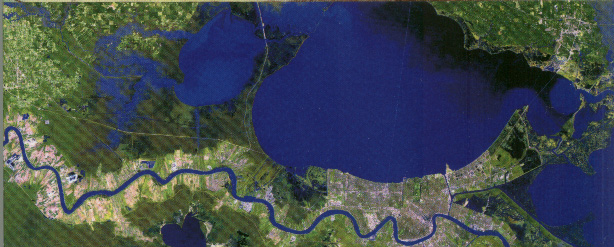
Beach & shore losses
Beach & shore losses Navigating the site:
Paz, Octavio
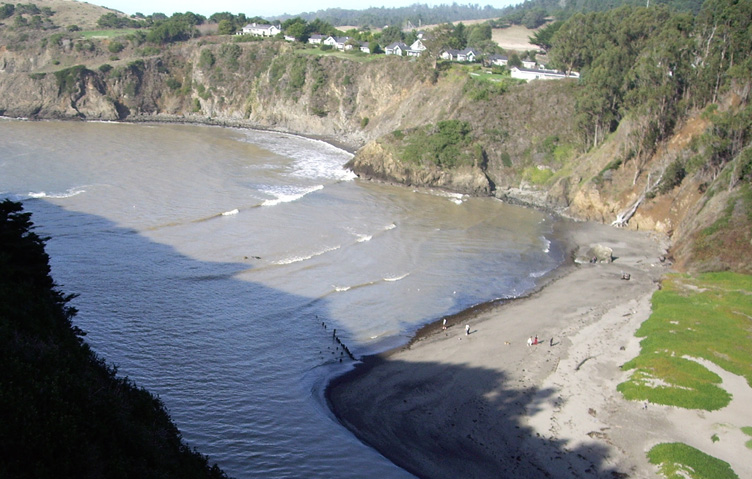
Beaches are ephemeral existences in constant metamorphosis because waves, currents and tides perpetually sculpt the beach reshaping the very contours of life in the sand.
visual description | type of habitat | sand shore | beach profile | grain size | Waves | longshore currents | overview | index
![]()
waves | themes | examples | myths | Dutch | habitats compared | patterns | sources
![]()
Oceans moderate temperatures creating less extreme climates along coastal shores.
Waves are periodic displacement of energy and matter with distinct patterns based on descriptive qualities of speed, frequencies, forces, and mass. Ocean waves behave differently from radiation waves.
Anything immersed in a wave pattern is not actually moved by the water's motion, but waves are indicators of a current and currents move the entire set of waves from one place to another. All waves have amass that is measured in terms of crests, troughs, amplitude, and frequency.
Profile of a wave |
||
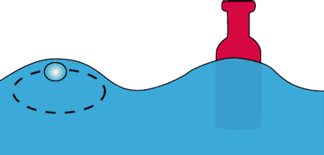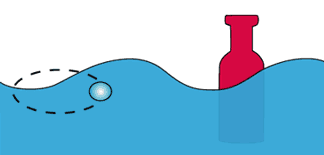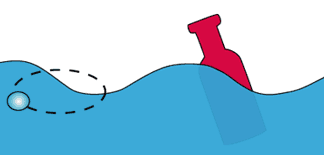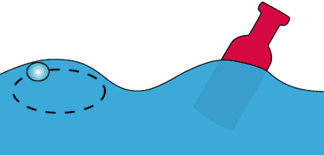 |
height | |
| Crest | ||
| Amplitude | ||
| Trough | ||
| depth | ||
The interval between crests (or troughs) is the frequency of the wave. |
||
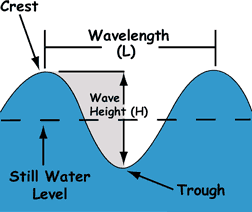 An Amplitude is the distance from the bottom of the trough to the top of the crest of the wave or its height.
An Amplitude is the distance from the bottom of the trough to the top of the crest of the wave or its height.
Waves in water behave very differently from light waves.
![]()
visual description | type of habitat | sand shore | beach profile | grain size | Waves | longshore currents | overview | index
Waves in motion shape the shorelines:
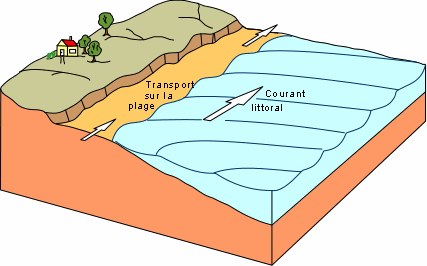
Long shore currents transport sand laterally along the shoreline in the direction of the prevailing wind-driven and current derived movement of water bodies called gyres.
visual description | type of habitat | sand shore | beach profile | grain size | Waves | longshore currents | overview | index
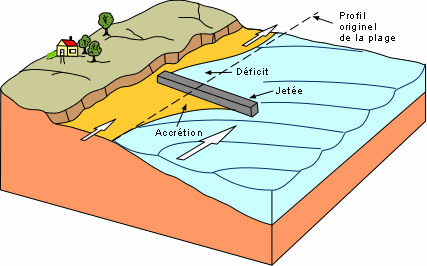
Interferences by jetties, groins or obstructions that leads to accretion and reliction (deficit).
visual description | type of habitat | sand shore | beach profile | grain size | Waves | longshore currents | overview | index
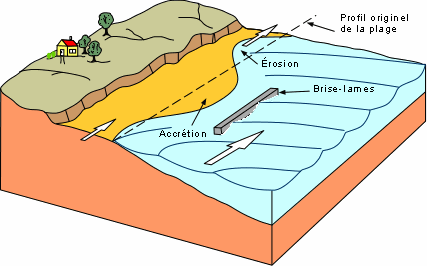
Newer means of marine engineering are designed to add sand to the beaches.
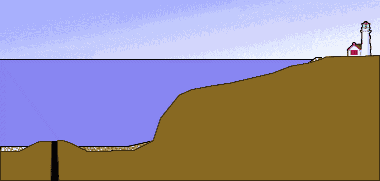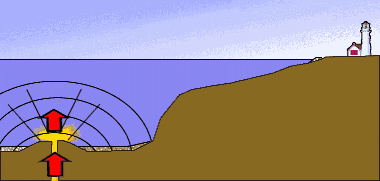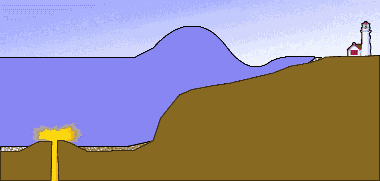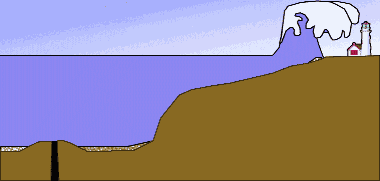
Coastal engineering and tsunamis
visual representation of a tidal wave or tsunami generated by a submarine earthquake.
visual description | type of habitat | sand shore | beach profile | grain size | Waves | longshore currents | overview | index
Theme of the ocean as an adversary
Those sub-themes in the history of coastal settlement are:
- the use of salt marshes for grazing and gathering,
- the fishing, fowling and game hunting , and
- the ambiguity of the sea defenses for control over the forces of nature.
- Dutch perspectives.
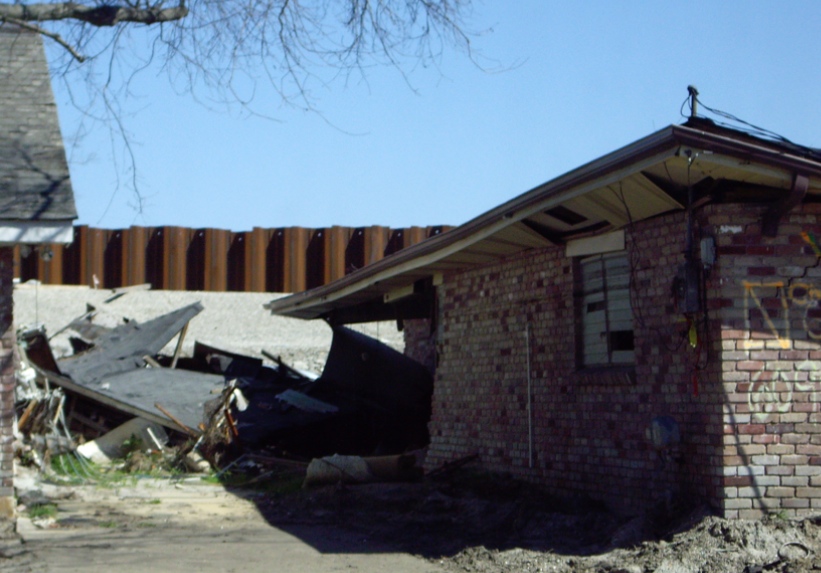
In the background is a repaired sea wall to prevent future storm waves and tides from eroding and flooding the shore, after 2005 flooding of New Orleans, seen below.
metamorphosis, literally to change shape or take on another shape or form, figuratively the ability to transform beyond recognition.