 Marine geology
Marine geology
words to know | objectives | visualize | Geology | basic terminology | essay | title | start | sources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Geology of the rising Pacific shore: the case of the | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mendocino Ecological Staircase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Memes:*
"This turn revealed a grand & glorious coast to behold." Mendocino, December, 2005. A marine terrace above an inlet of the Little River, on the edge of the Mendocino escarpment, California.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
VisualizeThe earth moves in three ways -- also!
1. Horizontally this island moves in the prevailing currents that move waves that move its sands:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rhodes, Greece | 2011 | settled in 408 BCE | |||||
| Population | Size | Concentration | |||||
| square miles | kilometers | density | |||||
| 115,490 | People per | miles sq. | kilometers sq. | urban | |||
| 541 | 1401 | 213.5 | 82.4 | ||||
| City of Rodos | 50,636 | 44% | |||||
| 27 inches of rain | annually | Climate is | Temperate, Mediterranean. | ||||
Rhodes is an island which lies off the coast of Asia minor in the Aegean sea and is part of the Dodecanese Islands of Greece. Much of this coastal area was created when the continent of Africa collided with Southern Europe and Asia Minor millions of years ago closing the circum-equatorial tropical seas that once tempered the climate of the Earth. This was called the Tethys Sea and accounts for the distribution of mangrove forests, marine turtles, tortoises, and marine mammals now isolated from one another in the Atlantic and Indian (Indo-Pacific) Oceans.
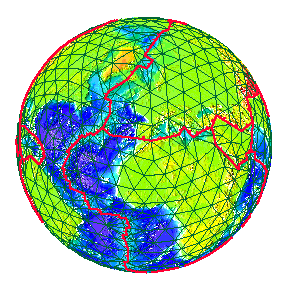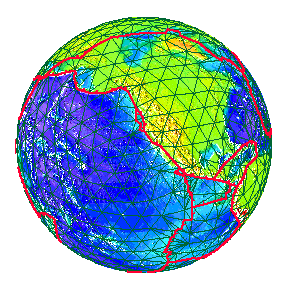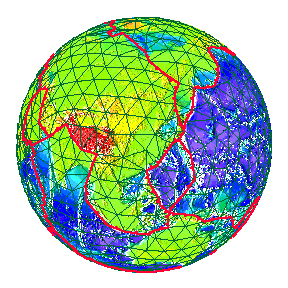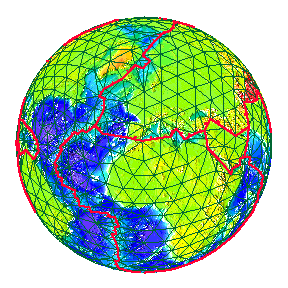
| The movement of the Earth's plates over Geological time. | |
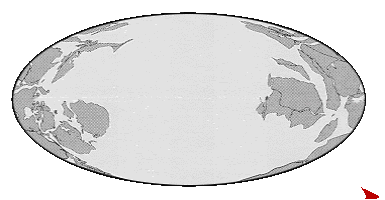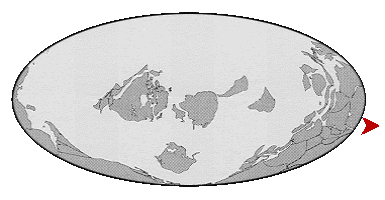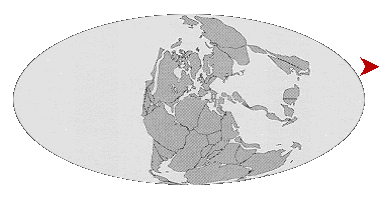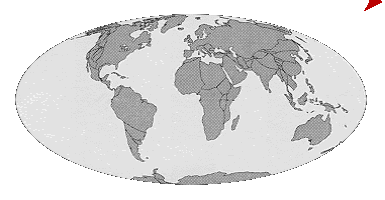 |
The Present |
| Cenozoic | |
| Mesozoic | |
| Paleozoic | |
| Hadean | |
Geological periods called Eras of long duration. |
|
The Oceans, however are far older than these Eras.
Visit the American Museum of Natural History, on line.
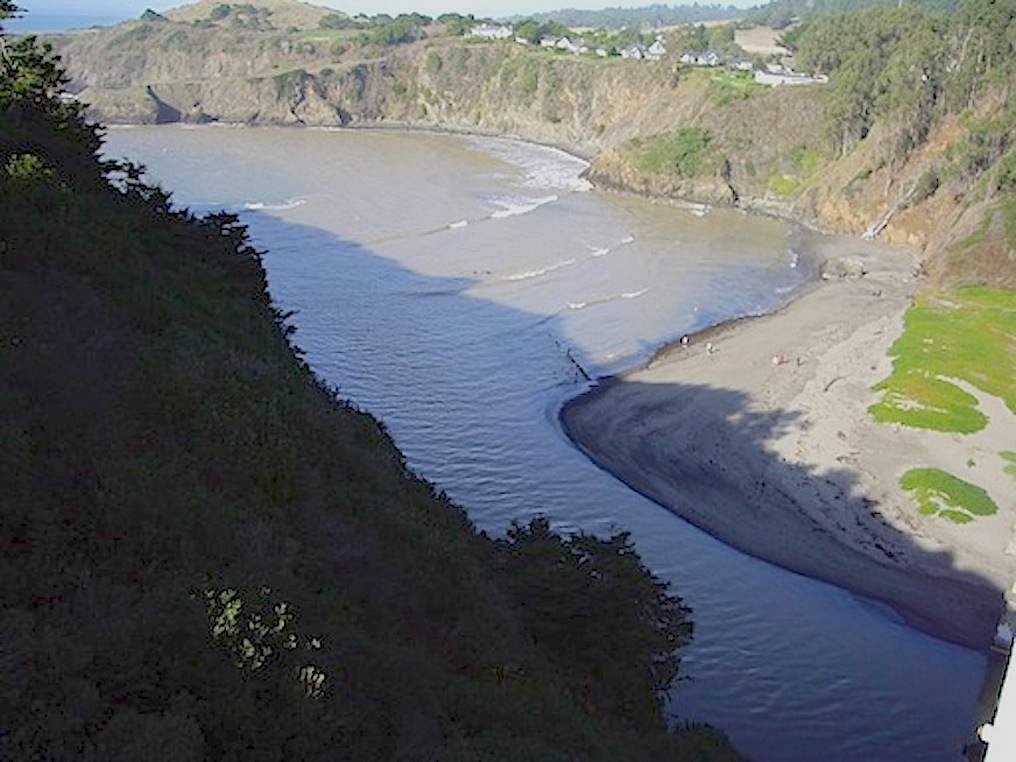
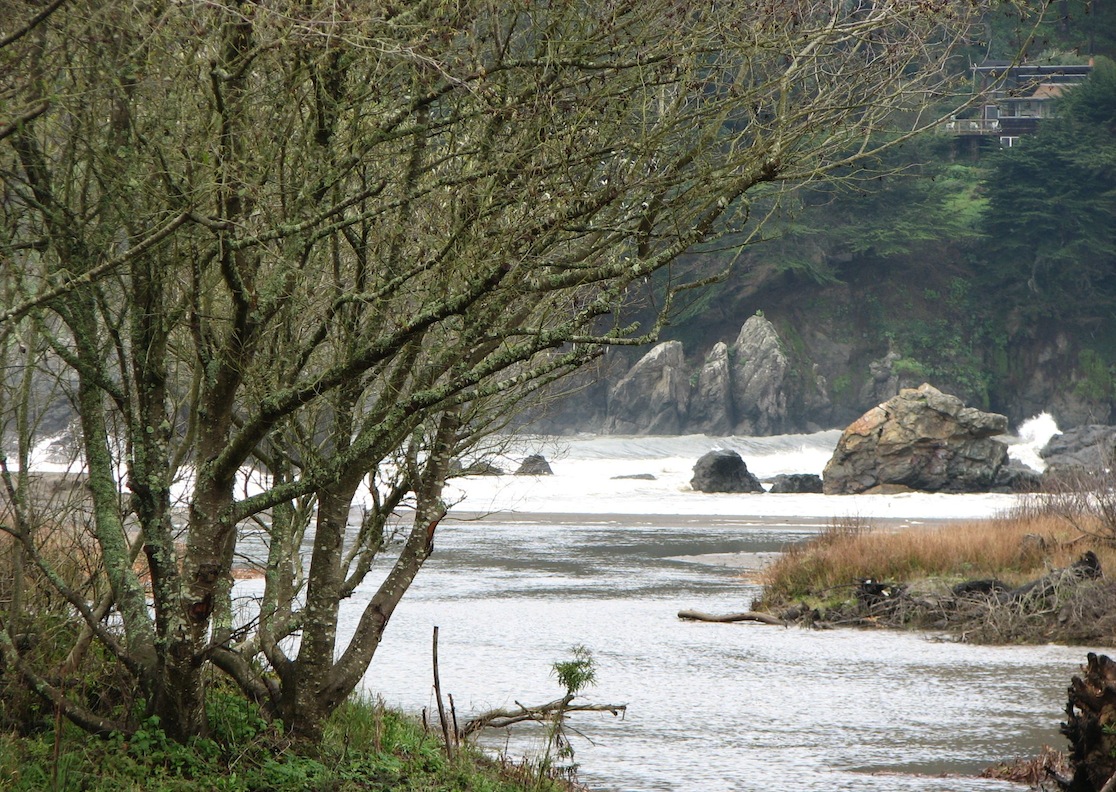
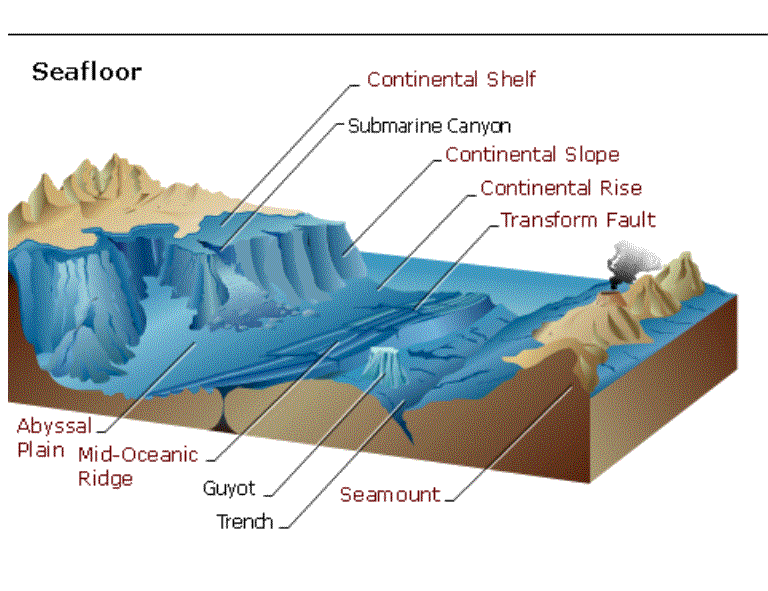
Shoreline patterns beneath the seas:
Erosive forces create reliction and accretion along the shores, or banks of the river.
Rivers shown here at flood stage are exquisite examples of erosion once mountains uplift due to movement of the Earth's plates.
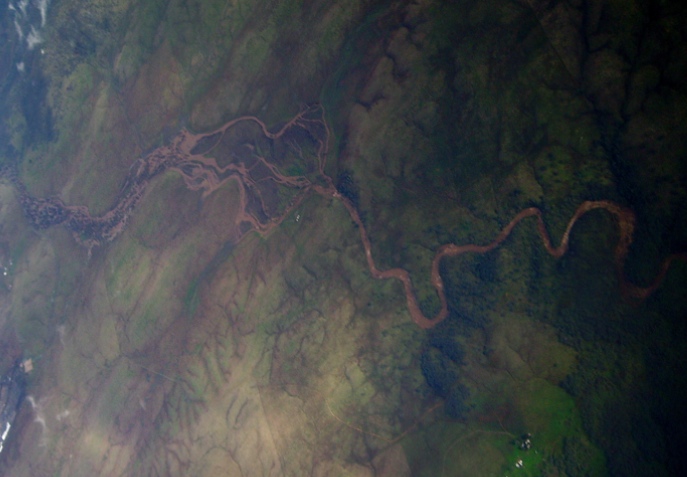

California foothills and the American River which drains the western Sierras.
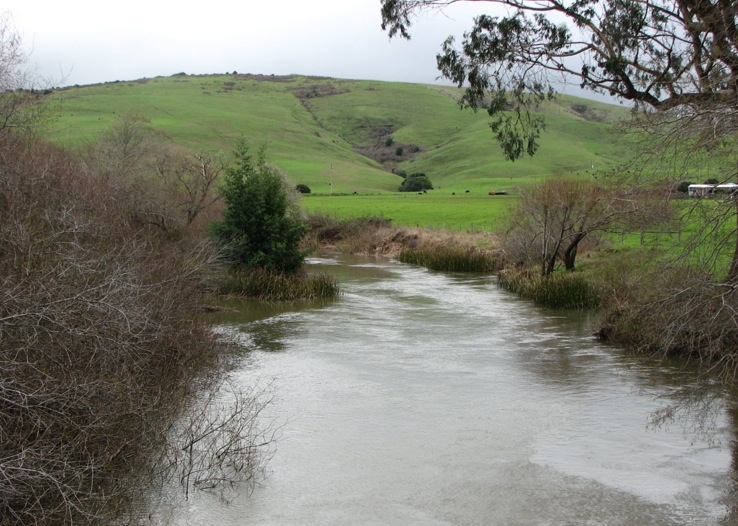

Eroded hillsides carry sediments including rocks and silt into the Tomales river.
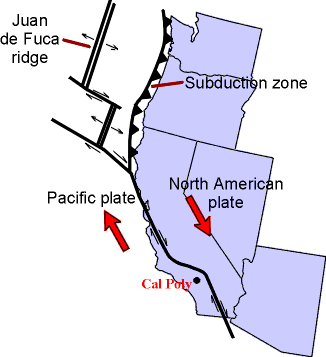
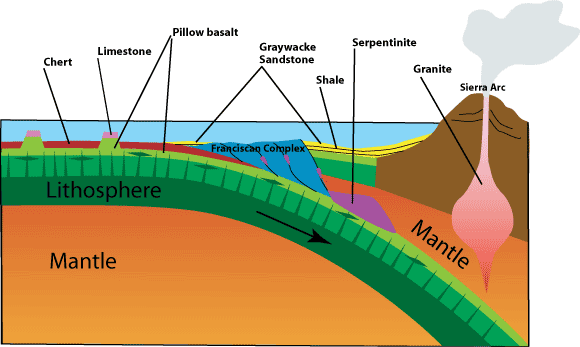
California's tectonic coastline
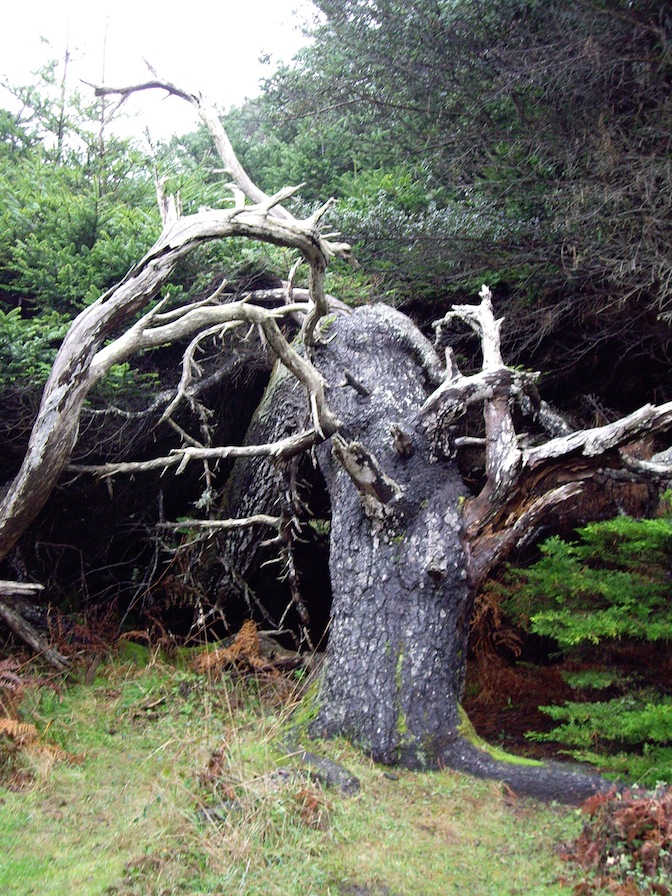
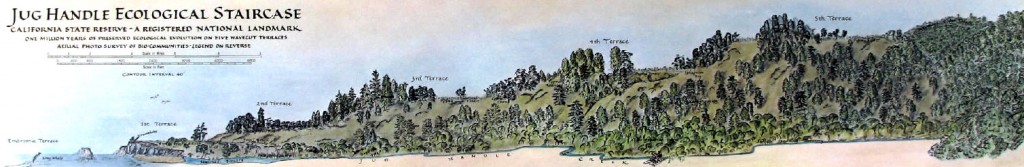
The Staircase:
The five terraces of the sea.
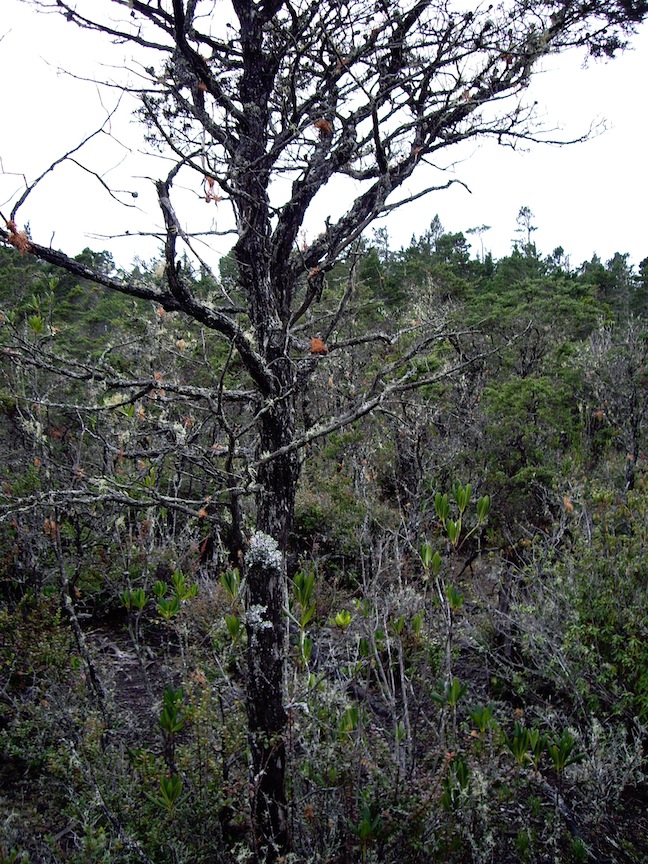
Nearest the sea the effects of wind and salt in the air affects the trees.
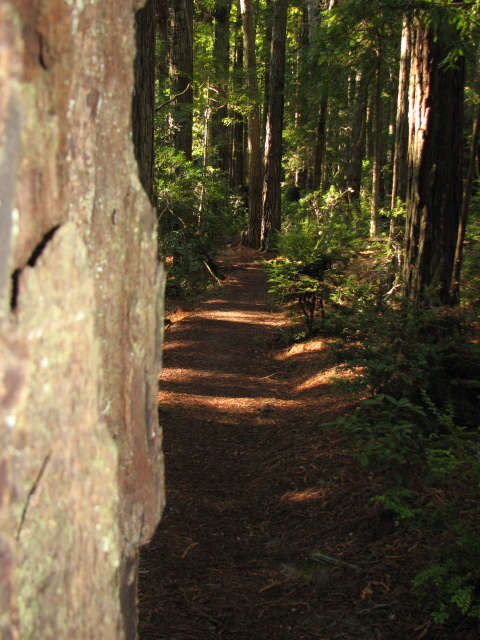
Into the trail . . . up the marine terraces to . . . .
Dwarf forest trees growing for centuries on hardpan clay.
Authority is:
An Essay
Coasts can be influenced by land, air and water in various ways, but the Western US along the Pacific coast is affected by tectonic, or geologically active forces, as much or even more so than other influences such as weathering or sea level rise and tides.
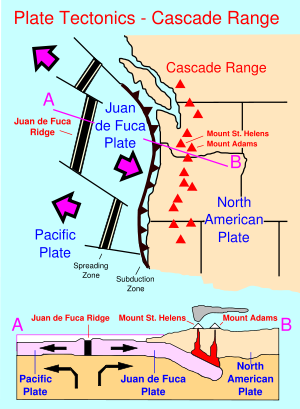
Very similar to Japan, this is a seismically active area associated with the impacts of the "ring of fire" a series of volcanoes that stretch along the Pacific Ocean rim from Indonesia, to the Philippines, up to Japan and Kamchatka in Russia, over to the Aleutian Islands and eastern Alaska, then down the coastal and Cascade ranges to Baja, Mexico and on down along the Andes of South America.
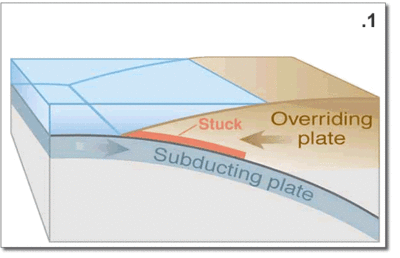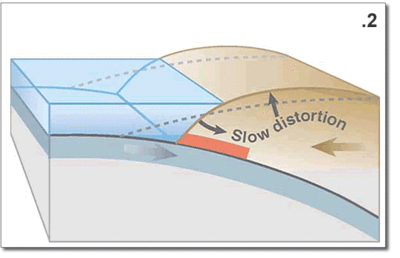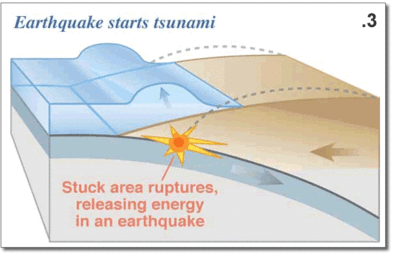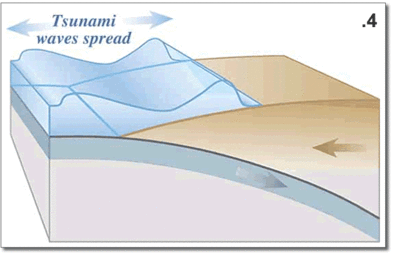
The earth's crust is restless in the sense of geological time and the Pacific area is a vast block of basalt that is fractured in many places. Those fracture zones, called transform faults --running laterally to one another and perpendicular to the California coast-- are numerous. But two very important fractures zones come ashore at Cape Mendocino and Point Conception forming among other terrain features, the Great Central Valley of California.
More recently (the last 15 million years) the movement at an angle nearly perpendicular to these lateral transform fault, fractures has caused the deformation of the Pacific Coast by the San Andreas fault system south of Cape Mendocino. The Channel Islands of Southern California and Baja are remnant of down faulted marine terraces that have sunk below the sea due to both tectonic forces and the slow rise in sea level in the past 10,000 years since the end of the last ice age.
J. Siry
This is an example of a post to the class wiki, use it to reflect what you think after reading Marston Bates & this page.
Terms defined:
A Meme is an element of a culture or system of behavior that may be considered to be passed from one individual to another by nongenetic means, especially through imitation.
See mimetic, from the Greek word meaning: imitation of
When the British scientist Richard Dawkins coined the word meme in his 1976 book The Selfish Gene, he wanted a word like gene that conveyed the way in which ideas and behavior spread within society by other than strictly genetic means.
Since then, the word has been picked up to describe a piece of information spread by e-mail or via blogs and social networking sites.
A meme can be almost anything—a joke, a video clip, a cartoon, a news story—
Defining other vocabulary terms to know
Plate tectonics, the concept that the Earth's surface is fractured into several internally coherent, but different blocks of either basaltic or pyroclastic and sedimentary terrains.
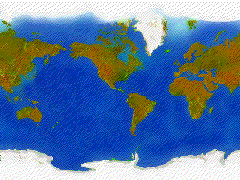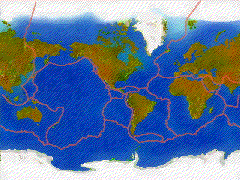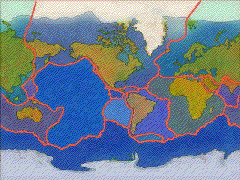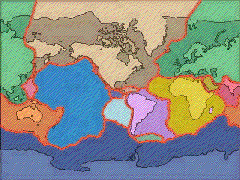 fracture zones are those areas of a large or small plate that --as a block of that plate-- break or slide apart from the adjoining mass at a different rate of speed than the entirety of the parent plate.
fracture zones are those areas of a large or small plate that --as a block of that plate-- break or slide apart from the adjoining mass at a different rate of speed than the entirety of the parent plate.
transform faults are associated with slippage and fracturing along a boundary, where neither one plate nor another --adjacent-- plate has any discernible vertical movement; and instead the forces push each block past the other. The stress of this lateral collision creates fault systems where seismic activity and earthquakes periodically relieve the stresses of one mass of rock grinding past another.
subduct, subduction: the term for one plate slipping under [sub], or going [duct] down, or moving beneath another.
Convergent plate boundaries are a characterized by subduction zones that are related to island arcs or hot spot activity where the melting of the plate going under an adjacent plates brings molten rock to, at, near or over the surface features of the landscape.
Divergent plate boundaries are areas associated with spreading, usually sea floor spreading  as in the East Pacific Rise, the Mid Atlantic Ridge, or as in the case of Iceland and the Great Rift Valley of East Africa these areas where plate boundaries are separating can occur over land. In these regions where plates separate (as opposed to coming together or converging) are forces that release magma from below the surface and extrude lava. As the lava solidifies on either side of the rift each side of the fracture moves apart from the other side of the magma well. This existence of an ever growing displacement of lava is the primary cause for the movement of one massive plate or block away from another at differential rates of divergence (different speeds at which the plates move out and away from one another).
as in the East Pacific Rise, the Mid Atlantic Ridge, or as in the case of Iceland and the Great Rift Valley of East Africa these areas where plate boundaries are separating can occur over land. In these regions where plates separate (as opposed to coming together or converging) are forces that release magma from below the surface and extrude lava. As the lava solidifies on either side of the rift each side of the fracture moves apart from the other side of the magma well. This existence of an ever growing displacement of lava is the primary cause for the movement of one massive plate or block away from another at differential rates of divergence (different speeds at which the plates move out and away from one another).
reliction and accretion
accretion is a term for the deposition of sediment along a shore or added material
reliction is a term for the erosion of a shore, or loss of land.
Edge of the Sea, an overview of concepts, themes and terms.
West coast geology
Edges of the Seas, an overview of concepts, themes and terms.

.gif)






 Guide
Guide 