Problem
solving
Problem
solvingA problem may be defined as a perceived difference between an existing and a desired state of affairs.
Ecology is a synthetic science | true ecology is not a subset | ecological science defines limitations
Ecological Literacy is ecolacy | ecolacy forms a related web
Because we perceive three dimensions, we must think in an expanded and "volumetric" manner.
 Ecological
problem solving conceives of three facets of a problem:
Ecological
problem solving conceives of three facets of a problem:
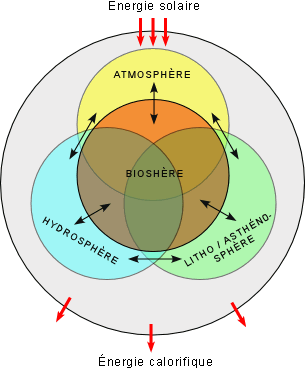
The physical and biological conditions create social challenges.
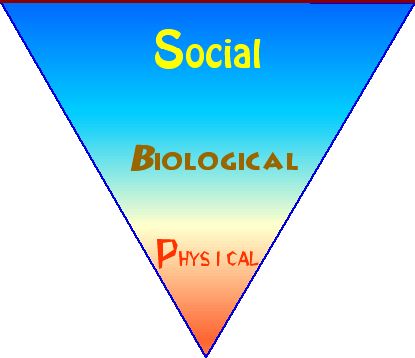
These three facets are physical, biological, and social components arising from observable conditions of existence.
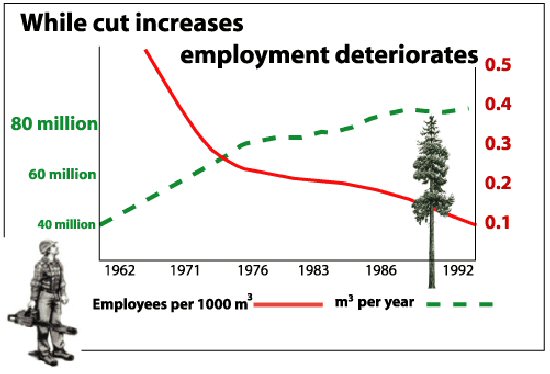
The social, biological and physical components can be viewed as a triangle resting on its apex since the wider the dimensions, the more difficult matters are to resolve in that component of the problem for us to solve such as acid rain and the loss of forests.
This kind of ecological problem solving always starts with the ecological imagination and sees these three inter-related and codependent components as the physical, biological, and social facets of the same problem.
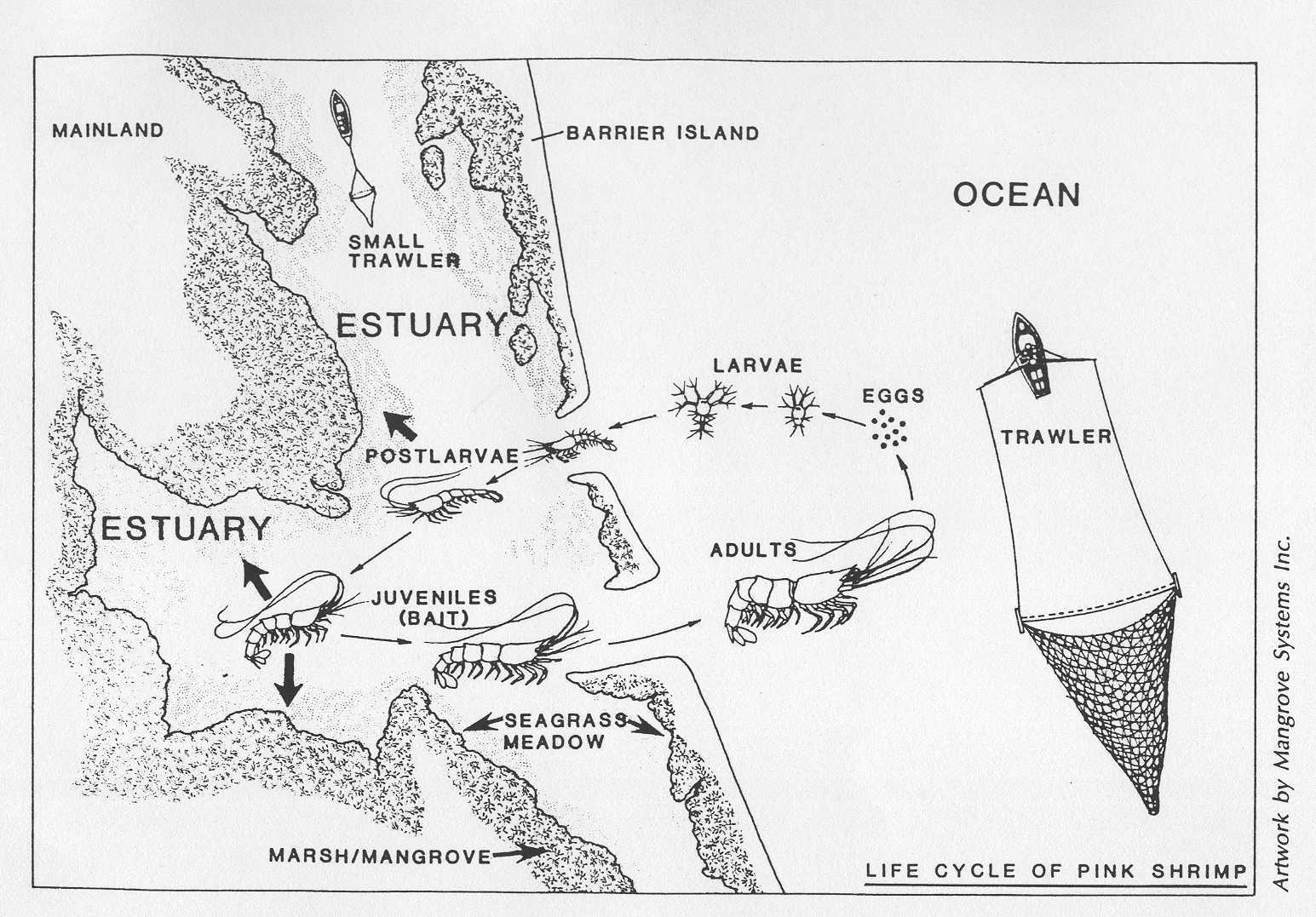
The social problems of forest decline, for example are more difficult to solve than the biology of the forest, although reforestation is not a simple science. They are also more complicated than the physical constraints of climate, soil, pH, limiting factors, or moisture loss.
Physical laws always set up the fundamental consequences of any ecological dilemma.
"To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction."
Technology as a means of solving problems, creating new problems and challenging our beliefs.
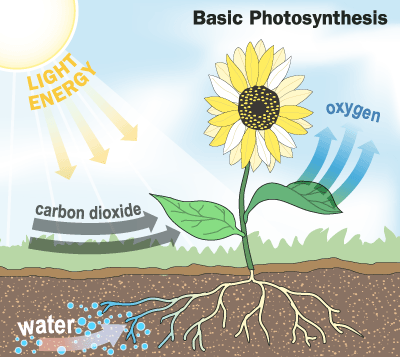
Biological components are dependent on biophysical conditions:
 Writing about problems should take this format: outline the physical situation, the biological components and the social consequences of the issues as you define an ecological problem; for example the deteriorating situation of the Indian River Lagoon.
Writing about problems should take this format: outline the physical situation, the biological components and the social consequences of the issues as you define an ecological problem; for example the deteriorating situation of the Indian River Lagoon.
So problem solving, involves knowing how to describe these three components that contribute to the conditions and use evidence to pursue more than one remedy.
Ecological problems thus, have several remedies possible, even simultaneously because:
"You can never do merely one thing."
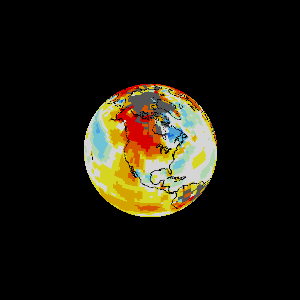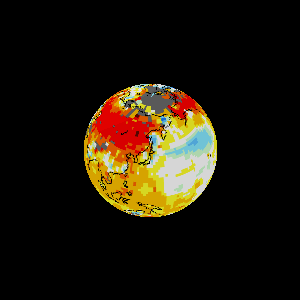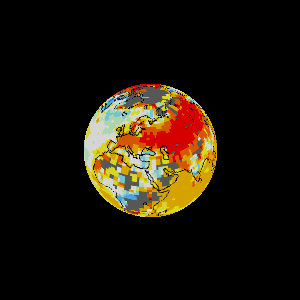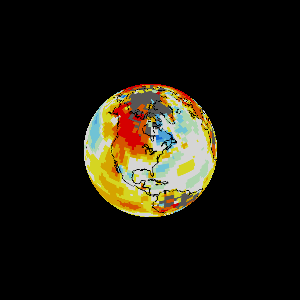
The world is more complex than we can think, warned J.B.S. Haldane and Rachel Carson
Climate, geology & chemistry make for a complicated mixture with which ecological problem solvers must face.
Examples:
Coastal storms Commons, what is one?
Ecological integrity, protection
Geochemical cycles, disruption of
Judgment about functional relationships, names and systemic thinking.
The goal of ecological problem solving
is to better employ means of protecting what we value from the unintended consequences of the ways we alter our surroundings.
- Protection
- Value, defined
- Landscape and values
- Contrasting views of value
- Technology and values
- Technology and politics.
- Technology solves and creates problems.
Adaptive management is the most recent in a series of methods that describes how to think about, plan for and evaluate the actions or measures we take to protect the ecological services that sustain our communities.
Because every ecological problem has three features, adaptive responses are essential to consider, if the desired solution fails to achieve the proposed goals because life is more complicated than we know.
- • Physical data
- • Biological data
- • Social data
- geographical information
- demographic information
- economic information
- psychological information
- Ecological model
- Ecological problem solving
- history of science
What is a good example of a problem? | 3 facets diagram | examining another problem | use of the model
Indexes:
Society | Dimension | Genetics Index | Geology | Global Warming | Nature | Population | Science Index
Technology index
landscape index
words index
photograph index

.gif)