Navigating the site:
ecological integrity
So what is it?
A capacity to sustain the world as fused in an intricate, but self-renewing manner – with no need of human intervention – while subject to increasing entropy.
An underlying, unimpaired coexistence of forms, functions, and participants inhabiting an area or dwelling in places, that maintain the flows of water, energy, nutrients, air, and trace elements used for shelter, nourishment, and growth based on the quality, quantity, timing, and distribution of essential resources.
Every human has the capacity to imagine how the world is tied together in an intricate, but self-sustaining manner – but has no need of human intervention and may even resist our interference.
An ecological imagination apprehends and understands the underlying integrity of forms, functions, and participants inhabiting an area or coexisting in any place, that sustains the world.
But the further need for such an imagination is necessary in order to protect the natural systems on which life and human society together depend.
- forms–meaning landscape features (forests, ridges, creeks, marshes), topography, sun angle, hydrology & geography,
- functions–such as food webs: producers, consumers and decomposers, and
- participants–bacteria, plants, fungus, animals, communities etc.
- being whole & undivided in its form and functionally unimpaired.
Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of | integrity | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity
Developing an ecological imagination means we learn to see reality coherently in what can be described as a place's ecological integrity because the structure and function of the assembled living organisms are understood as working together to form a functional unit.The effective functioning of the whole nourishes each member according to an elaborate system of interdependent services or feeding relations among all of the participants.
Ecological integrity is understood as a series of interdependent ways of thinking and describing the consistent qualities in the world we observe.
Thus, an imaginative faculty is used for conceptualizing the functionally necessary interplay of physical elements and biological processes that are codependent factors contributing to the nourishing conditions of existence.
Recognizing the unwritten agreement among living, dying, & dead.
In this way material reality is viewed as:1, a process
3, where mind is connected with nature
4, in a coevolving coexistence
5, that has symbiotic advantages.
6, Where cybernetic processes are both positive, "+" & negative ,"-" and both types of responsiveness are necessary!
7, Existing in multiple levels or multiple scales of organization from: molecular to regional scales!
8, In multidimensional (at least five) ways Space-time & Mass-energy are exchanged in an emergent patterns of coexistence.
9, Where the assimilative capacity is composed of the timing, distribution, quantity, & quality of re-shared and reused resources.
10, And that survival of the fortunate prevails since chance or risk plays a critical role in reproduction, fitness, and survival.
Scientifically speaking, ecological integrity rests on empirical observation, optimality theory and the inherent reciprocity of relationships on earth between inorganic and organic features of the ecosystem.
|
|
This Pontederia marsh, a fresh water form of vegetation is an example, below the surface is also a collection of chemical nutrients captured by the plant's organs and made available in the form of sugar and carbohydrates to animals that feed on these flowers, or take refuge among the plant's dense stalks. Pickerel weed is the common name of Pontederia and it is an indicator of a high water quality, fresh-water marsh. |
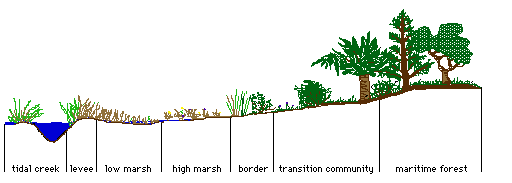
A diagram of the above tidal marsh and the elements that it traps would reveal both the sensory form and the underlying molecular or atomic structure as a functionally interdependent web of relations between the small and large scale.
Laws of ecology | Ten rules of ecology and their relation to humans
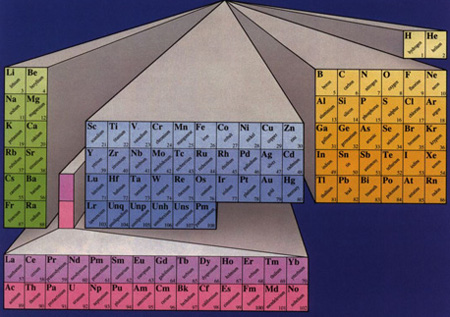
| Building from the molecular to the organism levels of integration every place on Earth represents an ecologically dynamic fabric comprised of geological, biological and chemical strands in a resilient web. Chemical elements that make up compounds are the natural accounting system we use to determine the degree of ecological functionality possessed by all places in differing degrees. |
 |
Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of
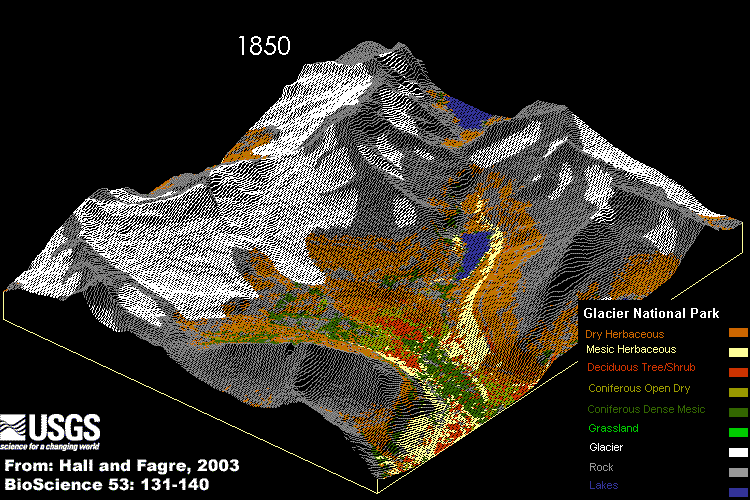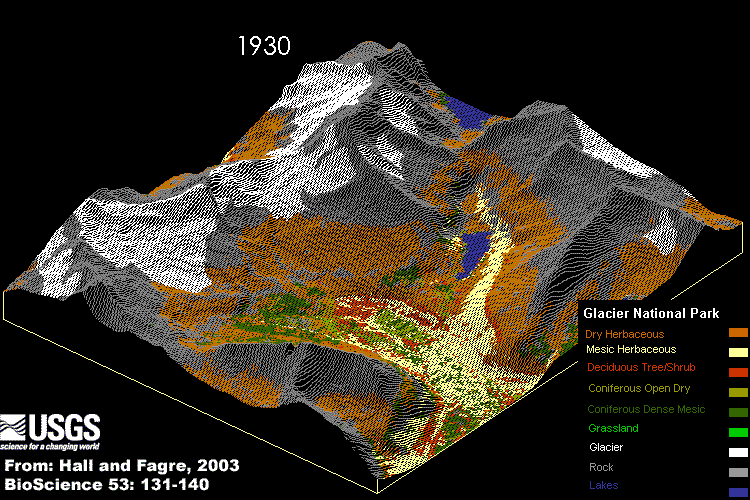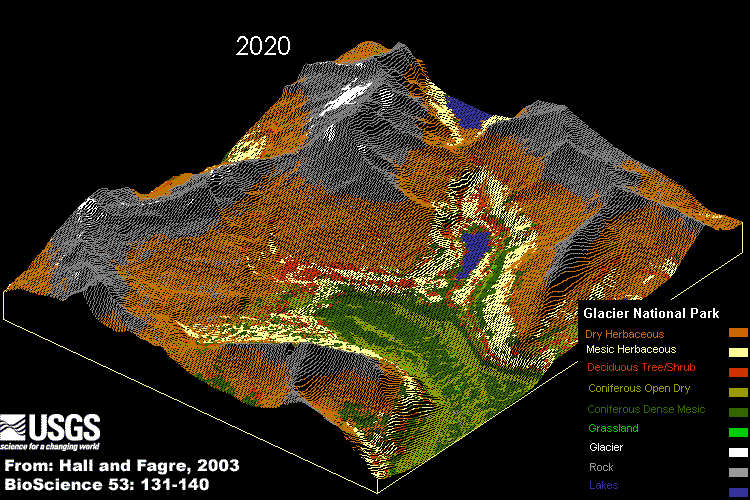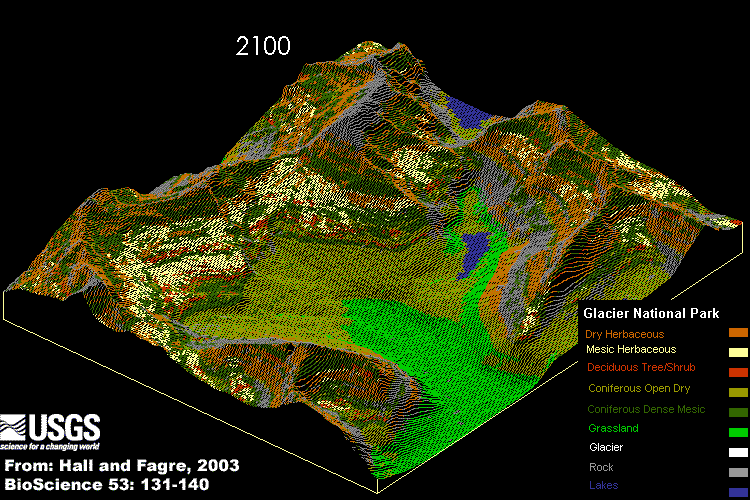
Glacier National Park, valley on the Idaho and Montana boundary:

An Idaho mountain valley's geographical and vegetational relationships are based, in part, on complex links among water, wildlife, fisheries and human recreation. There are Complex relations that contribute to ecological integrity:
Glacier National Park changes from 1850 until today and in the future.The functional and structural necessity of water, sunlight, temperature, climate, chemical nutrient cycles, moderate acidity and alkalinity (or pH), and the geographical access of living creatures to and from adjacent ecosystems. Each link in the chain of being ties each and every creature to the functional necessity of water, energy, air and landscape. This chain of being is no stronger than its weakest links.
Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of | integrity | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity

We are one entity with the inhabited world.

Nature is a problem for humans because we, in our ignorance, avarice, and insecurity, believe we can have something for nothing; cheat the natural system and get away with biocide.
The integrity of ecosystems depends on:quantity
quality
timing
distributionof water, nutrients, trace elements and minerals.
Rubric’s cube of integrated facets, as one changes they all change:
|
W |
E
|
A
|
L
|
|
|
water |
||||
|
energy |
||||
|
air |
||||
|
land |
Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of | integrity | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity
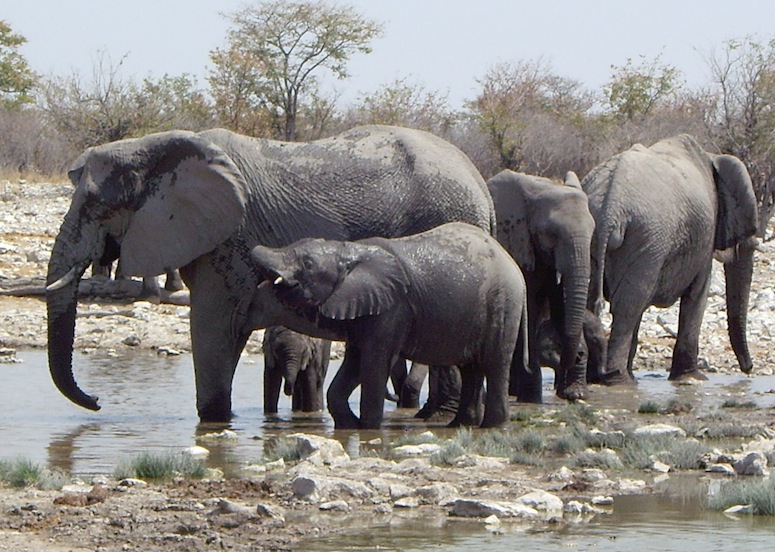
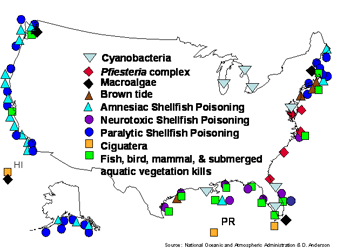
Animals are indicators of ecological conditions.
Elephants at the Goas watering hole on the Etosha Pan, Namibia, Africa.
Canaries in the coal mine analogy.
This metaphor means that animals are indications of damage or destructive situations and their death indicates not just the loss of a species, but the potential degradation of the places they had inhabited.
Bats, moths, mites, mosquitoes -- a simple systemic relationship, pollinators
Birds, 11% face extinction 70% in decline, tied to insects who are pollinators of food crops
Women’s breast cancer
Carson, “Obligation to Endure.”
Murray Bookchin & Rachel Carson 1962.Both writers warned of
chemical & radioactive wastes contaminating our very bodies, genes and fatty tissues.
People born in 1950s & 1960s have:
strontium - in our bones
DDT - in our fat tissues
dioxin - in our tissues
Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of | integrity | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity
Sandra Steingraber, Living Downstream: An Ecologist Looks at Cancer and the Environment (1997)Enzymes | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity
Nuclear tracers can help us understand nature, or they can kill us have we the wisdom to choose between the two alternatives?EDSTAC
Endocrine Disrupting Screening and Testing Advisory Committee, 1998 report (summer: 1998), public response is essential.Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of | integrity | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity
Environmental factors in cancer
genetic factors in cancer
transcription (RNA from DNA)
duplication (DNA replicates)
in enzyme manufacture (shut down cell division, repair DNA sequences, triggers)
oncogenes -- cancer causing viruses, P-53 gene, SRC or “sark” gene when expressed
retroviruses (RNA takes over nuclear DNA)
Genes adapt us to a range of conditions to which we may readily respond.Receptors in the body, cells & tissues alert glands & trigger responses in hormonal secretion.
Levels trigger certain other related responses in glands, organs & metabolism.
Endocrine disrupters are estrogen, androgen and thyroxin mimics (femaleness, maleness, metabolism)
Environmental factors in cancer
“Epidemiological studies .... Comparison of the incidence of various cancers among Japanese citizens, American citizens and Japanese who have emigrated to the United States shows quite convincingly that most cancers are attributable to environmental factors.”
stomach, colon, pancreas, lung, leukemia
1: “most cancers are environmentally caused.”2: “most cancers are preventable”
Gordon Edlin, Human Heredity, (Boston: Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 1990), p.188 - 189
Leukemia deaths among children in southern Utah was two to three times higher than children not exposed to above ground fallout from nuclear bomb tests.
Enzymes are critical to understanding human vulnerability:endonuclease breaks the sugar phosphate backbone of DNA
exonuclease removes damage nitrogen bases (thymine dimers from UV exposure)
polymerase I repairs gaps in the DNA sequence from the opposite strand
DNA ligase rebuilds the sugar-phosphate bonds
“loss of any one of the repair enzymes can be lethal... repair of radiation damage is essential to the survival of cells.”p. 191.
smoking * 20-25% of all deaths in the US attributed to smoking
flame retarding tris-BP
hair dyes (150/169)
burning, incineration
Occupational health risks from carcinogens
Chemical workers Benzidine, bladder
Napthylamine, bladder
glue & varnish Benzene, leukemia (Bone marrow cancer)
PVC manufacture polyvinyl chloride, Liver
Chromate manufacture chrome ores, Bronchus*
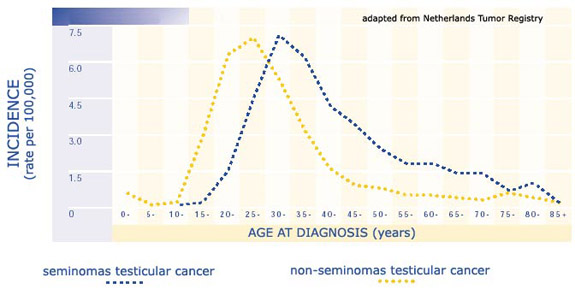
The incidence of testicular cancer.
“Recent experiments have shown that a chemical in cigarette smoke is converted in cells into a chemical that is able to activate certain oncogenes.”
“Somatic-cell mutations trigger the onset of most cancerous diseases. These mutations are caused by environmental agents and, because the affected cells are somatic, the defective genes can not be inherited, However, some rare heritable human disorders may predispose their victims to the development of cancer.”
The measure of disorder or increasing randomness in any system. The loss of order in a system due to the degradation of energy over time.
Second Law of Thermodynamics holds that over time kinetic energy becomes less available to do mechanical work because of a build-up of random motion in atoms and compounds that is measured as an increase in heat.
Sandra Steingraber, Living Downstream: An Ecologist Looks at Cancer and the Environment (1997).
Gordon Edlin, Human Heredity, (Boston: Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 1990), p.188 - 189.
Fritjof Capra, The Web of Life.
Rachel Carson, Silent Spring.
Garrett Hardin, Ecolacy.
David Orr, Ecological Literacy.
Lewis Thomas, The Lives of the Cell.
Terry Tempest Williams, An Unspoken Hunger.
|
|
|

Explanation | Science | Image | Ten facets of | integrity | endocrine disruption | mutagenicity