Science
findings and Policy advocacy in the current Atomic Age: The necessary relation among minerals, vegetals, & animals lies in small proteins.
The relation among animals, vegetals, & minerals necessarily lies in small proteins.
Several recent abstracts of findings on the roles of calcium carbonate, microtubules in cells.
"Microtubules are conveyer belts inside the cells. They move vesicles, granules, organelles like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are linear polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein."
Gwen Childs, Ph.D.
The hidden importance of?
See also: Nature: Microtubules and Filaments.
Discovering the structure: "Mystery of Vital Cell Protein Solved After 30 Years." Lynn Yarris, January 8, 1998.
"What are the functions of microtubules?" October 2014.
Microtubule functions.
Abstract
Microtubules, with intermediate filaments and microfilaments, are the components of the cell skeleton which determinates the shape of a cell. Microtubules are involved in different functions including the assembly of mitotic spindle, in dividing cells, or axon extension, in neurons.
In the first case, microtubules are highly dynamic, while in the second case microtubules are quite stable, suggesting that microtubule with different physical properties (stability) are involved in different functions. Thus, to understand the mechanisms of microtubule functions it is very important to understand microtubule dynamics.
- Historically, tubulin, the main component of microtubules, was first characterized as the major component of the mitotic spindle that binds to colchicine.
- Afterwards, it was found that tubulin is particularly more abundant in brain than in other tissues. Therefore, the roles of microtubules in mitosis, and in neurons, have been more extensively analyzed and, in this review, these roles will be discussed.
Microtubules
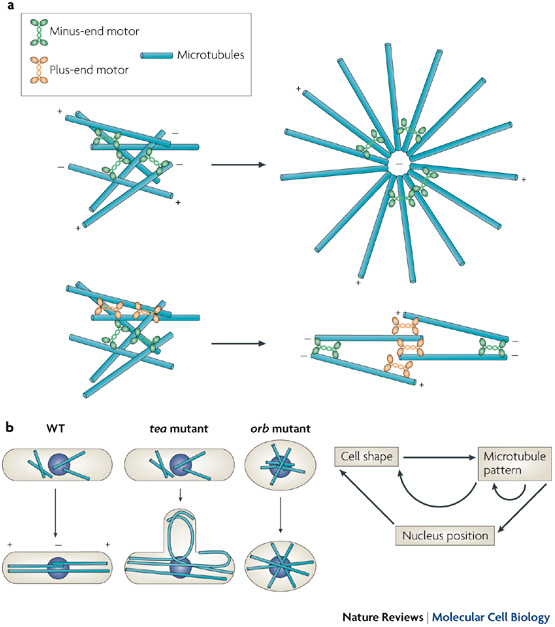
US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
Tubulin synthesis and assembly in differentiating neurons.
Abstract
Neurons are highly polarized cells that extend long processes, the axons and dendrites, to form contacts with target cells. The formation and maintenance of this specialized morphology relies on the assembly of an organized microtubule array that is the predominant component of the neuronal cytoskeleton.
• During this process there is an evolution in the composition and dynamics of microtubules, resulting in stable microtubule bundles that provide structural support and function in intracellular transport along the axon. In this essay we provide an overview of the mechanisms regulating the synthesis and assembly of tubulin in differentiating neurons with particular attention to the roles of multiple tubulin isotypes, posttranslational modifications of tubulin, and microtubule-associated proteins.
√ We conclude that, ultimately, the developmental regulation of microtubules in neurons may require the coordinated expression and posttranslational modifications of tubulin and microtubule-associated proteins to provide biochemical forms that favour specific interactions, each combination conferring distinctive dynamic and functional properties.
one | graphical depiction | two | three | four | question | fifth | sixth | wealth | 3-Ds of impacts | design
The microtubule network and neuronal morphogenesis: Dynamic and coordinated orchestration through multiple players.
Abstract
Nervous system function and plasticity rely on the complex architecture of neuronal networks elaborated during development, when neurons acquire their specific and complex shape. During neuronal morphogenesis, the formation and outgrowth of functionally and structurally distinct axons and dendrites require a coordinated and dynamic reorganization of the microtubule cytoskeleton involving numerous regulators.
While most of these factors act directly on microtubules to stabilize them or promote their assembly, depolymerization or fragmentation, others are now emerging as essential regulators of neuronal differentiation by controlling tubulin availability and modulating microtubule dynamics.
In this review, we recapitulate how the microtubule network is actively regulated during the successive phases of neuronal morphogenesis, and what are the specific roles of the various microtubule-regulating proteins in that process. We then describe the specific signaling pathways and inter-regulations that coordinate the different activities of these proteins to sustain neuronal development in response to environmental cues.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- PMID:
- 19660553
- [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
From signaling pathways to microtubule dynamics: the key players.
Abstract
Microtubules are highly dynamic structures whose regulation is crucial for cell division, cell polarity, cell migration, or neuronal differentiation. Because they contribute to most cellular functions, they must be regulated in response to extracellular and intracellular signals.
The parameters of microtubule dynamics are numerous and complex and the connection between signaling pathways and regulation of microtubule dynamics remain obscure.
Recent observations reveal key players that can both integrate the diversity of signaling cascades and directly influence microtubule dynamics. I review here how modifications of the tubulin dimer, tubulin modifying enzymes, and microtubule-associated proteins are directly involved in the regulation of microtubule behavior and functions.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
- PMID:
- 20031384
- [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Microtubules: functional polymorphisms of tubulin and associated proteins (structural and motor MAP's).
[Article in French]
Abstract
In neuronal cells, microtubules are built from a very large number of alpha- and beta-tubulin variants. This diversity is due to the expression of a multigene family and to a combination of several original posttranslational modifications. Similarly, structural and motor microtubule-associated proteins, which regulate the assembly of microtubules, the modeling of their network and the mediation of their functions, are also very heterogeneous.
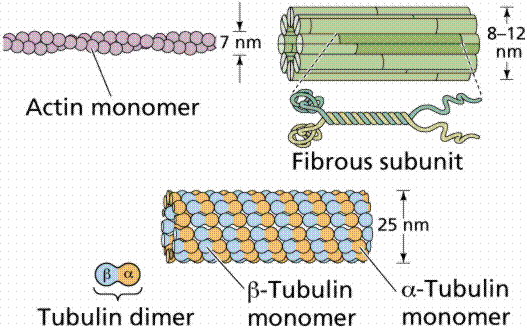
As a consequence, mixing of these two protein polymorphisms leads to the formation of functionally-distinct microtubules. We have shown that polyglutamylation, the major posttranslational modification of neuronal tubulin, was used as a progressive regulator in the binding of structural and motor microtubule-associated proteins, in modulating gradually the conformation of the tubulin carboxy-terminal domain, playing thus a crucial role in microtubule dynamics.
-
PMID:
-
8869236
-
[PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004 Dec;7(6):651-60.
Progress in understanding the role of microtubules in plant cells.
Wasteneys, Geoffrey O1. UBC. Author information
Abstract
Microtubules have long been known to play a key role in plant cell morphogenesis, but just how they fulfill this function is unclear. Transverse microtubules have been thought to constrain the movement of cellulose synthase complexes in order to generate transverse microfibrils that are essential for elongation growth. Surprisingly, some recent studies demonstrate that organized cortical microtubules are not essential for maintaining or re-establishing transversely oriented cellulose microfibrils in expanding cells.
• At the same time, however, there is strong evidence that microtubules are intimately associated with cellulose synthesis activity, especially during secondary wall deposition. These apparently conflicting results provide important clues as to what microtubules do at the interface between the cell and its wall.
• I hypothesize that cellulose microfibril length is an important parameter of wall mechanics and suggest ways in which microtubule organization may influence microfibril length. This concept is in line with current evidence that links cellulose synthesis levels and microfibril orientation. Furthermore, in light of new evidence showing that a wide variety of proteins bind to microtubules, I raise the broader question of whether a major function of plant microtubules is in modulating signaling pathways as plants respond to sensory inputs from the environment.
PMID: 15491913 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Mimicry of natural processes is worth careful study:
1. photosynthesis, productivity, and food;
2. cell separation & motility {movement}.
The present inefficient designs are a policy choice; and not a wise choice.
Nature uses carbon in the form of calcium carbonate to master and control cellular shape, communication, and movement.
Questions to consider:
Is work in the community
an opportunity to see design flaws?
What is creativity in
the design of communities?
How do we design with nature
in mind?
What is it we perceive?
When do we have to adjust
our assumptions?
Where do we see good designs?
return to the start of the
lesson.
The sources of wealth are forested slopes, minerals, and water.
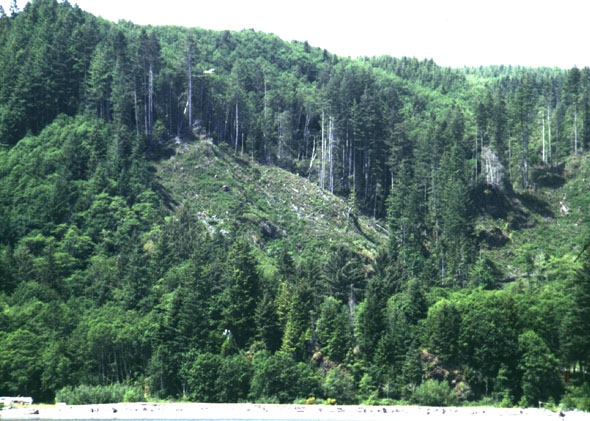


Forests are the largest and most extensive example of the power of plants to produce cellulose; a carbon product of photosynthesis. Pacific Yew trees grow ever so slowly in such "old growth forests" as depicted in this photograph of a clear cut in Oregon & Washington.
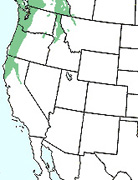 "Interest in tubulin structure heated up intensely in recent years when taxol, a natural substance found in the bark of the Pacific yew tree (The range of the species is indicated on the map [left]; the name "taxol" has been trademarked by Bristol-Myers-Squibb), was shown in clinical tests to be an effective treatment for a number of cancers including ovarian, breast, and lung. Cancer occurs when cell division runs amok."
"Interest in tubulin structure heated up intensely in recent years when taxol, a natural substance found in the bark of the Pacific yew tree (The range of the species is indicated on the map [left]; the name "taxol" has been trademarked by Bristol-Myers-Squibb), was shown in clinical tests to be an effective treatment for a number of cancers including ovarian, breast, and lung. Cancer occurs when cell division runs amok."
U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 1998.
" If tubulin (the subunit of microtubules) is labeled with a dye that fluoresces red, for example, microtubule dynamics can be followed second by second in a living cell. "
See "Visualizing Molecules in Living Cells," Molecular Biology of the Cell.
an enzyme called ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase converts CO2 to sugars in photosynthetic organisms, producing most of the organic matter needed for life on Earth."
See Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition.
Do these design flaws in each individual dwelling mean that the community suffers as a whole from excessive waste of resources?
Yes
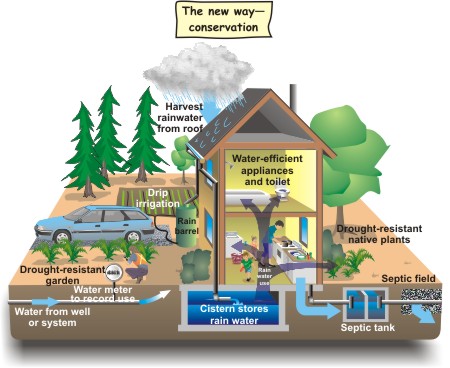
return
to the start of the lesson.
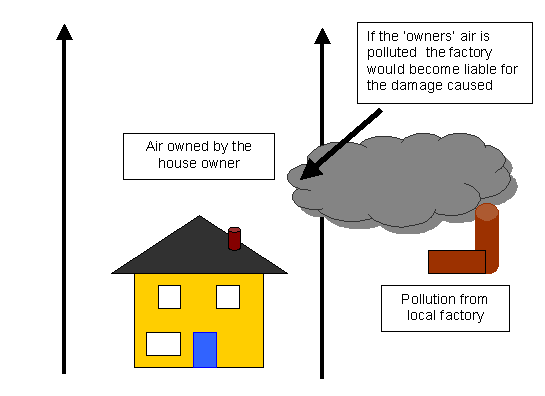
The notion of the individual home, apart form the community is out-of date because of trans-boundary pollution.
What is creativity
in a design?
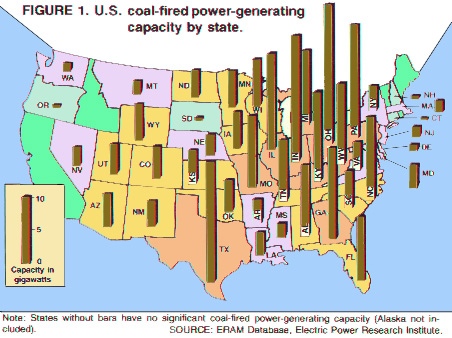
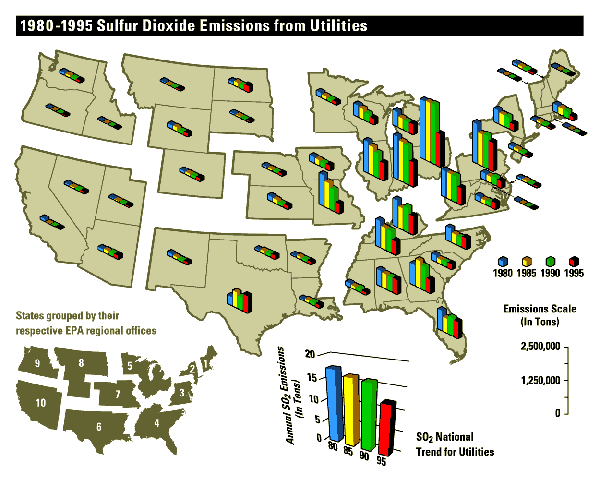
Where there is coal generating electricity, there are SO2 emissions or sulfur dioxide pollution generating acid rain.
A plan by which we can spatially separate
needed functions in society.
| Authors |
Hardin |
Sym Van Der Ryn |
|
What does the plan say? |
discoveries in nature as examples |
|
How do we account for it? |
sunlight, water, vegetation, landscape, aquifers, slopes. |
How do we design with nature in mind and learn from objects in our environs?
Think or do; feel or say?
| Authors |
Hardin |
Sym Van Der Ryn |
|
flaws can teach us what to value. |
Practice compels us to use multidisciplinary
approach to design |
|
|
|
What is it we perceive?
If we do not see it, then does it not still exist?
1. underground water.

Olgallala Aquifer
When do we have to adjust our assumptions?

Permaculture
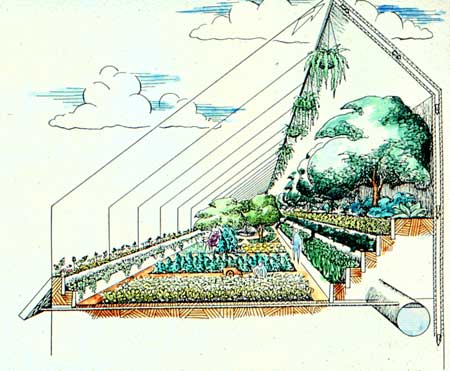
Where do we derive good designs from?
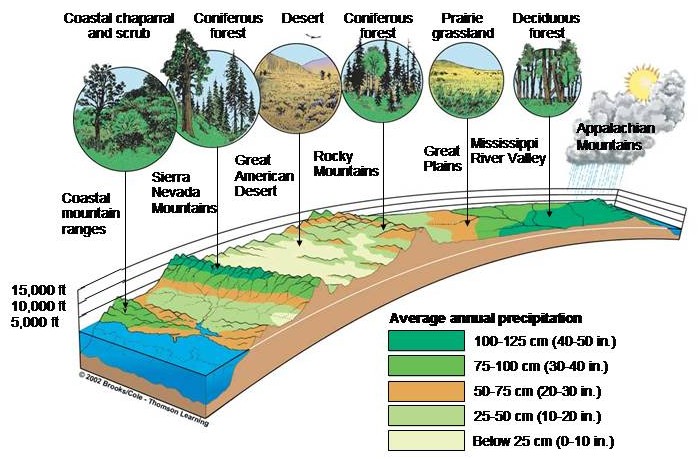 Amerca's biomes in cross-section.
Amerca's biomes in cross-section.
Background:
1985 - ozone depletion, acid rain and climate change; Three huge changes in the human habitation of the Earth
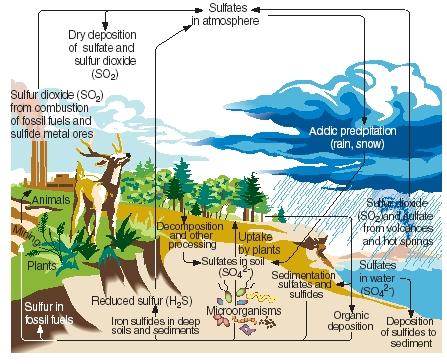 The sulfur cycle is a significant function disrupted by humans that damages natural processes and inhibits the growth of microbes, plants, and fungi.
The sulfur cycle is a significant function disrupted by humans that damages natural processes and inhibits the growth of microbes, plants, and fungi.
1997 - After the Rio Summit (1992) came the Kyoto Protocol agreement
on the United Nation's Framework Convention on Climate Change, UNFCCC; a Treaty to which the US is a party.
Focus:
Ecology is the focus of a synthetic assemblage of multiple disciplines defining particular constraints within which biological diversity persists overcoming challenges to sustain life.
Environmental reistance  versus
versus  biological potential.
biological potential.
A dozen authors to compare their texts to one another and these abstracts:
Terms used on this page defined
Vocabulary
aquifers are water-bearing rock layers beneath teh surface of terrains used for irrigation.
Atomic bomb otherwise known as A-bomb, a fission device using plutonium or radioactive uranium to explode with the power thousand of times greater than dynamite.
cellulose, is a protein that is essential to plant life and we know it as cotton fiber, paper, or wood. Because cellulose is made of many linked sugars, it is technically called a polysaccharide. "Cellulose is a long chain of linked sugar molecules that gives wood its remarkable strength. It is the main component of plant cell walls, and the basic building block for many textiles and for paper." see General Chemistry on-line by Antoine.
dimer is any molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together; such as tubulin.
Ecological Revolution the associated events in thought, social activism, and political reform that altered land, air, & water protection laws and regulations extending traditional conservation concerns to account for pollution, health, and toxic substances. (usually said to have occurred between 1950s-1980s; although the publication in 1962 of Silent Spring is a marker.)
Several new agencies & sub-agencies emerged in the reform period to administer new laws & uncover emerging science:
- CEQ, Council on Environmental Quality as advisors to the President
- EPA, Environmental Protection Agency
- NOAA, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- MMPA, Marine Mammal Protection Act
- EDSTAC, Endocrine Disruptor Screening and Testing Advisory Committee (findings)
- OSHA, Occupational Health and Safety Administration
proteins are a class of nitrogenous organic compounds that consist of large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids and are an essential part of all living organisms, especially found as structural components of body tissues such as muscle, hair, collagen, etc., and as enzymes and antibodies. See: how proteins are related to genes.
tubulin, probably among the most important proteins in well developed cells; cells that are characteristic of all eukaryotic organisms, such as plants, fungi, animals and some well-formed bacteria (called protoctista). Technically speaking the structural capacity of the protein tubulin is due to the fact that tubulin forms "into long chains or filaments that form microtubules, hollow fibers which serve as a skeletal system for living cells." See NCBI of the NIH text.
" Other proteins are used to build structural components, such as tubulin, a protein that self-assembles to make the cell's long microtubules—or histones, proteins that compact the DNA in chromosomes." See Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition.
| Five kingdom system of biological sciences: |
| |
|
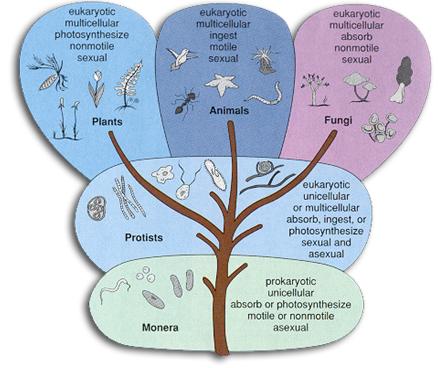 |
Eukaryotic organisms |
The graphic at left depicts the make up these four groups of life on earth:
"plants, fungi, animals and some well-formed bacteria."
They are more complex and possess, among many features, microtubules. |
| |
| Protoctista or Protists |
| |
| Simple microbes or Monera, are not eukaryotic. |
| |
| |
| Diagrammatic display of five kingdoms. |
|
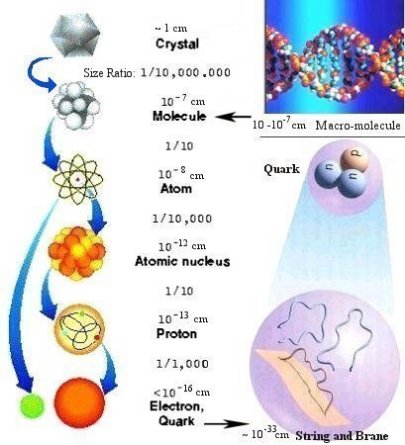
There exist more than six levels of organization in our universe.
Quantum insights in biology | Quantum physical strangeness | Quantum mechanics
schedule | Home | Atlas | site-map | Ecology | laws | quick look
Science
Index | Site
Analysis | Population Index | Global
Warming Index | Nature Index | Research sites.
Terms | Glossary | Word webs | Basic vocabulary | Advanced Vocabulary | Antonyms | Synonyms




 "Interest in tubulin structure heated up intensely in recent years when taxol, a natural substance found in the bark of the Pacific yew tree (The range of the species is indicated on the map [left]; the name "taxol" has been trademarked by Bristol-Myers-Squibb), was shown in clinical tests to be an effective treatment for a number of cancers including ovarian, breast, and lung. Cancer occurs when cell division runs amok."
"Interest in tubulin structure heated up intensely in recent years when taxol, a natural substance found in the bark of the Pacific yew tree (The range of the species is indicated on the map [left]; the name "taxol" has been trademarked by Bristol-Myers-Squibb), was shown in clinical tests to be an effective treatment for a number of cancers including ovarian, breast, and lung. Cancer occurs when cell division runs amok." 








 The sulfur cycle is a significant function disrupted by humans that damages natural processes and inhibits the growth of microbes, plants, and fungi.
The sulfur cycle is a significant function disrupted by humans that damages natural processes and inhibits the growth of microbes, plants, and fungi.

