The Dominant Animal: Chapter 7, Ups and downs of Population
an on line guide
Aldo Leopold, Thinking like a Mountain, A Sand County Almanac
Weeks
Seven
To human folly we can't attribute all the ills we see on the land and in the waters.
“ . . . the problems that continued rapid global population growth is now bringing to the planet, ...."
outline | argument | details | summary
1. human population growth's limitations
A. Biology: nine months pregnancy, delayed weaning & suppression of estrus
B. density dependent diseases
2. Gene pools and breeding population groups
3. Human population dynamics
4. Family planning
5. Curbing the explosive growth due to demographic transition
6. Arithmetic
7. Aging
![]()
De facto
"We need to know something of the population dynamics of particular species to find ways
a) to harvest fish stocks sustainably,
b) to control pest populations,
c) to preserve endangered species,
d) to predict the occurrence and spread of epidemics."p. 141.
The analytical approach trumps any typological biases.
Based on "all organic change" is a mesh between conditions and genes.
"...family finances seem to have been important."
p. 143
"Women's participation in society outside the family, moreover besides being a factor in reducing birthrates, seems to be essential for the successful economic development of societies."
p. 147
US Bureau of the Census on line
![]()
Population and constraints include gestation period and birth rates
"A population's size is basically the result of…. births and immigrants… deaths and emigrants."
"shifting population sizes have important consequences for the evolution of these populations."
The number of births or natality rates are measures of fertility:
- from 15 to 45 years of age, statistically speaking are reproductive years
- one to thirty offspring is the human biotic potential
- understanding the menstrual cycle
- delaying age at marriage
- breast feeding and weaning
- TFR or the total fertility rate is the reality
- The age structure of a population is the single best predictor of future changes in demand, consumption patterns, and the distribution of labor.
![]()
"changes through time in the composition of gene pools…"
Darwin's great contribution
A) Hard inheritance
- "(all the genetic information possessed by populations)"
{p. 140}
B) Soft Inheritance
- acquired traits
- Culture as an ambivalent factor in fertility patterns
- restricting marriage to similar ethnic identity
- prohibiting marriage to other religious faiths
- status of women
- enables increased fertility
- infanticide prohibitions
- birth control
or contraceptive's legality
(pp. 144-145.)
- poor nutrition {prehistoric means]
- coitus interruptus {ancient means]
- intra-uterine devices (IUD) {modern means]
- condoms {modern means]
- pills {recent means]
- other, RU-486, "a chemical means to terminating an unwanted pregnancy." p. 145.
- constrains fertility
- dowry; burden on male or female offspring's family
- gender solidarity
- patrilineal versus matrilineal pattern of descent
- access to abortion
- optimal nutrition
- enables increased fertility
![]()
Accelerating aggregate global numeration
- 1850 = one billion
- 1900 = one and one half billion
- 1930 = two billion
- 1950 = two and one half billion
- 1960 = three billion
- 2010 = six and one half billion
- 2012 = seven billion
6,964,340,334
2-25-2011
7,045,887,085
10-15-2012
United States population clock.
World Population Data Sheet by the Population Reference Bureau
National fluctuation over time intervals, cohorts.
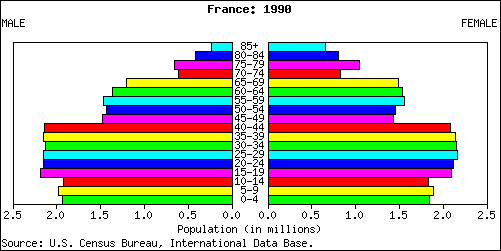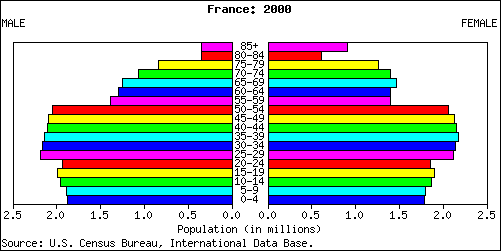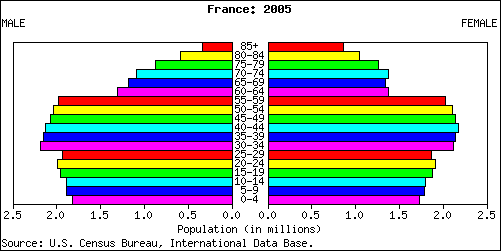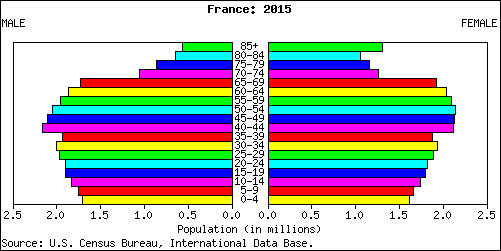
The French population is 63.8 million today and was 63 million people (2010) and is subject to aging because today the TFR is 2.0 or two children in a completed family. The aging will occur since 19 percent of their population is under 15 years of age 17 percent of the population is 65 or over. The life expectancy is 82 in the country with women living on average to 85 years old.
In 2010 with 19 percent of the population 15 or under and 17 per cent of the population 65 or older little has changed in two years of economic recession.
With less than 68 percent of the population in the reproductive years, the total fertility rate of 2.0 means that women in France on average are only replacing the present population. We call that zero population growth or replacement population rate if for thirty more years the number holds (the length of time it takes for today's 15 year old woman to have moved through their reproductive years and to reach 45. Of that reproductive population seventy six percent of the women report using modern methods of contraception, or birth control.
What accounts for family size?
![]()
Family planning
"the right of couples to determine the timing and number of children they would bear."
Natural rights versus legal bans?
"gaining the right for people, especially women, to control their reproduction was the principal motive of the family planning movement."
p. 144.
"Nonetheless, we should always remember that correlation does not necessarily indicate causation."
p. 145.
"Much of the struggle for the right to family limitation has been carried out in the United States, where the last state law against provision of birth control information and materials was struck down in 1962.
Since the, conservative anti-abortion groups have attempted, with some success, to establish state laws hat hinder access to abortion...."
p. 145.
![]()
Rule of 70 / 72, is actually the rule of seventy-two.
rate divided by seventy (or seventy-two) equals the time for any amount to double in size
- 7% growth rate doubles in a decade, 10 years
- 2% growth rate doubles in 35 years
- 1% growth rate doubles in 70 years (seventy two actually is more accurate)
Two means to measure
Unrefined population figures:
- birthrate
- minus
- death rate
- equals
- natural increase (The rate at which a population grows.)
p. 149.
Refined population figures
Average number of children born to a woman in her lifetime is the cohort fertility rate.
The reproductive success of live births per woman of childbearing age is the total fertility rate, TFR and it is the best predictor of future natural increase.
![]()
- Population is the key cause of environmental degradation where culture and behavior conspire to diminish the role and status of women.
- Without some form of fertility suppression the tendency of disease, famine, war, or behavioral abnormalities will encourage an eventual decrease in numbers.
- No population grows forever without a decrease in numbers.
- The global human population outpaced the planet's ability to sustain each member adequately between 1970 & 1990 according to demographic data.
- The ability of any population to outpace the carrying capacity of a surrounding environment leads to:
- migration
- partitioning of resources
- expansion of the resource-base
- depletion of the assimilative capacity of the land, air & water to sustain growth.
- Impact is a synergy among three or more factors.
![]()
Darwin's decisive contributions.
![]()
Mayr | Thomas | Wilson | Hardin | Darwin | Margulis | Steingraber | Carr | Keller | Watson