Rivers
are mirrors
Rivers
are mirrorsNavigating the site:
What can we find along a river?
"A working river never rests." Fraser River, near Kamloops, British Columbia, [JVS, 1988].
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythological values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
|
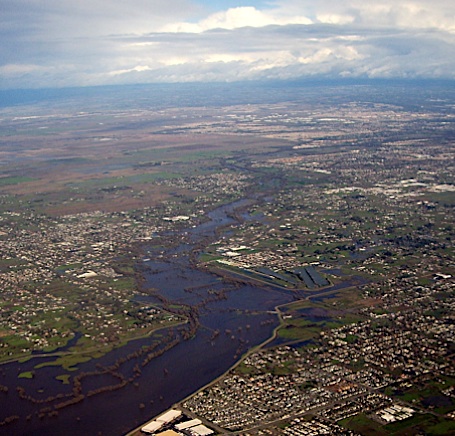
Sacramento
River levee |
Stylized
river valley |
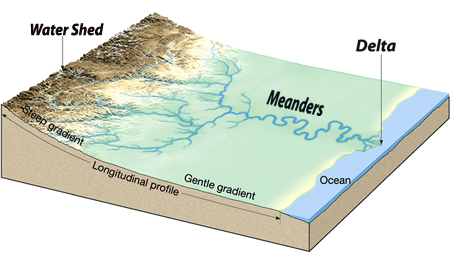
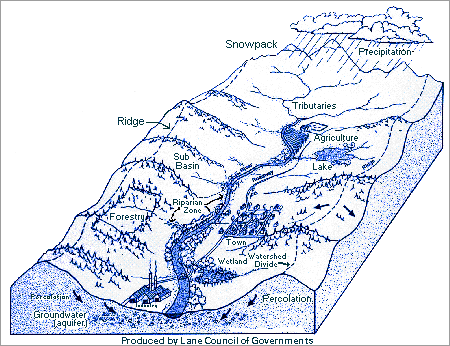
B - basin is characterized by the watershed, slopes, and adjacent bottom lands beside the river -- or riparian areas.
F - flood plain is the lowland or area surrounding rivers and their tributaries that is subject to inundation.
O - oxbow or water body cut off from the main channel by erosion; in Australia a billabong.
S - swamp or overflow land, periodically submerged by rain and flood.
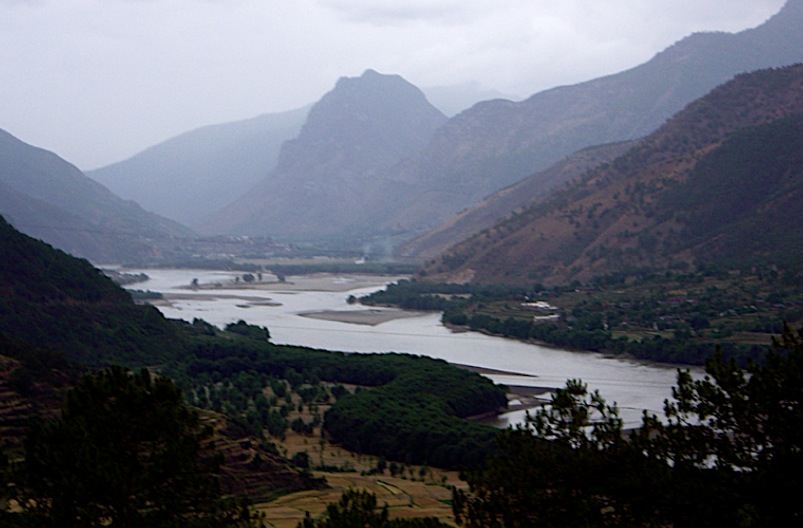
Yangtze River Gorge, Eastern China.
Rivers move silt as well as water and migratory animals.
But the Yangtze River of southern China has moved people, goods and food for commercial purposes for thousands of years. [JVS, 2006].
Siry book on rivers & marshland
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythological values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
To persist right alongside, or beside the stream ; referring to one's proximity to a river system.

- What
do we mean by riparian culture and cultural landscape in the studies
of rivers?
- .
- Many large rivers with yearly flows have their sources in high mountains where the accumulated snow melts and provides a year round source of water that peaks at a season corresponding to the river's flood stage. This is true of the world's greatest river systems: the Nile, Amazon, Yangtze, Hwang Ho, Danube, Rhine, Mississippi - Missouri - Ohio, Tigris, Euphrates, Indus and Ganges. Without snow and perpetual renewal of water provided by ice and glaciers the dependable flow --called stream-flow-- of the river is compromised.
The ecological history of rivers and their flood plains is allegedly the study of people's habits, livelihood, attitudes and inherited prejudices, attributes and customs that asks "How have rivers shaped our evolutionary development and our cultural understanding of natural areas?"
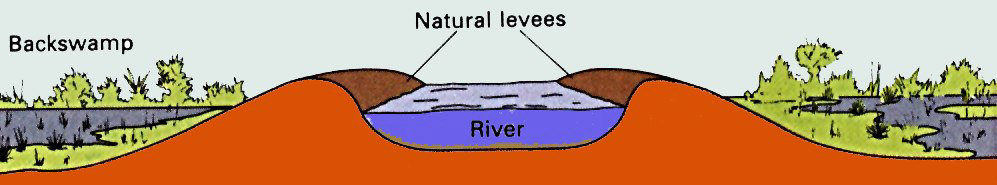
Riparian means stream side, living beside or along a stream or tributary of a river and hence being affected by its currents, flood patterns, and multiple resources. In the photograph of the Sacramento river at flood stage the levees are breached on both sides of the river's banks and most of the flood plain is under water from heavy winter rains, removal of trees and vegetation from forested slopes and ground cover upstream, and from reclamation of the flood plain's many streamside wetlands.
![]()
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
![]()
"What is a river's relation to rivalry?"
If we say it is a number of persons forming competing groups we have to understand that the original rival is the person on the opposite bank of a river:
- 1. Upstream owners: Claimants to sources of wealth.
- 2. Downstream owners: Claimants to residuals of wealth.
A Linguistic approach is impossible to ignore;
"Rivers are more than flowing waters -- draining the uplands on their way to the sea. But "rivers as a riparian ecosystem" muddles the distinctions we need to make between functional and evolutionary units that equally influence the life along the river. That is because animals that use the river, such as beavers, otters, salmon or wading birds depend on a complex food web. A functionally intact river supports fisheries, birds and other animals because the capacity of the river to concentrate and disperse nutrients simultaneously.
Over generations animals adjust to the constraints because to survive they partition the resources that rivers make available. In dry seasons and in flood seasons the extremes condition species that make up the ecological communities. The food webs that these species depend upon adjusts to the quality, quantity, timing and distribution of water, oxygen and trace elements needed by all the populations nourished by the river and its adjacent swamps, floodplain and forests. The more each of these related parts of the river are functioning units the greater ability populations have to adjust to changes in the river over time. The concept here is resiliency, without adjacent wetlands and forests, rivers are less capable of supporting large populations and there exists a greater threat to species whose descendents depend on the river's bounty.
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythological values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
"Rivers
as resources" is a phrase that also ignores the intrinsic, or inherent ways that
landscape  shapes
the watershed laced by rivers and streams and how rivers and streams
bring life to a watershed.
shapes
the watershed laced by rivers and streams and how rivers and streams
bring life to a watershed.
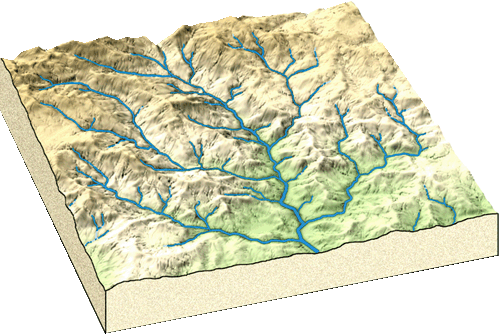
Rivers nourish the land and the rainfall shed across the surface and under the ground feeds the flow of the river. The term watershed , literally refers to the entire terrain onto which flowing water sculpts a basin that drains in to a single river system from innumerable smaller tributary streams. Without underground seepage of rainfall and the surface runoff that comes with snow and precipitation the capacity for vegetation to colonize the landscape is severely limited.
Land of Little Rain, by Mary Austin, 1910.
![]()
The delta of the Nile River was called the Land of Goshen.
 In Egyptian mythology the river is the origin and continuous source of
life, because rising high in the Ethiopian highlands and in the highlands of Lake Victoria, the nile floods annually. Fed by the seasonal monsoons in the African highlands from moisture derived out of the India Ocean, the headwaters of the Nile River flow north and inundate the valley leaving enormous amounts of silt behind. This deposition called alluvium is rich in organic material that replenishes the flood plain where farming is intensely practiced. Here, in the alluvial mud of the Nile Delta, Isis–the ancient goddess–finds the serrated parts of
her lover Osiris' dismembered body. The god must await here gathering all of his body parts and she then reassembles his remains. Isis
breathes life back into the corpse through intercourse.
In Egyptian mythology the river is the origin and continuous source of
life, because rising high in the Ethiopian highlands and in the highlands of Lake Victoria, the nile floods annually. Fed by the seasonal monsoons in the African highlands from moisture derived out of the India Ocean, the headwaters of the Nile River flow north and inundate the valley leaving enormous amounts of silt behind. This deposition called alluvium is rich in organic material that replenishes the flood plain where farming is intensely practiced. Here, in the alluvial mud of the Nile Delta, Isis–the ancient goddess–finds the serrated parts of
her lover Osiris' dismembered body. The god must await here gathering all of his body parts and she then reassembles his remains. Isis
breathes life back into the corpse through intercourse.
In this sense the overflowing river reconnects the fragmented region represented by Osiris scattered remains. Like Isis, rivers tether fragmented landscapes, re-impregnate the dead soil with nourishing trace elements gathered all along the valley and deposit silt all along the levees on down into an awaiting delta or devouring sea.
Hence,
the oldest meaning of the the term river  reveals a profound hope, a bitter
warning, and a commitment to renewal. Often beyond comprehension, people are deeply aware of the river as a nearly immortal power with respect to mortal humans.
reveals a profound hope, a bitter
warning, and a commitment to renewal. Often beyond comprehension, people are deeply aware of the river as a nearly immortal power with respect to mortal humans.
The river literally and figuratively holds for us a promise, in the Bible it is the twin promise of redemption and sustenance, the promise to a desert people that the land is renewed by divine grace.
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
![]()
The historical understanding of the term river in human ecology
1, rivers as the site of settlements: from hamlets to metropolises
2, rivers as sources of agricultural, fishery and wildlife resources (Mitchell, Marsh, Baird, Bache)
3, river as a system of transportation -- 1820s to 1890s (Ellet, Powell)
4, conservation of rivers as watershed (1890s -1930s) relational and place based comprehensive riverine management (McGee, Pinchot, Roosevelt)
5, rivers as a self-organizing microcosm (1910s - 60s) Leopold metaphor of Round River (1940s)
6, rivers as agents of flood control (1920s - 1970s) Floyd Dominy, differences in patterns of flow and change
7, rivers as text ? (1860's to now) Twain, Hemingway, Faulkner, Reisner,
8, rivers as (1970s - present) material nature split into sources, storage and sinks of nutrient exchange, flow and reuse and banks of wild biodiversity
Rivers related to forests? | Luna Leopold on Rivers | Downstream | Round river | Rivers of Empire | Rivers in time
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
What is a river but a flood of stories? To live with a river is to understand that sooner or later a flood develops and the course of the stream changes according the the mass of the water moving over ana area against the friction of the streambed and the opposition of the relative sizes of different materials that the flow has been able to dislodge from upstream and carry downstream with sufficient force.
Evolution or development of a river from youth to maturity implies a geologically significant life span in which watersheds give birth to rivers, the rivers scour a deep bed moving silt and debris, as the river shapes the drainage patterns of the river basin and their adjacent valley floors.
.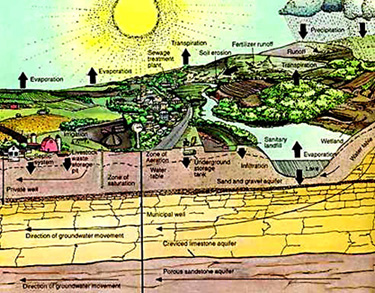

Diagram of a cross section of a watershed contrasted with the Lake Tahoe basin in winter, [JVS, 2003]
The context of the way we use words, phrases and terms is critical to determining the meaning of what we are saying. Watershed is a critically important concept. That is because it embodies the entire topography and underground geology through which water permeates and reinvigorates the terrain we settle, use, or leave alone as refuges.
When using words such as forest, river, or swampland we ought to be aware of the ecological community, by using very precise language. Even as these rice fields suggest, without swampy lowlands, the production of rice –that feeds roughly half the world's people– could never have been developed nor sustained.
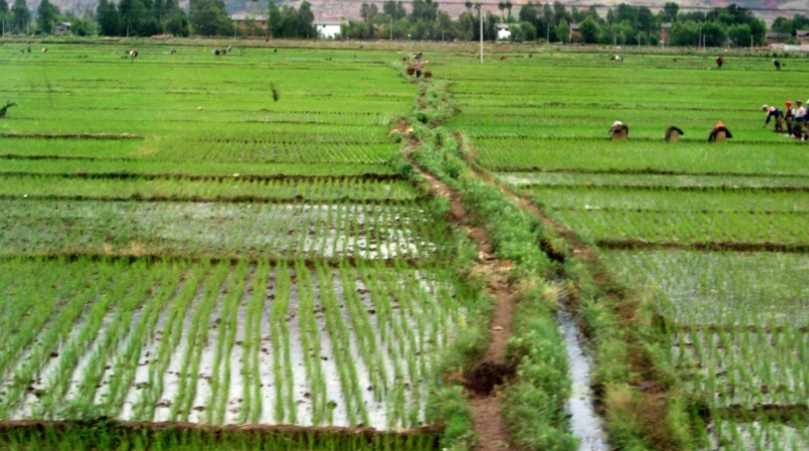 Often, our words do not portray nor do they convey the evidence for the salient and defining features of a system; an ecosystem nourished by a river has special, functionally needed attributes that words can easily obscure. The words we use will become fused in our imaginations with the
very conditions we describe. And if we are not careful, some people will confuse our descriptions with the reality of rivers that run through us, they trickle even through the grains we digest, and filtrate into the lives of all creatures in or far from the reaches of these riparian regions.
Often, our words do not portray nor do they convey the evidence for the salient and defining features of a system; an ecosystem nourished by a river has special, functionally needed attributes that words can easily obscure. The words we use will become fused in our imaginations with the
very conditions we describe. And if we are not careful, some people will confuse our descriptions with the reality of rivers that run through us, they trickle even through the grains we digest, and filtrate into the lives of all creatures in or far from the reaches of these riparian regions.
Rivers related to forests? | Luna Leopold on Rivers | Downstream | Round river | Rivers of Empire | Rivers in time
Lesson: In the development of our language one may discern evidence that reveals the persisting importance
of rivers, forests and wealth to the endurance of civilizations.
Meaning that:
Forests are sources of rivers because as vegetative landscapes they give rise to springs.
Weald is the English word for forested area.
Forests and streams differ for many reasons some physical, others biological and some acquired by the ecological and evolutionary contingencies that they are subject to over the course of the life of the watershed.
| Inherited | Acquired |
| biological | learned |
| instinct | practiced |
Animals living in estuaries, the river mouth or along the river inherit and acquire adaptive means of adjusting to the flow of conditions.
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
Rivers related to forests? | Luna Leopold on Rivers | Downstream | Round river | Rivers of Empire | Rivers in time
Riparian tidal shoreline in cross section, is where water flows in opposite directions:
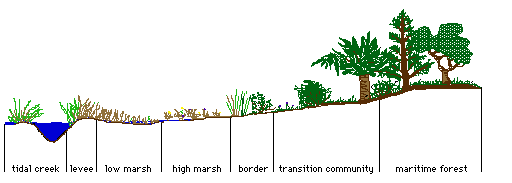 As the river floods or the tide rises the vegetational response to periodic inundation or flooding indicates to what extent and for how long the submerged land remains water logged, limiting the kinds of plants along the shore.
As the river floods or the tide rises the vegetational response to periodic inundation or flooding indicates to what extent and for how long the submerged land remains water logged, limiting the kinds of plants along the shore.
Characteristic plants indicate a riparian zone along the edge of any stream, creek or river. The cross section of this tidally affected creek shows how regular flooding selects for grasses that can tolerate prolonged submergence, although along some rivers shrubs and riparian forests grow.
Estuary, is the name for the mouth of a river where the tidal shoreline is most evident because water flows in two directions each day rising on the flood and falling on the ebb tide.
| The Amazon river forests stand submerged for up to five or six months in thirty feet of water because the annual flood of the river fed by the snow of the Andes Mountains, the longest chain of mountains on earth, is considerable and prolonged. | |
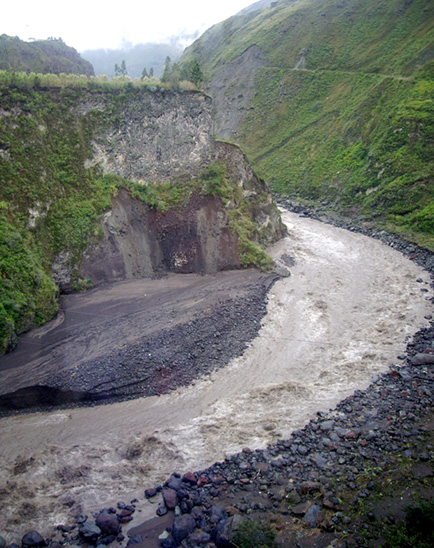 |
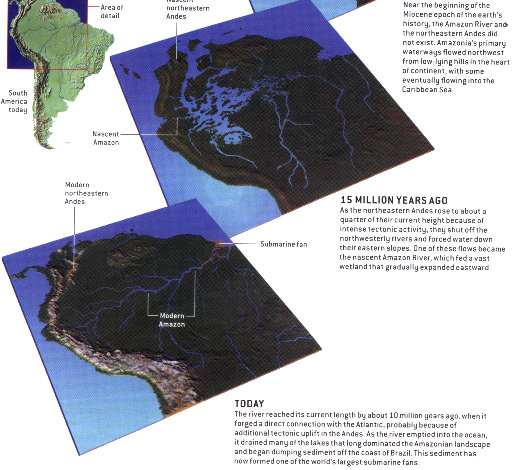 |
| At the headwaters of the Amazon in the east-side of the Andes the silt, mud and rocks eroded form the steep riparian cliffs is evident in the deposition here beside the current. | |
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
Rivers related to forests? | Luna Leopold on Rivers | Downstream | Round river
![]()
A
significant acquired concept
Rivalry is the Latin word derived from rivas, those on opposite sides of a river.
In this photograph of a portion of the watershed from the Himalayan Mountain foothills taken in the 1990s the lighter patches are areas where forests have been cleared by rival owners. Where removal of vegetation causes loss of topsoil and increased siltation downstream, the affect of the upland owner is to degrade the capacity of the river to sustain life downstream.
The many rivers pictured above reveal the core of a basic reality. The watersheds defined by how rainfall moves from higher terrain to lower by way of related tributaries to a main river influences the natural and cultural development of the surroundings beyond the obvious topographical features associated with stream flow, flooding and landscape alterations.
Sacramento | Yangtze | Nile | Amazon | Himalayas
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
Rivers related to forests? | Luna Leopold on Rivers | Downstream | Round river
|
|
|
|
Words | Terms | Glossary | Word webs | Basic vocabulary | Advanced Vocabulary | Antonyms | Synonyms
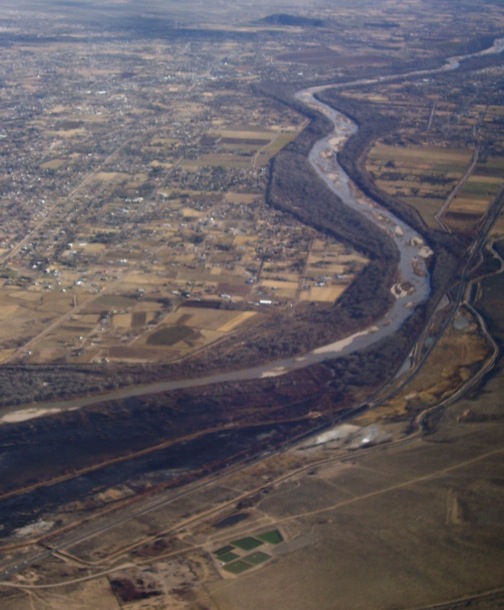

Rio Grande, south of Albuquerque , New Mexico.
Cross section | riparian means? | ecological history | cultural history | linguistics | mythical values | use | evolution | tidal | rivalry | lesson
![]()
Writing | Interviews | Free Writing
![]()

.gif)