Navigating the site:
The geological, geographical, biotic and human setting: of the Columbian Exchange
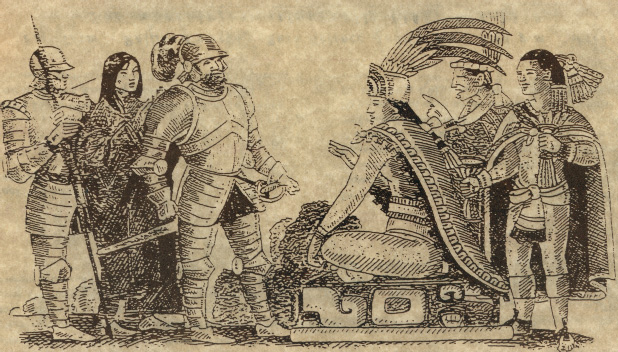
The European invasions associated with the Columbian expeditions between 1492 and 1517, caused the ethnic identity of Caribbean & Latin American peoples to be a mixture of distant –but nonetheless similar Asians, Africans and Europeans with Indigenous island peoples– who are called, mistakenly, Indians.
A. Crosby, Germs, Seeds and Animals.
"Perhaps European humans have triumphed because of their superiority in arms, organization, and fanaticism, but what in heaven's name is the reason that the sun never sets on the empire of the dandelion. Perhaps the success of European imperialism has a biological, an ecological component."
Ecological Imperialism, p. 7.
Biological amalgamation or (homogenization) was the greatest revolution of all.
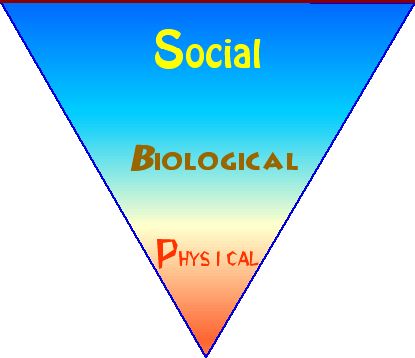
Physical | Biological | Social
Three aspects of the depopulation and repopulating of the Antilles created a context of cultural fusion.
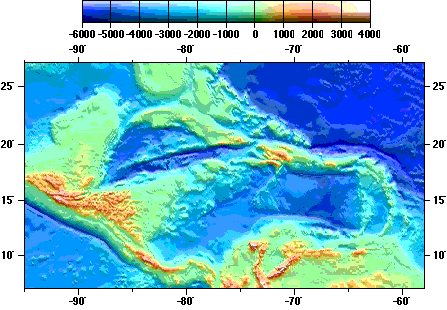
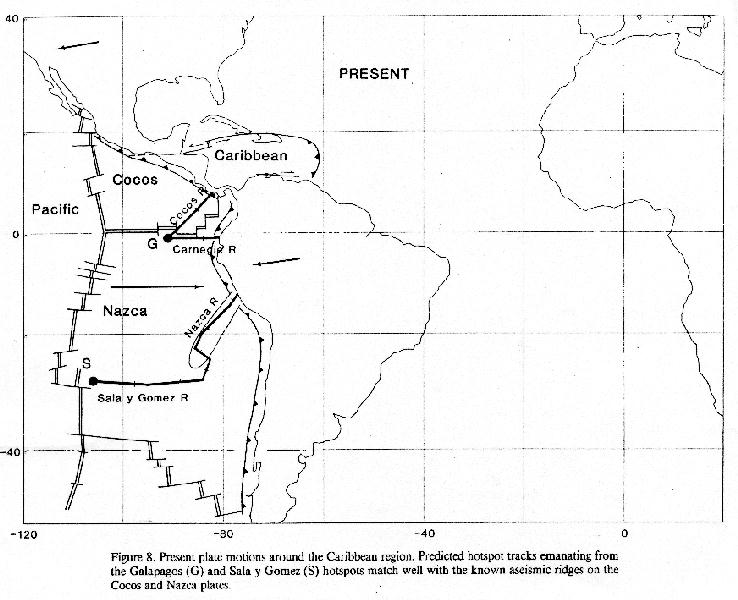
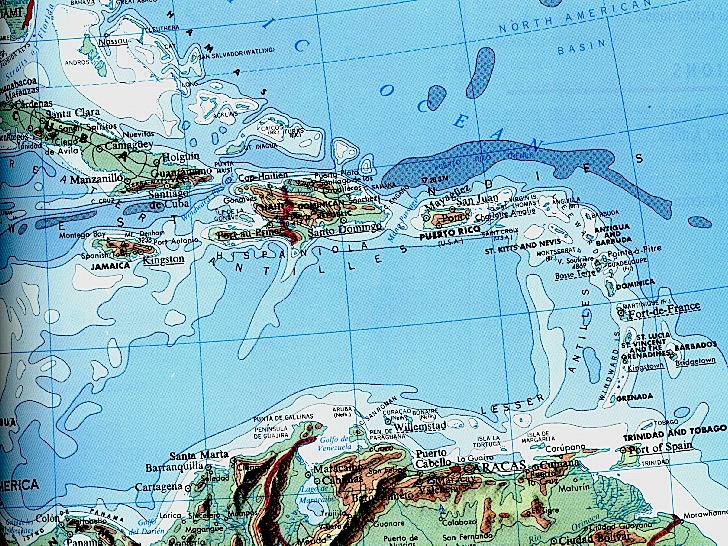
A bathymetric map of the Caribbean
Physical -- defining the shape of the Indies:
Antilles are an island arc and transverse faulted group of archipelagos forming the core and the periphery of the Spanish borderlands of North America.
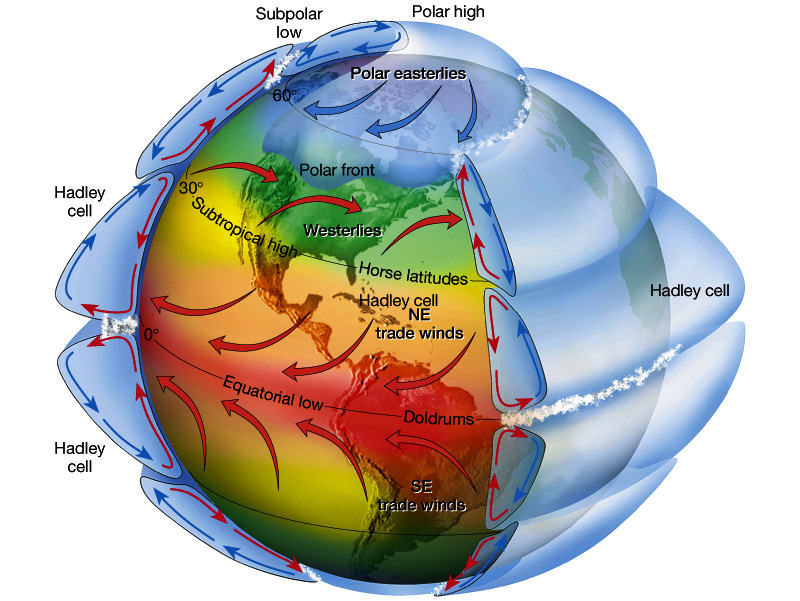
Intertropical convergence’s annual motion north & south brings seasonal rain.
Geomorphology of the greater & lesser Antilles, Caribbean & Nazca Plates moving.
transverse faults form the greater Antilles mountains’ (catch rainfall) watershed.
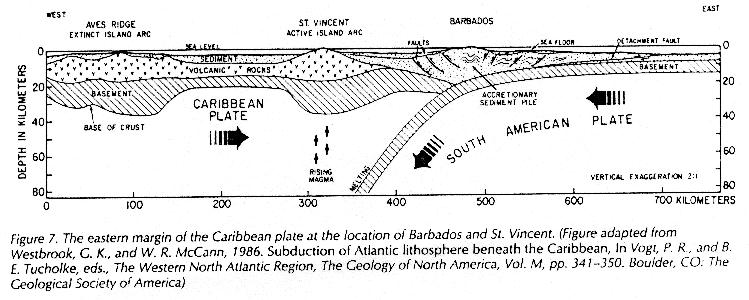
subduction zone generated volcanic mountain chains of the lesser Antilles.
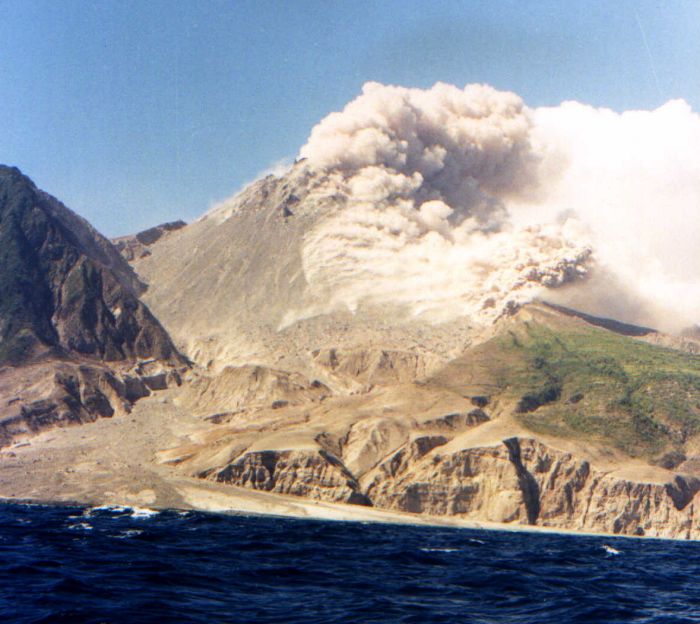
cordilleran boundary versus coastal plains produced a variety of ecological systems.Montserrat's Soufrière Hills volcano erupted –having displaced over half of the population– in July 1995 and again in 1997.
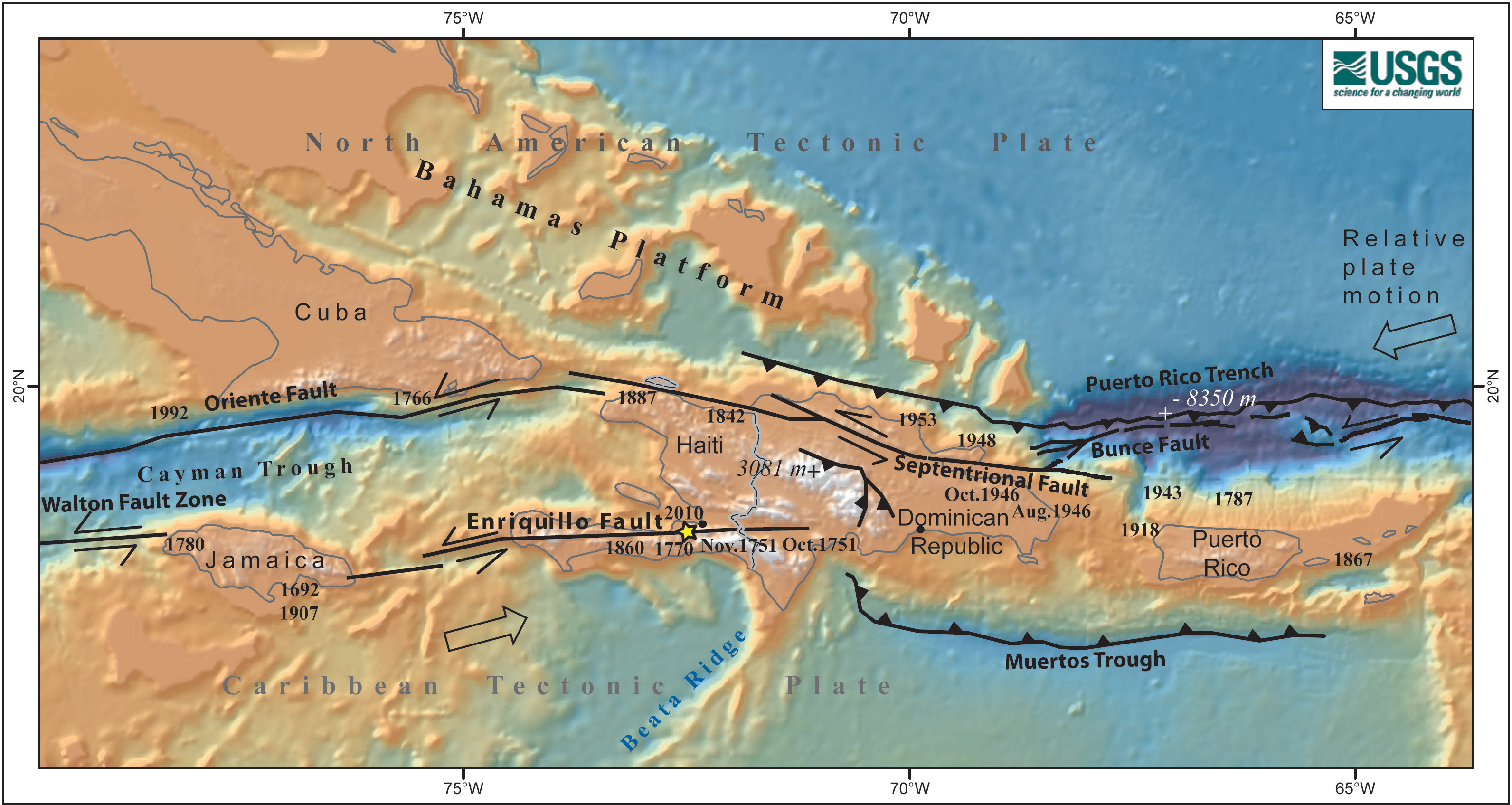
The seismically active Caribbean basin is due to transverse faulting in the greater Antilles and and volcanic activity in the Antilles island arc. The movement of the Caribbean plate with respect to the South American and Atlantic edge of the North American plates drives this process with often sever resulting earthquakes or volcanic explosions.
January 12, 2010: Haiti earth quake was a 7 on the Richter scale, causing over a 100,00 deaths. "Death toll from a relatively modest quake was due to poor construction. The death toll is only a rough guess since no systematic count was kept as bodies were buried."
Nov. 13, 1985, Nevado Ruiz, Colombia erupted killing 23,000 due to mudflows
Mar. 28, 1982, El Chichon, Mexico erupted killing 1,880 due to ash falls
April 24, 1902, Santa Maria, Guatemala killed 4,000 due to ash falls, disease, & starvation.
May 8, 1902, Mount Pelee, Martinique erupted killing: 28,000 due to pyroclastic flows.
In 260 AD, the Ilopango volcano in El Salvador had a significant eruption producing more than ten cubic kilometers of ash.
Over time among the most active volcanoues are: Arenal in Costa Rica and Pelee in Martinique, lesser Antilels with 19 eruptions recorded and Cotopaxi in Ecuador with 10 recorded.
University of Wisconsin
The West Indies remains a "cauldron of unaniticpated vulcanism" as shown in 1995.
In July 1995, Montserrat's Soufrière Hills volcano, dormant for centuries, erupted and soon buried the island's capital, Plymouth, in more than 12 metres (39 ft) of mud, destroyed its airport and docking facilities, and rendered the southern part of the island (the "exclusion zone") uninhabitable. Nearly two thirds of the islanders fled.
"Montserrat, Island Partially Abandoned After Volcano Eruption, Is Slowly Being Consumed By Nature," The Huffington Post 10-8-2013.
A New World Mediterranean Sea.
The core
Mexico & the Andean Cordillera (gold and silver): altitudinal zonation.
Valleys, Tenochtitlan, (chinampa) Aztecs as a trail to the NA Southwest.
The periphery
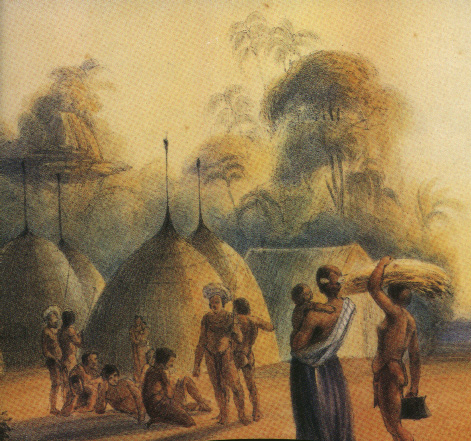
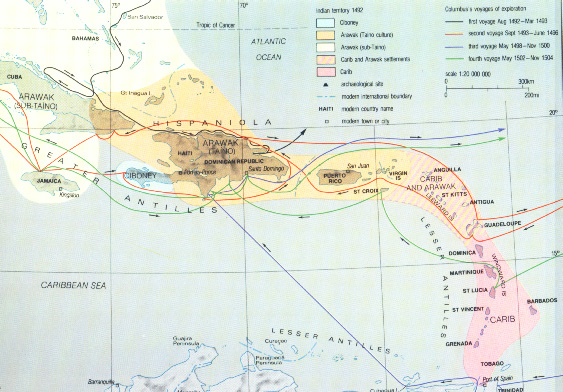
Greater Antilles: Ciboney & Taino, inland and maritime cultural diversity.
Lesser Antilles: Taino & Carib, maritime cultures from South America.
geography as destiny, “nature” is a harsh task-master as it sets rigid conditions.
Biological -- Biomes, bioregions & a study of living things, life sciences, the life cycle.
Virgin soil, weeds, diseases & the apparent absence of communities of settled farmers.
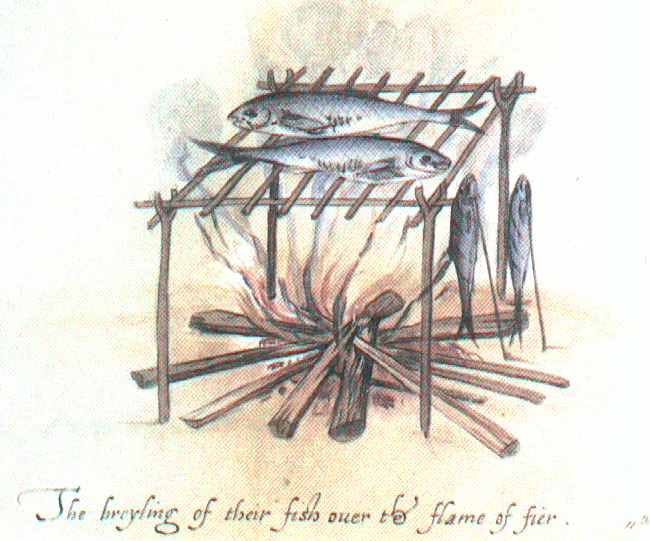
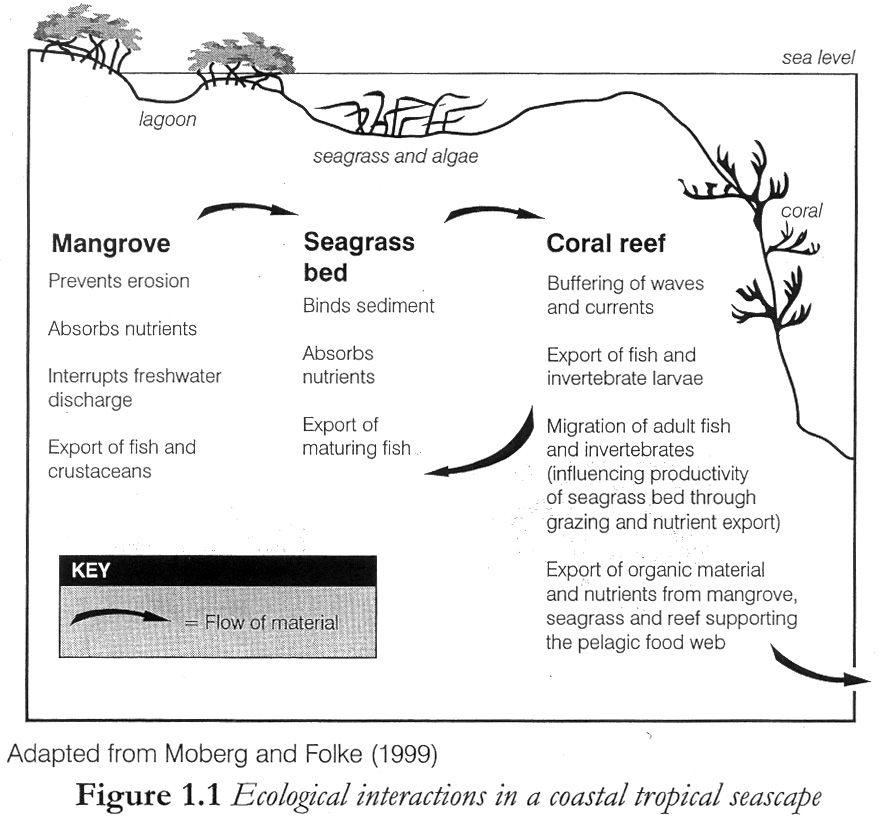
Whales & Marine Turtles, Mangroves, & fisheries from the Canary Isles to West Indies.
Manioc, corn, & vegetable staples fed invaders
The corn bearer in Mayan cosmology.
European invaders came with immunity to Eurasian diseases.
Isolation, endemism and exotic introductions, not religion explains Euro-successes.
Isolation allowed for the development of biological diversity and suppressed immune response to otherwise common and now less virulent sickness.
Genetic variability, today, explains the outcomes of the Columbian Exchange, as the mixture of European and American flora & fauna.
Settings variable, and the flora diverse; fauna sustaining.
Coasts as boundaries or bridges?
Pump of the Gulf Stream: North Atlantic gyre (clockwise currents).
Turtles, sea turtles, manatees, birds
Social -- European cultural dominance (language) & Amerindians staple foods.
Sugar, Encomienda system, communal water rights, cattle, horses, swine, wheat & oats.
West Indies as the doorway, to the Americas; a staging ground, incubator.
acclimation of Euro-fauna and flora required “seasoning” in the Antilles.
sugar islands as a source of investment wealth fed the industrial revolution.
European Feudalism as transplanted to the America's favored:
- Royal families in Europe.
- Granted rights to the eldest male heirs
- Encouraged absentee landlords
- granted special status to clergy and church lands
- operated monopoly enterprises for the sole benefit of the state.
Indian labor after a precipitous decline was insufficient to meet the needs.
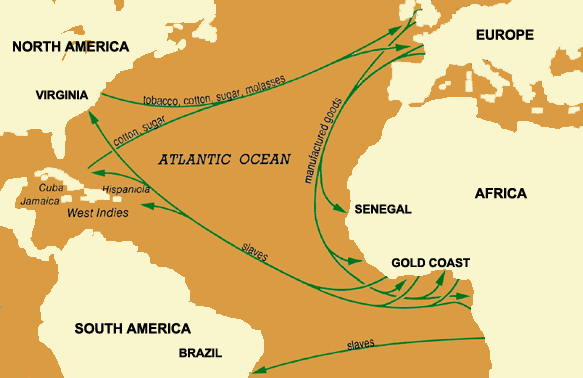
African slaves, 25 million transported in 250 years.(conservative est.)The biological elements of culture are evident in the character of and quality of outcomes from the Columbian Exchange
Health and security rest in part on – food, fuel, fiber & forage derived from natural conditions called the "four Fs".
- food: subsistence and production led to depopulation in America, but population growth in Europe.
- fuel: water and human power versus wind and animal power left Indigenes at a disadvantage
- fiber: fabrics from vegetation such as Amerindian cotton versus hides & tallow from European cattle
- forage: Indigenous turkey versus variety and life cycles of European domestic animals: pigs, chickens, sheep, goats, oxen, horses, and cattle.
Divergence in attitudes about land, vegetal and animal life and peoples' well being:
- Indiginistas were largely vegetarian, worshipped corn, sun and storm deities
- Europeans were cattle and stock owners, land was inanimate property, believed in the trinity as a mystery and saints as mortal yet transcendent beings.
Context of settling the Americas
A series of changes:
depopulation of the island people, Indigenes or native "indiginistas" was coupled with forced migration from other parts of the Americas and eventually western & southern Africa.
land grants to lesser nobility in exchange for military service and a percentage return.
trade monopolies (mercantilism) given to merchant adventurers (companies) with proceeds going in shares to investors and the government.
Psychological and ideological, impact of disease on beliefs and ritual behavior, such as civic and religious obligations, observances, and labor.
The Caribbean as gateway:
Staging ground or proving ground for the European mastery of the two Americas.
Arawaks & Columbus: Two worlds collided, yet partly fused to enrich Europe and impoverish "the Indies".
Plantations, mining, & commerce for export all emerged within 50 years.
Cortez & Pizarro, domestic animals & diseases helped conquests.
African slavery was originally based on Portuguese trade on gold & ivory coasts.
African Negro slavery thrived as Spanish discovered silver in Mexico and gold in Peru.
Completed: August 10, 2014, by J. Siry



.gif)