A visual annotated
index for sciences
A visual annotated
index for sciencesNavigating this site:
return to previously viewed page
Science–in English usage is a very narrowly defined word–as opposed to the broad body of information implied by the German and French use of the word has three meanings: a corpus, a means, a doing.
Search here to browse this site
LoadingBlackholes | Themes | Science as a way of knowing | How to know | Doing something with knowledge | Body of knowledge | Ecology | Lessons
In doing experiments scientist's findings can be challenged and, inevitably, what we currently know may change.
Defining science is not quite as simple as the word may suggest, because different cultures have classified knowledge in divergent ways.
Discovering you are wrong! | What is here? | describing science | Subjects | means to know | Doing things | Alphabetical list | Ecology | Seven lessons | graduate books | primary source
Return to Feynman | Go to Gell-Mann | go to Einstein | Karen Horney: personal growth | unseen genome | Uncertainty as a guide |
Kip Thorne, Cal Tech theoretical physicist has written that "In the decades since 1967, some things we thought were sure have been proven wrong. (For example we could never have believed in 1967 that a black hole can evaporate.) This has taught us caution."
A black hole–predicted by general relativity theory–is the result of a far more massive star than our sun after it collapses and the gravitational forces are so great that light cannot escape the gravity field. Even at 186,000 miles per second the speed of light is less than the "escape velocity" needed to break free of the collapsed star.
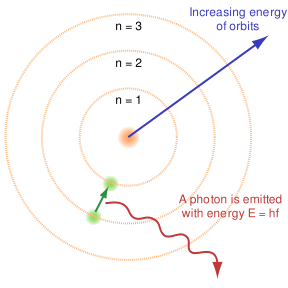
As Stephen Hawking explains "Radiation from black holes was the first example of a prediction that depended on both great theories of this century, general relativity and quantum mechanics."
Here is a broad thematic index to important places on this site for discussing science.
Apparent motion of the planets in time-lapsed photography, from the earth.
Earth as if it were the central feature of the universe.
Science is a means of knowing the world systematically.
Caveat:
Defining science is difficult:
"The French and German triads that correspond to our plain English 'natural sciences, social sciences, and humanities', are 'les sciences natruelle, les sciences sociales, et les sciences humaines' and 'die Naturwissenschaften, die Sozialwissenschaften, und die Geisteswissenschaften.' In both the term for studies of poetry, language and philosophy–studies that are humanistic and decidedly literary in form–includes a 'science' word.
The point is that the foreigners have gotten it right. 'Literary criticism is a science' or 'Economics is a science' should not be the fighting words they are in English. The fighting lacks point because, as our friends across the water could have told us, nothing important depends on its outcome. Indeed, science is a collection of literary forms, Not a Science. And literary forms are scientific."
Deirdre N. McCloskey, The Rhetoric of Economics. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1998 (2d ed.) [1985]. p. 21.
Science | nature | ecology | lessons | scientific related topics | technology | additional material

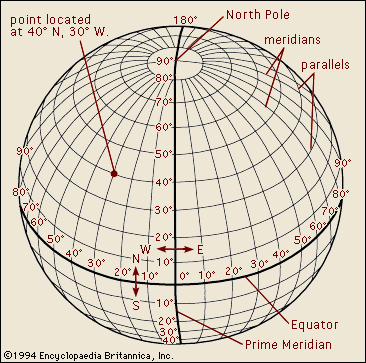
How to know: This is the Greek concept of epistemology, the study of how we know things.
Science is a means of knowing systematically with some certainty, so how we know is as crucial as what we know.
How we know something is called a method:
Methods: these are two related pages that discuss, examine in some detail and diagram the means we have from distinguishing facts from opinions. See also certainty, science, and vocabulary.
Model here is a schematic diagram of ecological relationships in any place.
method, Scientists commenting on the means they use to understand nature
Doing something with what we discover:
Science as related to technology
Technology is discussed and examined as the means we have to solve the apparent difference between an existing and a desired state of affairs or conditions.
Technology is defined here as the application of knowledge to human affairs.
Atomic What are atoms, nuclear fusion, neutron decay, fission and the bombs?
Biological diversity explained in detail.
biological game of life is a very different view of nature.
Biogeochemical Cycles, Biological, geological and chemical cycling of nutrients for growth.
Bohr model of the atom.
Bronowski on Science and human values.
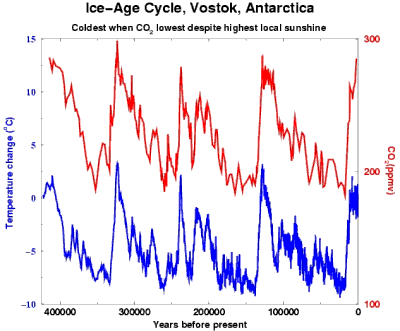
Climate change, a guide to pages related to global warming, the issue examined and discussed.
Complexity of nature and the biosphere
Darwin, On the Origin of Species, (1859)
Diversity of Life, E. O. Wilson
Einstein's thoughts about research and society
Evolution was Charles Darwin's revolutionary proof of common descent by means of natural selection.
Evolution, what is it?
Feedback is defined and examples of how it is used in these pages is explained.
Five dimensions, not three?
see below for lessons:

Science | nature | ecology | scientific related topics | technology | Genes

Frequently asked questions, about climate change
IPCC's Fourth Assessment findings
Genes: visualizing chromosomes and cell nuclei.
Genetics, the history of in brief.
Genetic resistance to disease, an example.
Genetics: genotype differs from phenotype.
Genome, highlights of traits from across the chromosomes.
Hawking's theories, Stephen Hawking.
Universe in a Nutshell, Stephen Hawking.
Lewontin, The Triple Helix.
Living Downstream, an ecologist looks at cancer.
Mayr, Ernst, One Long Argument.
Mayr on species.
Mayr's diagram of Darwin's theories
Margulis, Symbiotic Planet.
Corals are symbiotic creatures
Medicinal values of plants, an example.
Miller, G. Tyler on ecosystems.
Ockham's Razor, the importance of avoiding pleonasm in your writing!
On the Origin of Species, by Charles Darwin, (1859)
Darwin's study at Down House.
Plutonium and its use.
Scientific method, three necessary features of
Scientists commenting on the method
Water and energy as twin necessities.
Science | nature | ecology | scientific related topics | technology
Ecological biotic community: examined and defined
Ecological subjects connected at this location; three laws
Ecology, definition, examples, commentary and links
Ecology used as a model of relations among integrated parts
Energy as an ecological concept
Ehrlich and Ehrlich - The Dominant Animal
Hardin, ecology as a synthetic science
Carolyn Merchant's idea of ecological revolutions.
Total fertility rates in the world
The Great Thirst -- California water and growth
keys to analyzing ecological problems
Keystone species by habitats

Science sources.
lesson one: on the meaning and confusion of terms.
lesson two: means of knowing the enveloping mystery.
lesson three: revealing the order in the mystery.
lesson four: The body of knowledge about this mystery.
lesson five: the planet Earth is on the verge of exhaustion.
lesson six: understanding symbiosis and coevolution.
lesson seven: expressing worldviews in writing from texts.
The intrinsic value of character and the importance of the life we are protecting
Museums and Library sources for research
Annotated index of science subjects – is Science Added index
Visual index to of science subjects
Science subjects
new to the sight

Terms | Glossary | Word webs | Basic vocabulary | Advanced Vocabulary | Antonyms | Synonyms

Science | nature | ecology | scientific related topics | technology
Science revolutions index | added material index | Science index
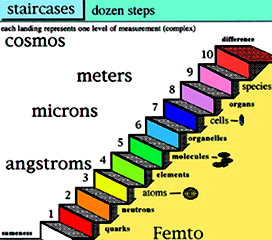
.gif)