Technical Glossary
Technical Glossary
Words used by ecologists, engineers, or economists to describe nature can be intimidating, but here are some to learn:
Brackish an area of a waterway where salt water is diluted by freshwater, or marine water has traces of fresh drinking water dispersed among the heavier salt water. Ocean water is typically 33 parts per 1000 [or 3.3%] of sodium chloride diluted in the H2O. Oceans are filled with salt water of variable concentrations above 3.3% salt (NaCl) or sodium chloride.
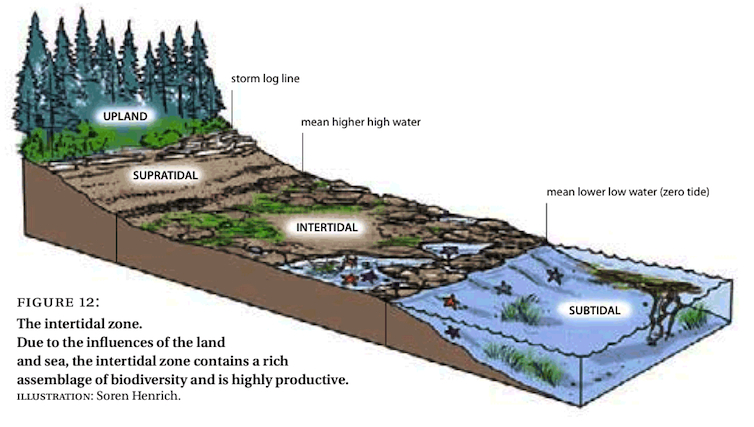
Ecotone is an area where a perceivable number of species from two or more different and adjacent biological communities reside or migrate through a shared area and thus there is an increase in either numbers of creatures or the diversity of different species overlapping because the conditions of the ecotone are a mixture of the neighboring plant, bacterial, and fungal associations that sustain the animal life of this mixing zone. Oak-savannah woodlands, and estuaries are two examples of ecotones.
Oak savannah woodlands are a mixture of species from grasslands and forests.
Edge effect is the perceived increase in either numbers of species or populations along the borders of two adjacent ecological communities or living systems (biomes), or biotic communities because species from each of the adjoining habitats have a greater number of niches to exploit. Areas where forests and prairies meet, estuaries, or where temperate and tropical savannah grasslands converge and overlap.
Equilibrium
MacArthur and Wilson's species equilibrium model predicts that species diversity will increase with island size and with proximity to a mainland.
Field experiments have supported the model.
Indicator species those animals and plants that reveal best the conditions of the habitat, or alert land or water managers to the quality of ecological conditions.
Birds are excellent indicators of conditions can serve as an early warning of damage to a community because they reproduce seasonally and feed from a wide variety of foods from fruit and seeds to insects, amphibians, fish and small mammals that are all herbivores.
inertia, the tendency of something to stay in motion, or at rest, unless acted upon by an external force.
Insolation, not insulation, is the amount of solar radiation that strikes a particular position in any place. Insolation refers to the amount of sunlight falling on the earth. Or, the solar energy received at the Earth's surface. Only a fraction of the insolation is absorbed, some of it reflects into space from opaque, or shiny surfaces.
Intraspecific competition the struggle between members of the same species who require the same scarce resources, such as among elephants, bears, wolves or panthers.
The more the niches of two species overlap, such as those of lions and wild dogs, the greater the degree of interspecific competition.
irradiance is the amount of solar radiation available to be acquired by plants or instruments in a particular location. The amount of light --electromagnetic vibrations-- or radiant energy incident on a given area of surface in a given amount of time, measured in Watts per square meter. The initial measure of available resources for production in a natural system.
Keystone species is an animal so central to a food web that its demise sends a ripple effect through an ecosystem. Examples are alligators, gopher tortoises, sea otters or beavers whose behavior or centrality to feeding relationships in a biotic community influence the integrity of food webs. This means many other creatures depend on these species existence for their survival.
Native species are those creatures whose ancestry are found in and are thus endemic to the place they currently inhabit.
The introduction of nonnative species, which are creatures from habitats that are remote from the new place they inhabit can lead to invasive exotic species crowding out native species This accounts for kudzu vine taking over southern US forests, skunk vine (Padera sp.) crowding out central Florida vegetation, or Japanese honeysuckle in New England.
Precautionary principle in the absence of complete knowledge or perfect predictable certainty, actions taken to disturb an ecological system, in say the extraction of resources, should be done in such a way as to reduce the risks of damaging the system. Thus by limiting the harm done to keystone species, or reducing interference with the turnover of scarce nutrients or not diminishing the supply of those characteristics that act as limiting factors, careful use of resources can enhance ecological integrity.
The use of extraordinary care, due to extreme uncertainty, in the use of valuable, needed and vulnerable resources. These actions may include adversely affecting endangered species, overgrazing of grasslands, over fishing, or the removal of too much timber, soil, or instream water flow in areas of critical habitat concerns such as may exist in ecologically endangered lands.
Predation is the eating of another species by a predator which benefits a predator at the expense of its prey. Carnivores feed on mobile prey; herbivores feed on plants. Predators have evolved a variety of ways to increase their chances of finding food, and prey have evolved various ways to defend themselves against or avoid predators.
Productivity
Production is the amount of energy available when converted by plants and bacteria into food, fuel, forage or fiber by photosynthesis of chemosynthesis.
A comparison of grassland productivity with different communities and their divergent potentials for producing living matter called biomass as measured in tons of dry-weight material accumulating over the course of a year.
PV- photo voltaic, photovoltaics, is a bit of a "jargon" term experts use for solar electricity to keep the hoi polloi from understanding what they mean.
The photo-electric effect was discovered by Albert Einstein in 1905 in a paper where he described the frequency of radiation to cause certain atoms' electrons to become so agitated or energy enriched that they move away from their "mother" nucleus when exposed to ultraviolet or stronger forms of electromagnetic photons. Hence the streaming electrons form a current of energy.
Photo stands for the photon of light quantum and voltaic, from volt the measure of electrical charge (force) derived from the behavior of the electrons when exposed to ionizing radiation.
Resource partitioning or the division of a habitat into zones for predators to exploit, or time periods during which otherwise mutually exclusive demands on a resource may be satisfied for two competing species. The division of the range, or the exploitation of niches at different times may enable species with similar niches to coexist.
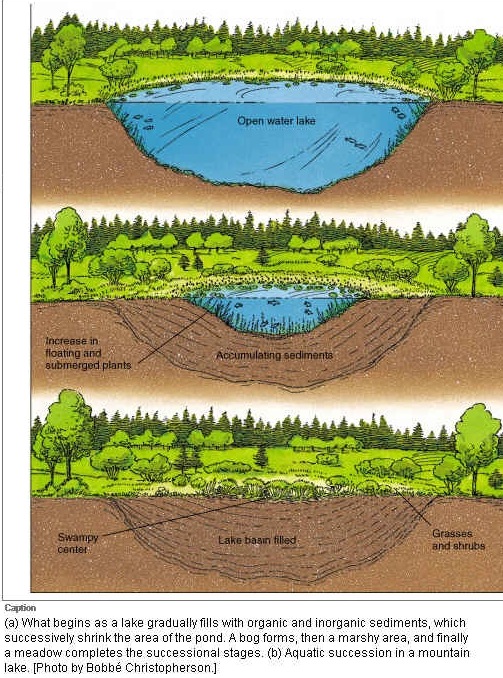
Succession is a major concept in habitat ecology.
Succession, is the change in a habitat over time due to the activity of living creatures that subsequently changes the species composition of an area. The two types of ecological succession are
- primary succession or community change by plants on a bare substrate
- secondary succession changes in the plant and animal community brought about by forces that alter the dominant species in a community over time.
With primary succession, pioneer species colonize an area.
Over time, pioneer species, such as, grasses, or r-strategists may be replaced by early succession plant species, such as brush, bushes, or mixed grasses (greater diversity) and willows after which these and related species may be replaced by mid successional plant species, such as pine trees, oak forests, or sycamores.
These species can give way to late successional plant species such as maples, hickory, walnut or other hardwood associations further increasing the diversity of trees and selecting for k-strategists. However, research indicates that we cannot predict the course of succession or view it as progress toward an ideally adapted climax community.
Symbiosis
There are three types of symbioses --meaning living together in the same supra-organism-- such that the genome of both partners assures the success of either partner's genes in succeeding generations:
- parasitism, relation characterized by one partner gaining an advantage to the detriment of the host partner.
- mutualism, partners both benefit, such as lichens, or corals.
- commensalism, living together without harm to either partner
The lake as a microcosm | Estuaries | Nature | Biological diversity | Abrupt Climate Change
![]()

.gif)