.000 grams of carbon-12. That number of particles is Avogadro's Number, or 6.0221415 times 1023 or a huge quantity.
The inverse square law:
This rule describes the certain decline in intensity of gravity, light, or magnetism at a particular and known extent ("d" for distance) from the source of those different forces. So that at twice the distance there is but a quarter of the intensity.
Science
vs.
scientism
measurement | reliable information | accuracy | doubt | tested | reinforced | modified | discarded
![]()
Descartes | Feynman | Galileo | Hawking | Hooke | Newton | Einstein | Tattersall | Wilzeck | Gell-Mann
Spencer Weart | Gale Christianson | James Hansen | Contemporary | Robert Musil | David Archer | Gavin Schmidt | data
Darwin | Ehrlich | Hardin | Margulis | Thomas | Watson | Wilson
nature | many meanings | nature's geometry | natural capital | role of plants | production
Science Index | Nature Index | Population Index | Population Index | Genetic index | genetic graphics | Climate Analysis
![]()