When old dogma dies
When old dogma dies"An estuary's wealth is unseen, and hence the seas resilience diminishes as these vaults are robbed and their rich contents despoiled."
J. V. Siry"Estuaries: Beyond the surface features"
102 estuaries exist in the United States of varying sizes and with different mixtures of species and variable amounts of biological diversity.
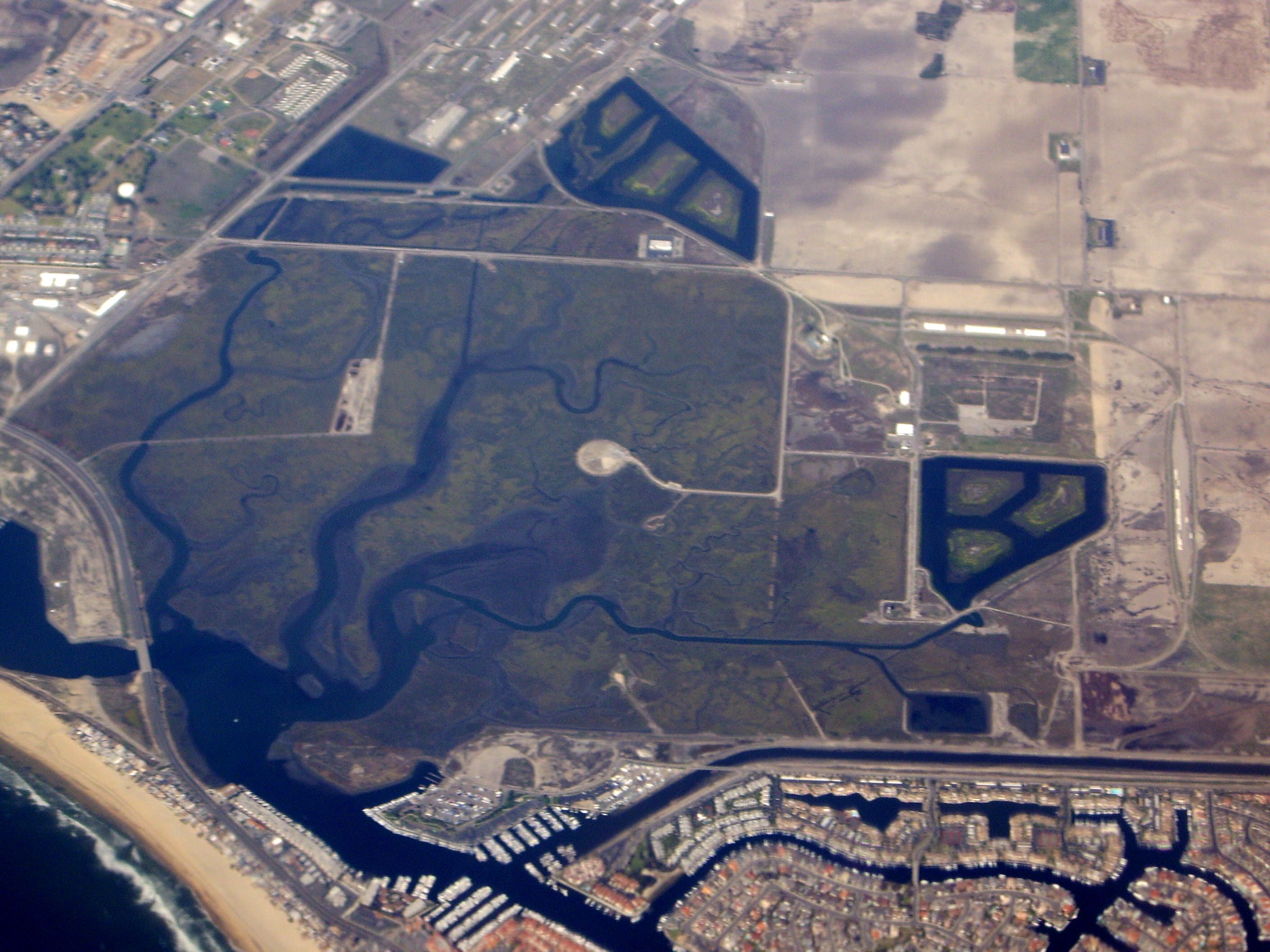
But these geographical terrains where fresh and salt water meet are rare ecotone of unimaginable bounty beneath their still waters the currents of history and ecology run deeply.
Estuaries are really a set of structures maintained by a series of keystone species arranged in a pattern of vaults that support the entire edifice.
- oyster reefs
- amphipods
- salmon or alewife
- blue crabs
- mud and / or fiddler crabs
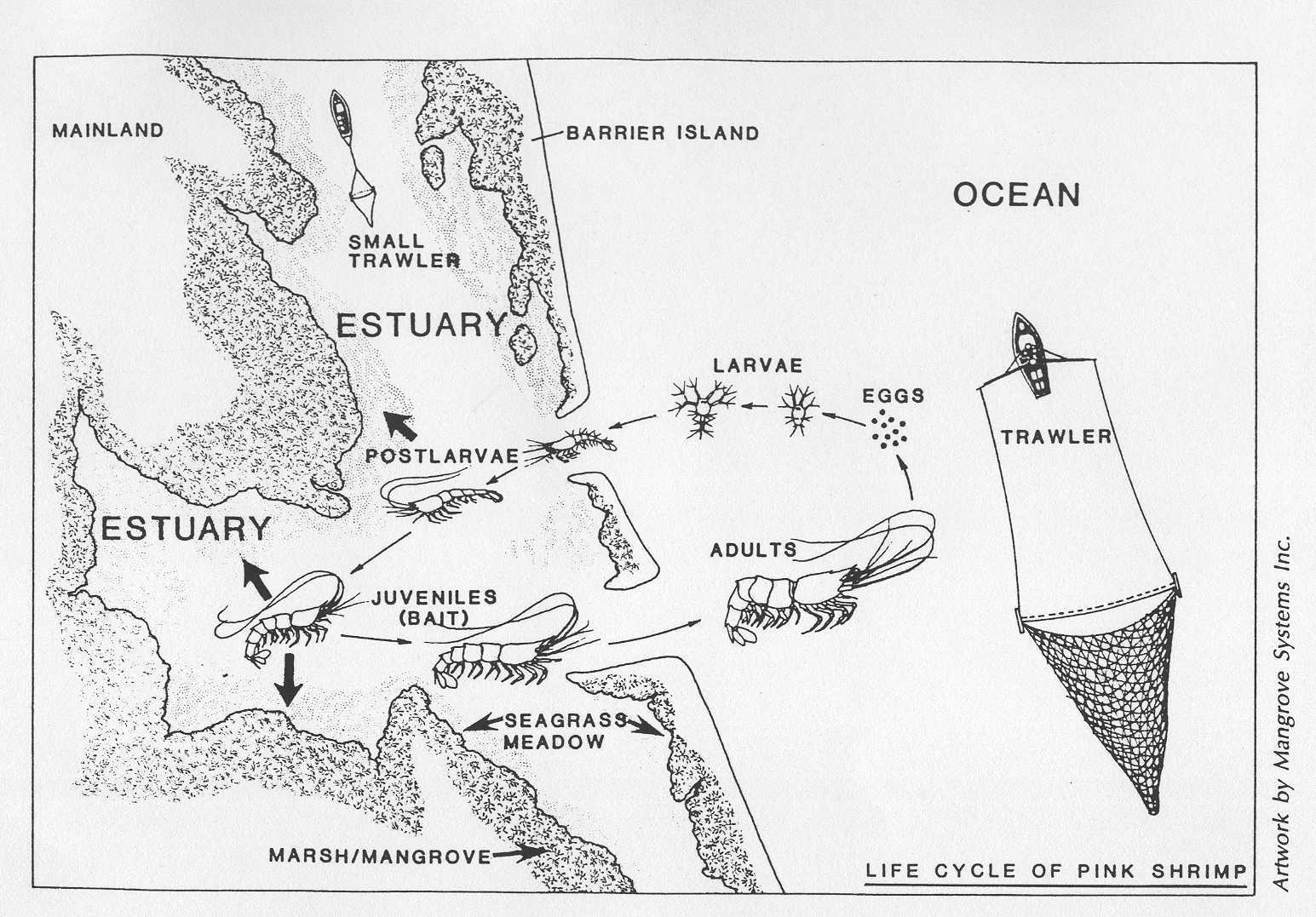
- shrimp
- ducks or geese
As seasonal changes occur in rivers, each biological association from mollusks or worm reefs to crabs and invertebrates perform tasks that end up maintaining the water quality and nourishment for food fish over the episodic changes that could disrupt one or more of these productive agents of the ecotone.
oyster reefs act as filtration mechanisms removing algae.
amphipods are a source of food for flounder.
mud crabs and fiddler crabs turn over sediments.
salps (marine ascidians) absorb water, nutrients and diatoms.
shrimp consume huge amounts of detritus.
The ecological services that sustain these productive agents of the ecotone found in estuaries are the initial conditions on which some economic values depend.
metaphor | anomaly | Glossary | extension : regression | episodic changes | Factors
The existence of fisheries at sea is dependent on the shore and their nourishment in tidal seas or estuaries.
The food on your plate:
- clam chowder
- crab cakes
- oysters Rockefeller
- lobster bisque
- shrimp scampi
- shad roe
- caviar
- scallops
- salmon
- striped bass
Delicacies that all depend on the health of the water, the extent of the wetlands, the clean air, and the forested landscapes of river mouths, known as estuaries.
Both commercial shore and deep sea --in addition to subsistence-- fisheries rely on estuaries and clean coastal waters.
Glossary of Terms:
- Productivity
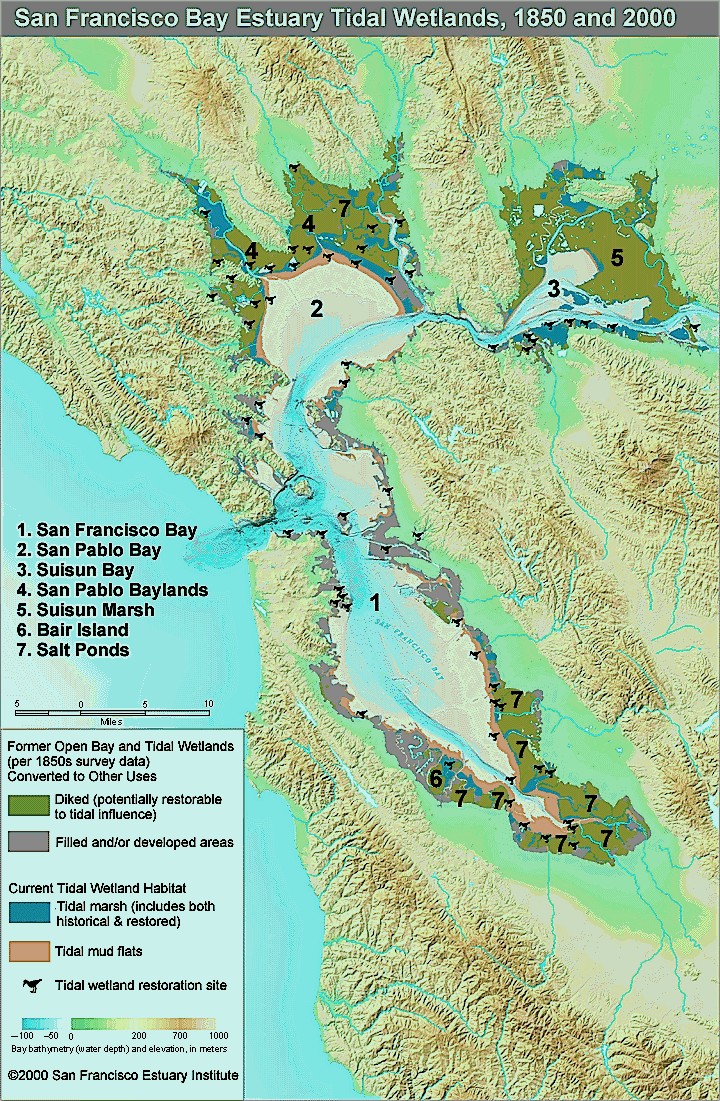
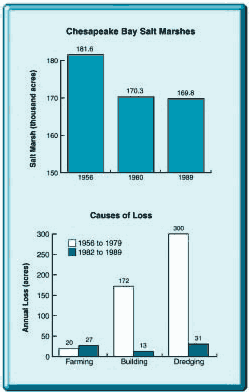
- San Francisco Bay estuary and tidal wetlands lost half its marshlands from 1850 to 2001 and thus its oyster fishery was destroyed.
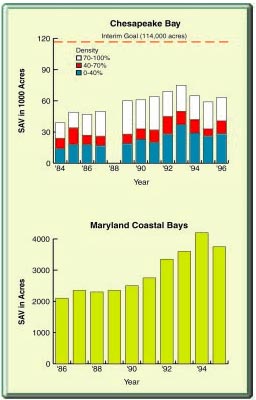
Density , determining the amount of development and conservation that is achieved given the constraints of water, energy, air, and landscape's terrain under the limitations imposed by carrying capacity and assimilative capacity on the number of residents per area.
-
- area of the inland sea (tidal seas)
- extent of the marshes and other productive units
- the volume of the water
- drainage from the land
- surge from the sea
- location of the null point or mixing zone,
- the extent of the watershed's vegetative cover and biotic communities as an inheritable matrix having four distinct roles in the quality, timing, distribution, and duration of discharges into the tidal sea.
metaphor | anomaly | Glossary | extension : regression | episodic changes | Factors
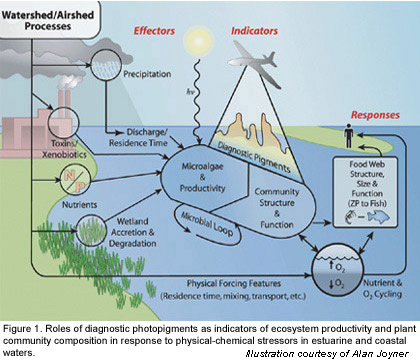
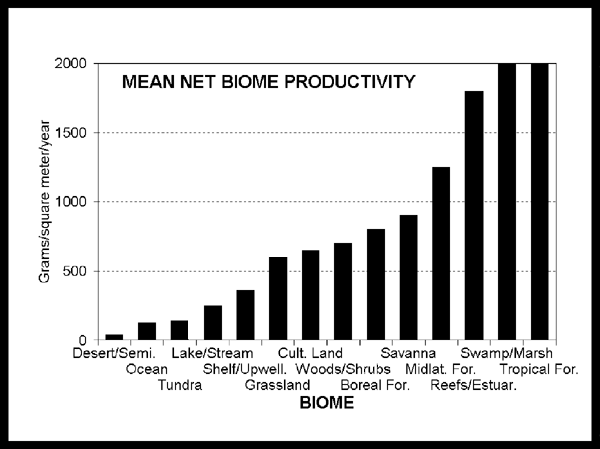
Net primary productivity and gross primary productive sectors:
- tidal variation pumps water in and up then down and out to sea.
- marsh grasses, diatoms, mud algae, seagrass beds, symbiotic worms are all productive factors in the photosynthetic trophic level that accounts for estuarine primary productivity
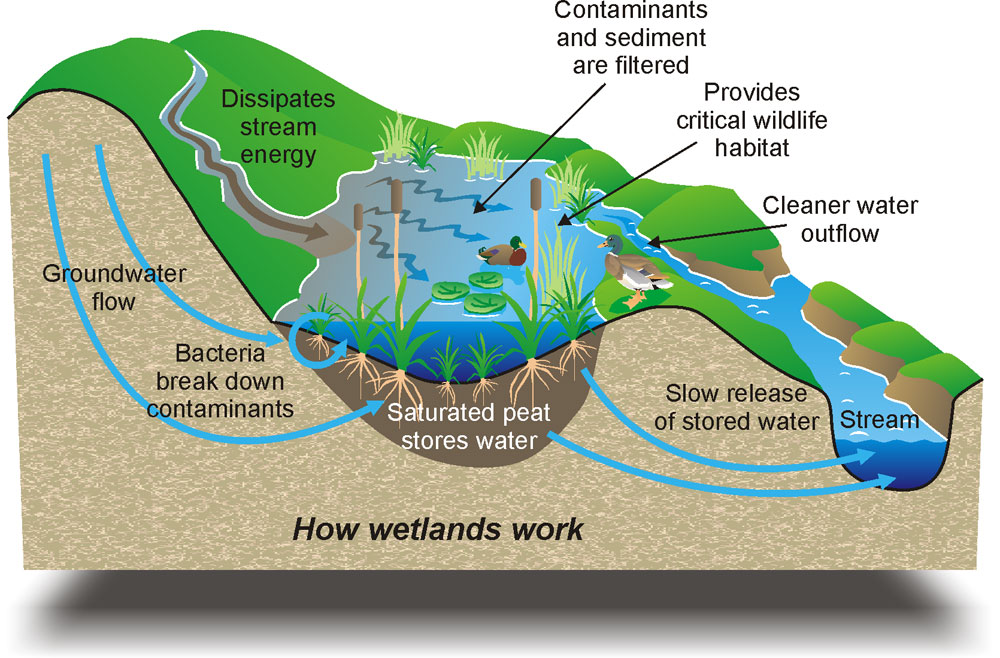
- forests and wetlands above the littoral zone contribute to the health of the downstream system acting as regulators, filters and nutrient traps for runoff from the landscape into the edge of the tidal seas, or bays.

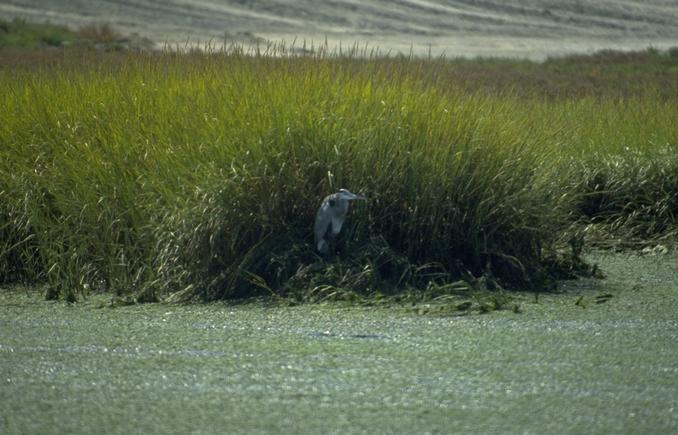
Here along Waccasassa Bay, Gulf of Mexico, the sea level is rising and the salinity will affect the vegetation.
"replenishment depends on the sustained yield approach to fisheries and the investment in clean air and water that infuses the estuaries at the points where the productive sectors of the system rely on the quality, quantity, timing and distribution of the necessary ingredients."
p. 111.
metaphor | anomaly | Glossary | extension : regression | episodic changes | Factors
"Volume Control for Estuaries" graphic of five factors in productivity
- chemical changes to water; acid or alkaline shifts
- temperature and salinity gradient changes
- an alteration of tidal scour
- alterations of the watershed affecting runoff and ground water in the drainage patterns that feed the estuary.
- timing and distribution of rainfall, precipitation and snow melt.
p. 112
metaphor | anomaly | Glossary | extension : regression | episodic changes | Factors
"Currently the state of estuaries is on the decline from pollution and density of development."
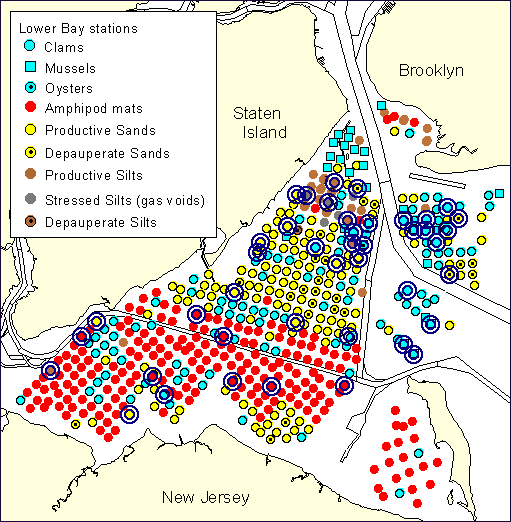
The new view of the ergonomic machine is emerging ....Those 102 estuaries in the US --so important yet so mutable-- are not only ground zero for accelerating sea level rise, but they are exchange areas for nitrogen and phosphorus run-off that, if not sequestered by vegetation, can lead to hazardous algal blooms. Some of these blooms are fatal to human health.Non-economic areas matter. The shape of the basin matters. And all of these are subject to manipulation by storms, filling, dredging, runoff, and development.
"There is a whole new universe out there that we have been blind to," to quote a genetics researcher Dr. Bestor, while he was speaking of molecular biology, much the same is true for estuaries. That is because chemistry, physics, and biology conspire with climate and geography to enable abundant life to flourish in diverse ways.
"we are the current caretakers of a delicately coevolved maritime garden whose produce must always we thoughtfully harvested."
The maritime grasslands of the shorelines that skirt an estuary are among several separate sources of primary productivity nourishing fisheries near and even far offshore. The chemistry of the water when combined with the quality of the substrate and the shape of the basin all influence how the natural capital of an estuarine biocoenose is distributed throughout the tributaries, adjacent marshes and ocean depths.
metaphor | anomaly | Glossary | extension : regression | episodic changes | Factors | Summary
see further:
Legal protections afforded under laws
restoring the disturbed harmonies
Genetics | Science Index | Site Analysis | Population Index | Global Warming Index | Nature Index | Brief