I am also stunned by the unity of nature.
So, please do browse this site and read about the vibrant tones we see as colors emitted by the material elements around us if not to satiate at least to feed your curiosity.
![]() fundamental science
fundamental science ![]() spectrum is?
spectrum is? ![]() Bohr's idea?
Bohr's idea? ![]() dozen basic concepts
dozen basic concepts ![]()
Ich denke
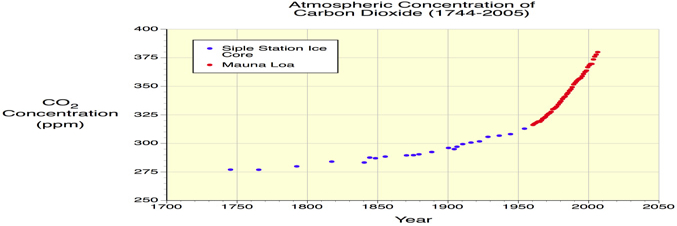
Carbon dioxide strongly absorbs energy with a wavelength of 15 μm (micrometers). This makes carbon dioxide a good absorber of wavelengths falling in the infrared radiation region (1500 nm) of the electromagnetic spectrum.
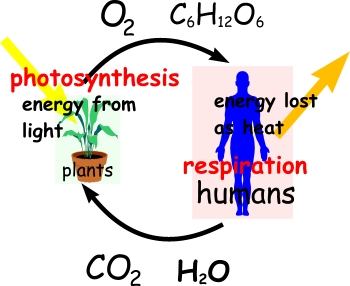
Carbon dioxide moves persistently into and out of the atmosphere through four major processes: photosynthesis, respiration, organic decomposition (or decay), and combustion or the burning of organic material.
• learn more about carbon dioxide and the carbon cycle here.
| High frequency | Low frequency | |
| high energy | low energy | |
| small wavelength | large wavelength |
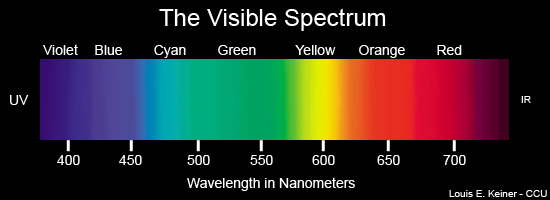
Visible
Ultraviolet
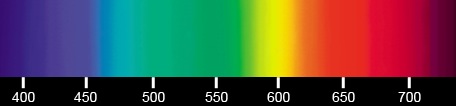 Infrared
Infrared
Visible wavelengths of radiation in nanometers
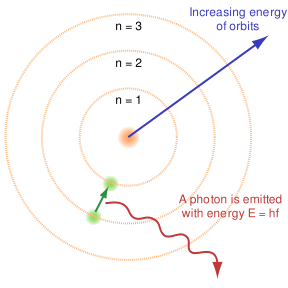
Niels Bohr, 1915.
I visited with my mentor Dr. Garrett Hardin before he died and we discussed what every student needed to know about biology.Upon reflection he quickly said that resistance organisms develop because of natural selection. The common capacity of bacteria and insects, for example, to pass on the immunity to the surviving generation.Hardin feared that by ignoring the power of evolution further damage could be inflicted on the natural world and human health by the deniers of Darwin and Wallace's discovery of evolution by means of natural selection.
|
Conversations with Garrett Hardin, Santa Barbara, 1999. |
The inoganic is tied to the organic conditions.
Critical thinking is fundamental to an effective college education
|
|
synthesis is at the core of scientific thinking.
|
|
It is needed for critical analysis of enduring problems in environmental studies and science such as the half life of radiation, persistent organic pollutants, or abrupt climate change due to global warming. |
|
Remember details, understand concepts, apply these rules and evidence to analyze ecological problems, evaluate the probable consequences and then ecolately ask what we must create to adapt, reinvent, and endure?
![]()
![]()
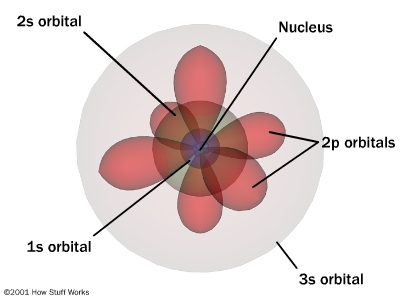
Dialectical thinking is not a novel, nor a recent means of description.What has happened in 20th century physics that bears directly on ecological problems is the duality of description inherent when comprehending elementary material particles. If duality is inherent on the sub-atomic and atomic levels of behavior, then comprehending how the world functions must involve similar reciprocal thinking when dealing with chemical reactions that drive, guide, and sustain life in all its complexity. Such complexity emerges out of simple arrangements in ever more variable combinations. All atoms dually emit and absorb radiation. As atoms "shine" the particularity of their spectrum reveals their signature because the emission frequencies indicate a sort of signal distinguishing hydrogen from carbon, or oxygen from nitrogen. But these atoms cannot emit unless they absorb radiation1. At elementary levels the universe self-constructs matter and energy so tightly that a dualistic understanding is basic to comprehending the oppositional characteristics in how carbon emits and absorbs radiation in specified or distinguishable frequencies. That is to say thinking in terms of opposites reveals that carbon absorbs in the ultraviolet frequencies (high energy; ionizing radiation) and emits in the infrared (low energy; heat radiation) frequency ranges. The situation is not either one, or the other; but it must be both for a full comprehension of nature's functional and systemic organization.
|
|
 |
|
Depth requires three dimensions.
Crucial concepts in ecological science, historical ecology & ideas to use are:
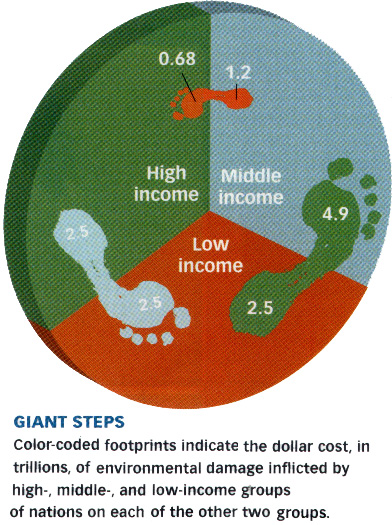
Your ecological footprint.
Ecological Literacy. by David Orr.
Walden "A model of the possible unity" among "personhood, pedagogy, and place."
Natural capital | Accounting for natural assets | Worth of ecosystem services
![]()
1 Continuous, Emission and Absorption Spectra: Key Points
Astronomy web site: http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/astr162/lect/index.html
Authors: a partial bibliographic listing of authorities used, quoted, and sited with links on this web site.
Non Governmental Organizations
Search the Internet an easy way
These buttons below work as navigational aids.
Science index ![]() Technology index
Technology index ![]() landscape index
landscape index ![]() words index
words index ![]() map index
map index ![]() social sciences
social sciences ![]() photograph index
photograph index
![]()
![]() words index
words index ![]() photograph index
photograph index ![]() social science index
social science index ![]() landscape is?
landscape is? ![]() dozen basic concepts
dozen basic concepts ![]()
Where next? | atoms | radiation



 BBC World News
BBC World News