| laws
of nature |
Natural
law |
|
|
Laws
of Ecology
WEAL
Value
Worth of trees
& forests. |
is
an Ancient and Medieval ideal to guide our behavior.
There is a hint in the origins of this word and the descendant words about what European valued.
Ways to comprehend the importance of timber and forested lands |
| Ecological
design. |
This
view of the lower Colorado River valley is an example of the tension between
human designs based on economic demands and the natural dictates of the
organic arrangements of rivers and floods. |
Three laws
Three Laws
of Ecology:
Connectivity
- you may never merely do one thing. (entanglement)
Conservation
- everything must go somewhere. (persistence)
Nature
knows how - there is no free lunch. (indifference)
Basic ecological terms

Interpreting
nature as one approach to natural law.
How ought we to think
about nature as to better express the complexity of a forest?
As the source of wealth,
from the German word for forest "WALD" is derived the English
word "WEAL" meaning woods, or forest. The weald is the name for a particular English forest but it derives
from the old English word meaning a forested area.
Water, energy, air and land contribute to the "revolving fund of life" that
is manifest in any forested landscape.
- Since trees are the
source of primary productivity in a forest taking sunlight, water and carbon
dioxide to make oxygen, all forests are carbon sinks.
- Trees also pump water
from the land and hold the soil to store water for rivers and springs.
- By shading the countryside,
forests lower the temperature and trees cool structures that they cover.
- Forests provide habitat
for plants, called epiphytes, and animals to live, hunt, nurse, or reproduce
- Vegetated land retards
erosion that would otherwise destroy fisheries in lakes or streams.
- Forests are a source
of timber and grazing land for herd animals or game animals.
- Forests are often a
symbiotic relationship of trees, root fungus and lichens.
The
Weald
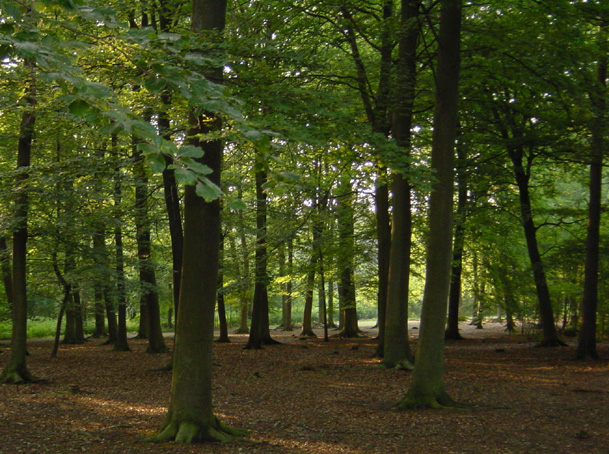

A
section of the English forest called the Weald.
What are the
values of nature?
Scientific or ecological,
utilitarian, aesthetic, historic places, cultural identity, intrinsic qualities
all inhere in natural areas; so these are called the values of natural areas.
They are derived from the laws of nature.
- ecological,
functionally necessary parts of the earth, sea, and sky in any locale.
- utilitarian,
the greatest use for the largest number of people of the natural resources
in a place.
- aesthetic,
the beautiful or stimulating sensory features of any terrain.
- historic
places, the commemorative, or memorialized events that took place in
a site.
- cultural
identity, rituals, observances, or requisite behaviors that natural
places evoke in people.
- intrinsic qualities,
such as dry wind, liquid water, radiation from sunlight; found in any setting.
That means inherent
or intrinsic to all places, terrain, locations, or areas are a variety of human
values. These six complementary or competing values are very different and can
be antagonistic to one another depending on the features and elements in any
geographical setting.
For example not all scientific
values are ecological in that mining for uranium may be scientific, but the
waste generated may harm ecological processes.
Natural Law is
not synonymous with laws of nature, but they are related in that both refer
to the organic relations as useful to explain either our duties, in the case
of Natural Law, or our limitations in the case of the three
laws of ecology as examples of laws of nature.
A law of nature,
for example, is gravitational attraction that causes rivers to flow
from high sources to low basins and as they do they meander, or shift also
from one side or bank to another.
Natural law, on
the other hand is a belief that humans share a divine reason with their creator
and that human life is endowed with inalienable rights. From such rights Franklin
Roosevelt articulated the four freedoms during the Second World War; the freedom
to live freely, worship without fear, freedom from want, and freedom from
disease or ill health.
There
are two dialectically different approaches to valuing natural objects:
Both
from utilitarian (calculable or measurable) and ecological perspectives forests
serve a worthwhile purpose.
Studies
show that trees are so valuable that each one
contributes $225 worth of ecological services in
terms of:
Only
the last of these six complementary values has a market
price determining the economic value
of the tree, yet the other five ecological services performed by trees have
little or no monetary worth.

Related
discussions of forests:
Forest
ecology
Forests
and civilization
Lessons
from a walk in the woods
Wildlife
and forests
Wildlife
and the public trust
Antilles
forests of the Americas.
Ancient
word for forests reveals their wealth.
National
Forests and Parks are often unhappy neighbors.
The
Olympic National Forest surrounds the Olympic National Park.
Suppose
that you are a member of a technical advisory committee to determine the
fate of a forest?

Ecology
| Models | Forests | Externalities | Symbiosis | Margulis | Thomas | Site
map | USA map
Natural Capital
| Accounting for natural assets | Worth of ecosystem services
Ehrlich & Ehlich on outmoded beliefs




