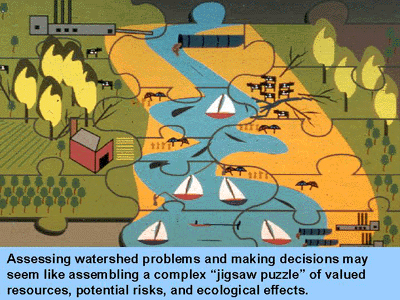
Changes in ecological conditions
Changes in ecological conditionsNavigating the site:
How can we know if the earth's life support systems are functioning well, or poorly?
Ecology is a synthetic science | true ecology is not a subset | ecological science defines limitations
Ecological Literacy is ecolacy | ecolacy forms a related web
Three facets of ecological problems | What is ecological change? | Selection | Labor | Example |
Monitoring change | Biota | Nature
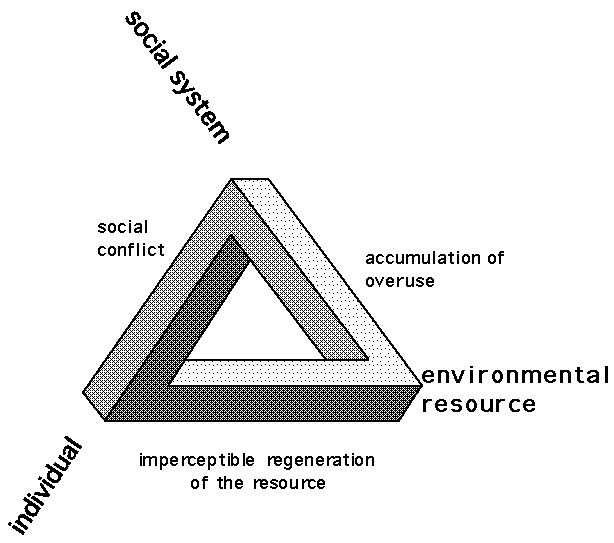
Human problems appear in many shapes and possess a depth of different influences but many have ecological origins and consequences.
Three facets of ecological problems are always:
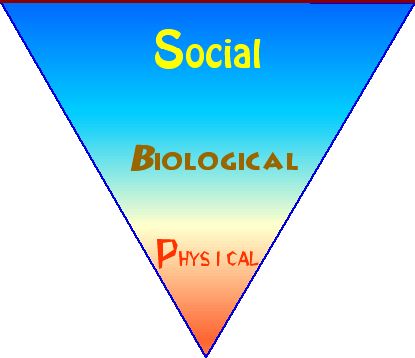
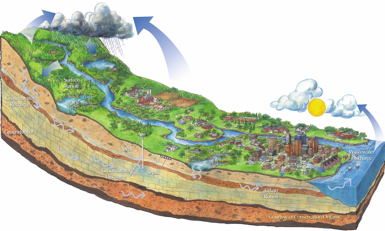
Ecological Change can be seen and understood as alterations in the physical, biological and consequentially the social relationships existing at any time among these three different, but related components of the labor theory of value:
The above categories of land, labor and wealth – or three components of the labor theory of value – are related because John Locke, among several others, believed that the time it takes to produce something determines its value, worth or true contributions to wealth.
A real Arbiter of Value:
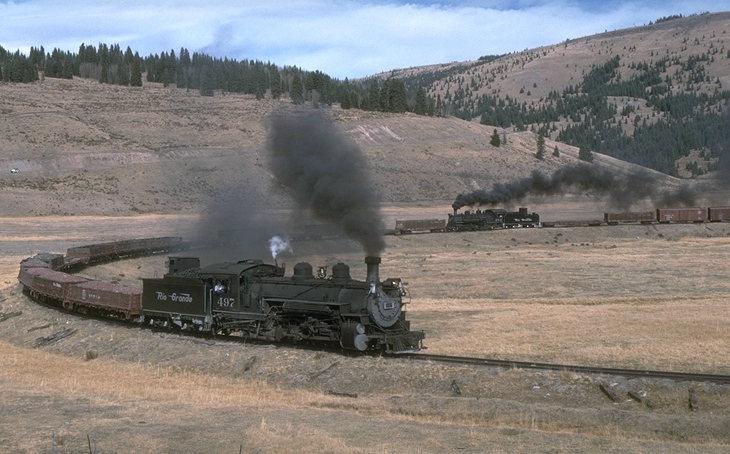
the steam engine changed everything, even how we think.
The steam engine reversed the importance of land and labor after its introduction.
The time it took to do something was no longer a single measure of value or the worth of anything. Instead the costs of resources, especially energy and waste heat became important measures of efficiency. Even the definition of what constituted resources had changed by the introduction of and dependence upon steam engines.
physical | biological | social
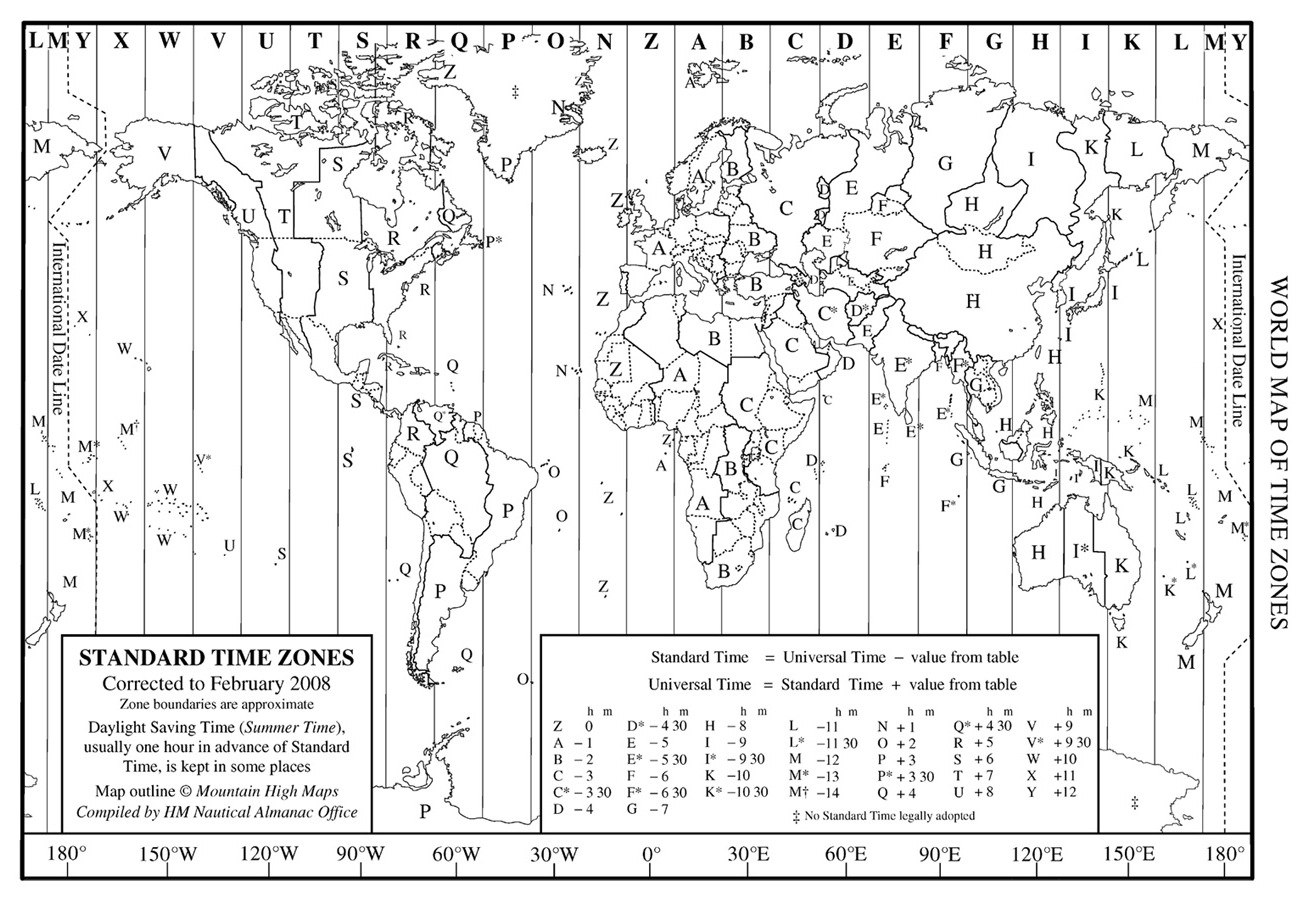
Physically: the time zones were standardized and distances seemed closer.
The proximity of location & water became commercial necessities as were terrains with gently rising slopes for railways to get over mountains and around obstacles. New resources were constructed out of materials such as iron ore, coal, and oil that were before considered mere accessories to living. Reservoirs of water were a need thus flooding some formerly open valleys.
Electricity was needed to operate telegraph lines that alerted the existence and arrival of oncoming trains.
Biologically: New uses for forests as timber or as fuel and construction material raised the price of some land. Railroad freight transportation created the ability of cattle grazing and fruit growing to spread due to access to markets and refrigeration of fruits and vegetables.
Socially: Railroads created new population centers drove the price of real estate up in areas of settlement and down in areas far from the rail junctions and stations. New industrial jobs and a variety of clerical, communication, and managerial positions came into existence. Artists reflected a shift in observation due to speeding trains.
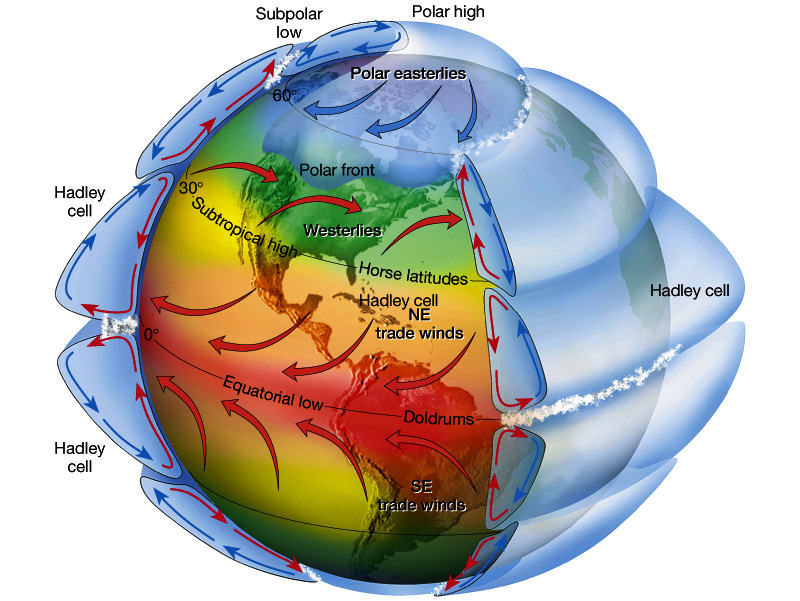
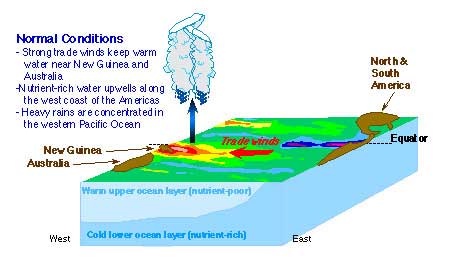
The Southern Ocean Oscillation, called alternately the El Niño / La Nina conditions, affect societies from Australia and Indonesia to Ecuador and Peru.
Three facets of ecological problems
physical | biological | social
What is ecological change? | Selection | Labor | Example | Monitoring change
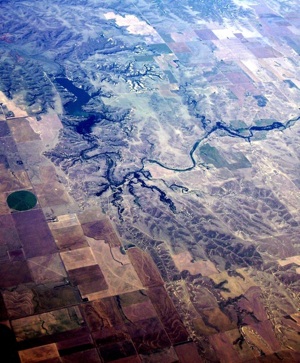
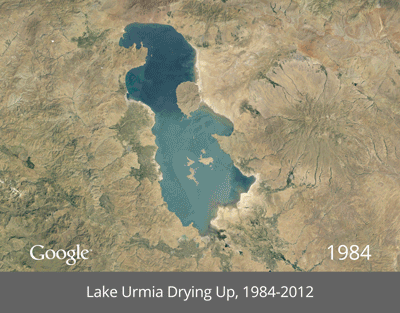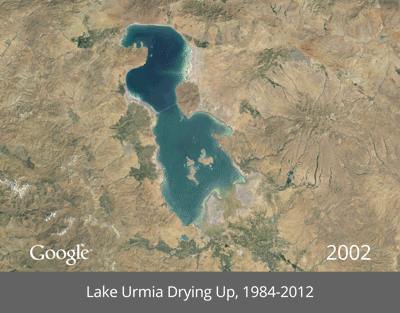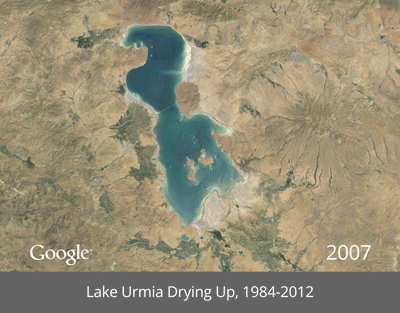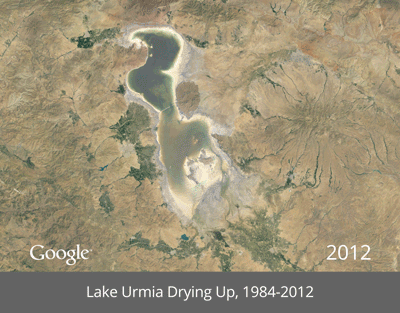
The loss of glacial cover will mean long-term changes for ecological communities worldwide.
Long term ecological change is monitored at 26 sites in North America and Antarctica as part of a scientific effort to generate baseline data against which to measure field responses to conditions.
Rules or laws of ecology | Sources | Solving ecological problems
The Long Term Ecological Research Network, LTER, at – http://www.lternet.edu/sites/
The Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) Network was created by the National Science Foundation (NSF) in 1980 to conduct research on ecological issues that can last decades and span huge geographical areas including sites that "encompass diverse ecosystems."
For example coastal California, Florida and the Chesapeake Bay, in addition to mountain forests or grassland steppes, are examples of some of the sites for which good evidence exists to see changes in productivity, populations and turn-over of soil and vegetational nutrients.
The California Current System (CCS) is a coastal up welling
biome, as found along the eastern margins of all major ocean basins. These are among the most productive coastal ecosystems in the world ocean. The CCS sustains active fisheries for a variety of finfish and marine invertebrates, modulates weather patterns and the hydrologic cycle of much of the western United States, and plays a vital role in the economy of myriad coastal communities.
The Santa Barbara Coastal LTER is located in the coastal zone of southern California near Santa Barbara. It is bounded by the steep east-west trending Santa Ynez Mountains and coastal plain to the north and the unique
Northern Channel Islands archipelago to the south. Point Conception, where the coast of California returns to a north to south orientation, lies at the western boundary, and the Santa Clara River marks its eastern edge. The site lies on the active boundary of the Pacific Oceanic Plate and the North American Continental Plate. High levels of tectonic activity have created dramatic elevation gradients in both the terrestrial and the underwater landscapes of the site. The Santa Barbara Channel includes some of the deepest ocean basins known on the continental shelf along with remarkable submarine canyons and escarpments.
Research activities of the Eastern Shore of Virginia's VCR/LTER focus on the mosaic of transitions and steady-state systems that comprise the barrier-island/lagoon/mainland landscape of the Eastern Shore of Virginia. Primary study sites are located on Hog Island, Parramore Island and mainland marshes near Nassawadox VA. The VCR/LTER maintains a laboratory facility in Oyster, VA.
The Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest (HBEF)
is a 3,160 hectare reserve located in the White Mountain National Forest, near Woodstock, New Hampshire. The on-site research program is dedicated to the long-term study of forest and associated aquatic ecosystems.
The majority of Florida Coastal Everglades LTER sites are located in freshwater marsh, estuarine mangroves, sea grass estuary ecosystems in Everglades National
Park. As the major source of water for millions of south Florida residents, Everglades National Park covers approximately4300 square kilometers of south Florida and is part of the greater Everglades ecosystem which extends north to Lake Okeechobee and the Kissimmee River. Research Our research focuses on understanding ecosystem processes along the two major drainage basins in Everglades National Park: Shark River Slough and Taylor Slough. We are particularly interested in the dynamics at the estuarine ecotone, where freshwater and estuarine wetlands meet. This ecotone is dynamic in the landscape in response to changing freshwater inflow (with Everglades restoration), sea level rise (climate change responses), and disturbance (particularly hurricanes and fire). This represents the third largest wilderness area in the lower 48 states.
Our SGS site encompasses a large portion of the Colorado Piedmont Section of the western Great Plains. The extent is defined as the boundaries of the Central Plains Experimental Range (CPER),which is
managed by the Agricultural Research Service (ARS), and the Pawnee National Grassland (PNG), which is managed by the US Forest Service. Expansion into the PNG has allowed us to explore the biotic interactions of the SGS ecosystem across a range of climatic, geologic, topographic and land use conditions. The CPER has a single ownership and land use (livestock grazing). The PNG is characterized by a mosaic of ownership and land use. Ownership includes federal, state or private and land use consists of livestock grazing or row-crops. There are NGO conservation groups that exert influence over the area, particularly on federal lands. This varied land use and diversity associated with land users and managers substantiates the importance of the sgs-lter to the area.
Three facets of ecological problems
physical | biological | social
What is ecological change? | Selection | Labor | Example | Monitoring change
Garrett Hardin, Filters Against Folly, How to Survive.., New York: Penguin Books, 1987.
E. O. Wilson, Consilience, New York: Vintage Books, 1999.
Charles J. Krebs, The Message of Ecology (1988).
Ehrlich & Ehrlich , The dominant Animal.

.gif)