Darwin's critical synthesis of observed facts.
![]()
"I am tempted to give one more instance showing how plants and animals, most remote in the scale of nature, are bound together by a web of complex relations. I shall hereafter have occasion to show that the exotic Lobelia fulgens, in this part of England, is never visited by insects, and consequently, from its peculiar structure, never can set a seed."
Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, p. 73.
| He revealed life's unity and thus, human descent from a common ancestry. | |
|---|---|
| domestication biogeography taxonomy behavior deep time orderly universe |
 |
Darwin | The road he took | His query | Darwin's metaphor | Classification system | Consequences of Darwin's discoveries |
|
Do apparent patterns, designs, or habits among natural phenomena obscure or reveal the hidden commonality of the world?
Wings on insects, birds, and bats for instance are different from hmology.
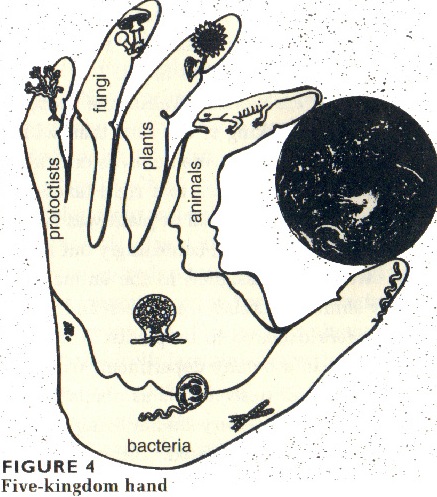 |
Five Kingdom system
|
| The five kingdoms portrayed as a hand of life after a diagram by Dr. Lynn Margulis, Symbiotic Planet. | What are these hidden likenesses of this image of life ? |
Lynn Margulis and others argued on the basis of genetic similarities, functional considerations and common descent that the previously described plant and animal kingdoms could be better understood as two of five kingdoms, including fungi and protoctista bacteria that were all descended from Moneran microbes over the course of four billion years.
"evolution by means of natural selection"
p. 68.
"the fifth . . of Darwin's great evolutionary theories . . . . dealt with the mechanism of evolutionary change and , more particularly , how this mechanism could account for the seeming harmony and adaptation of the organic world."
"Darwin . . . for him there was a steady production of individuals, generation after generation, some of whom where 'superior' in having a reproductive advantage."
"Darwin stressed that he 'collected facts on a wholesale scale, more especially with respect to domesticated productions, by printed inquiries, by conversations with skillful breeders and gardeners, and by reading.' . . ."
p. 83.
"The natural selection of individuals with particular heritable qualities, continued over many generations, automatically leads to evolution. . . . In fact, this process is sometimesused as the definition of evolution. In this connection it must be emphasized once more that Darwin's inference is exactly the opposite of Malthus, . . . "
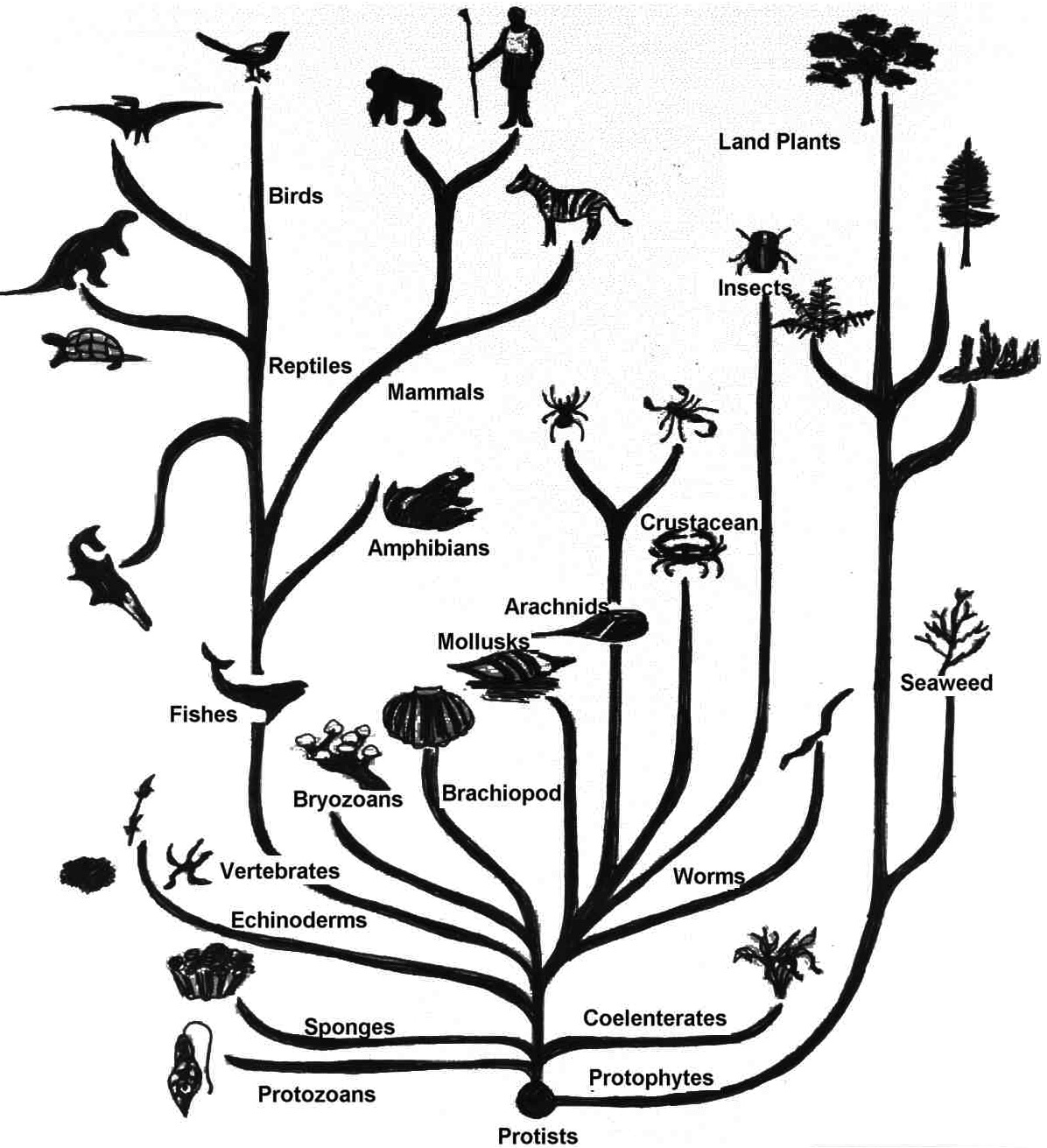
| Tree of Life | |
"As buds give rise by growth by growth to fresh buds, and these, if vigorous, branch out and overtop on all sides many a feebler branch, so by generation I believe it has been with the great Tree of Life, which fills with its dead and broken branches the crust of the earth, and covers the surface with its ever branching and beautiful ramifications." Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, Chapter 4. p. 130. |
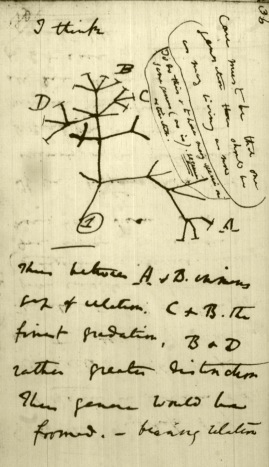 |
Darwin's own sketch of a tree of descent. The original is in the Cambridge University Library, U.K.. |
|
Joshua tree, a variety of Yucca brevifolia, that branches symbolize genus and leaves stand for species |
|
 |
|
|
|
![]()
human hands
![]()
In 1858, Darwin received in the mail a manuscript written
by Wallace and sent to him from Indonesia, where Wallace had been collecting
specimens for the museums and collectors in England. In 1859 Darwin published
On the Origin of Species: or the Survival of Favoured Races in the Struggle
for Life, in which he proposed five
theories to account for change, variation and chance in nature.
|
|
|
Darwin contributed concepts that have emerged as lasting contributions in biology because of these discoveries:explanations
domestication -- The means by which a wide variety is readily observed.
biogeography -- The means by which isolation causes divergence among related descendents.
taxonomy -- The classification of varieties into species in relation to a sort of Tree of Life.
behavior -- The means by which acquired traits (soft inheritance) are passed on to offspring.
deep time -- Lyell's and Hutton's idea of uniformitarianism creates great geological ages pointing to an enormous duration of life on Earth.
orderly universe -- The belief in a harmony of natural changes and the adaptive potential of life to sustain itself ecologically, despite gradual changes or abrupt upheavals.
genetic evidence -- The discovery of the phenotype (form, shape or appearances) and genotype (underlying organization of proteins and DNA base pairs) as fitting into and not refuting the concepts associated with natural and sexual selection advanced by Darwin.
| contributions meaning the consequence of his ideas: | New Synthesis |
| 1. domestication, variation, natural selection | sexual selection |
| 2. biogeography, adaptive radiation, horizontal speciation | continental drift |
| 3. taxonomy, common descent, embryological sameness | genetic drift |
| 4. behavior, ethology, instinct | soft inheritance |
| 5. deep time, geological formations, extinctions | 6 mass extinctions |
| 6. orderly universe, gradualism, adapting to change | punctuated equilibrium |
| 7. Chance Evolution, random (stochastic) variation | biodiversity |
On the Origin of Species: or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. 1859.
Darwinism | Ernst Mayr | Consequences of Darwin's Revolutions | His contributions
Word index | Terms | Glossary | Word webs | Basic vocabulary | Advanced Vocabulary | Antonyms | Synonyms
Genetics Index | Science Index | Population Index | Global Warming Index | Nature Index | Brief | Social Analysis
Writing | Interviews | Free Writing